SEBA Class 7 Science Chapter 4 Reproduction in Plants – Textbook Solutions & MCQ (Part II)
Find Class 7 Science Chapter 4 “Reproduction in Plants” Solutions for SEBA Assam (English Medium) students. This chapter, from Part II of the Science book, explains the different modes of reproduction in plants, including asexual and sexual reproduction. It covers methods like budding, fragmentation, spore formation, and vegetative propagation along with pollination and seed formation in flowering plants. Our solutions include detailed textbook answers, multiple-choice questions (MCQs), and well-explained concepts, making learning easier and improving exam preparation.
Class 7 Science
Chapter – 4 (Part II) Ospin Academy
Reproduction in Plants
EXERCISE
Q. 1. Fill in the blanks:
(a) Production of new individuals from the vegetative part of parent is called ____________.
Ans: Vegetative reproduction.
(b) A flower may have either male or female reproductive parts. Such a flower is called ____________.
Ans: Bisexual flower.
(c) The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same or of another flower of the same kind is known as ____________.
Ans: Pollination.
(d) The fusion of male and female gametes is termed as ___________.
Ans: Fertilization.
(e) Seed dispersal takes place by means of __________, __________ and __________.
Ans: Wind, water, insects.
Q. 2. Describe the different methods of asexual reproduction. Give examples.
Ans (i) Binary Fission: During this process, two daughter organisms of equal sizes are formed from one parent by the division of the parent body. This is the most common method of reproduction in algae, fungi and bacteria.
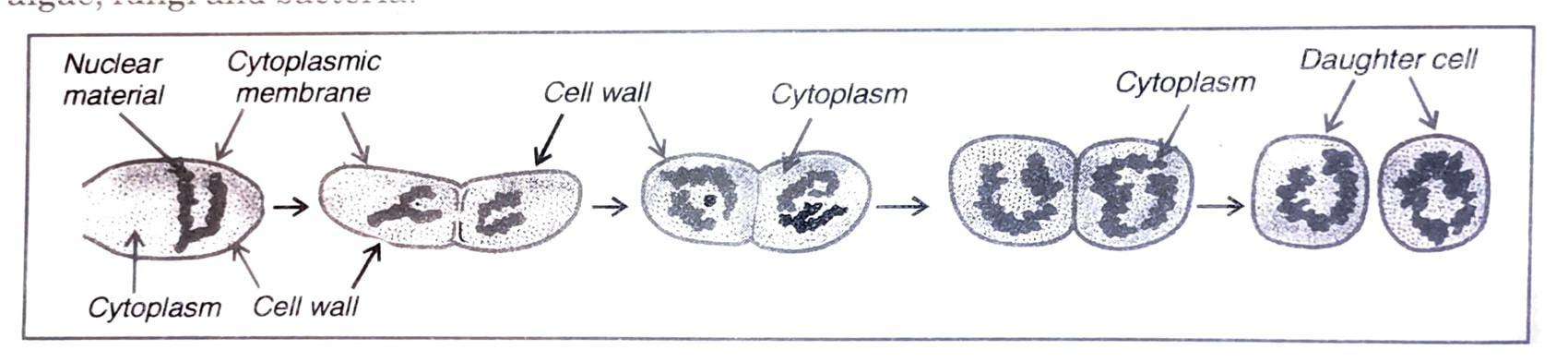
Fig. 12. 31. Binary fission in bacteria.
(ii) Budding: In this type of reproduction, a small outgrowth appears on the body of the organisms. This outgrowth is called a bud. The buds grow and finally detach from the parent body and begin to live as independent organisms. (see Fig. 12.32)
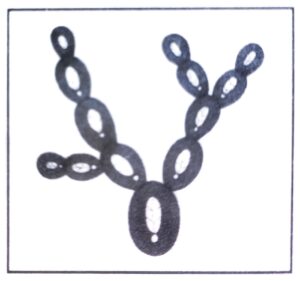
Fig. 12.32. Budding in yeast.
Q. 3. Explain what you understand by sexual reproduction.
Ans: Sexual reproduction means involvement of two parents in the process of reproduction. It is found mainly in higher plants. Male gamete and female gamete fuse to form a zygote. These zygotes develop into individuals which are not identical. Offspring inherit the characteristics of both the parents. In sexual reproduction bech parents survive after the process of reproduction.
Q.4. State the main differences between asexual and sexual reproduction.
Ans:
|
Asexual Reproduction |
Sexual Reproduction |
|---|---|
|
1. Only one parent plant is involved. |
1. Both male and female parents are involved. |
|
2. Reproductive parts are not present. |
2. Fully developed reproductive parts are present. |
|
3. Processes like gamete formation or fertilization is not seen. |
3. Fertilization of gametes give rise to zygote. |
|
4. Characteristics of only one parent is inherited. |
4. Characteristics of both parents are inherited. |
Q. 5. Sketch the reproductive parts of a flower.
Ans:
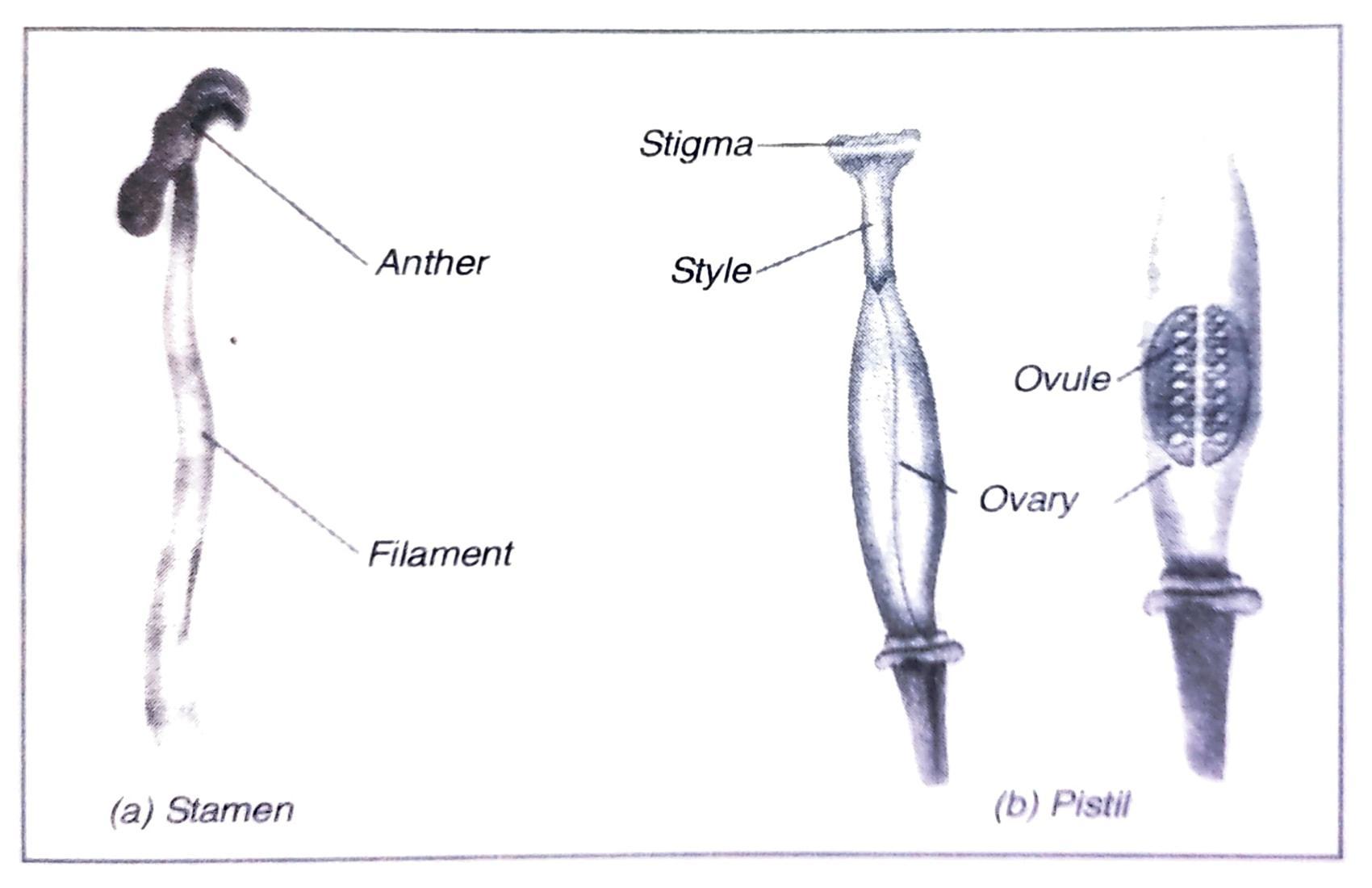
Fig. 5. Reproductive parts of a flower.
Q.6. Explain the difference between self pollination and cross-pollination.
Ans:
|
Self-pollination |
Cross-pollination |
|---|---|
|
(a) Pollen grains are transferred to the stigma of same flower. |
(a) Pollen grains are carried to stigma of another flower from one flower. |
|
(b) Occurs in bisexual plants having anther and stigma maturing at same time. |
(b) Occurs in bisexual flowers having anther and stigma maturing at different times. |
|
(c) It takes place in plants like wheat, peas etc. |
(c) It takes place in plants like lady’s finger, tomato, brinjal, etc. |
Q. 7. How does the process of ferti- lization take place in flowers?
Ans: When the pollen grain reaches the stigma of a same flower, it starts growing out in pollen tube of the stigma. This tube continues to grow inside the style till it reaches the ovule. Male cells are released in the ovule for the fertilization with female cells and thus the zygote is formed. After this process of fertilization, the ovary develops into fruit and ovule into seeds.
Q. 8. Describe the various ways by which seed are dispersed.
Ans: Following are the ways in which the seeds get dispersed:
(i) Some light seeds like that of Madar, which are hairy, dry and small are carried away by the wind to different places. Some seeds having winged structure eg. that of Maple and Drumstick are also dispersed by air.
(ii) Spiny seeds and fruits like that of Xanthium and Gokhru, the seeds stick to the clothes of passers-bye and animals. These seeds are carried away by these agents to different places.
(iii) In some cases having heavy seeds like that of Coconut, water acts as the dispersing agents.
(iv) Some seeds are dispersed when the fruit bursts like in case of Balsam and castor.
Q. 9. Match the items in Column I with those of Column II:
|
Column – I |
Column – II |
|---|---|
|
(a) Bud |
(i) Maple |
|
(b) Eyes |
(ii) Spirogyra |
|
(c) Fragmentation |
(iii) Yeast |
|
(d) Wings |
(iv) Bread mold |
|
(e) Spores |
(v) Potato |
|
(vi) Rose |
Ans:
|
Column – I |
Column – II |
|---|---|
|
(a) Bud |
(iii) Yeast |
|
(b) Eyes |
(v) Potato |
|
(c) Fragmentation |
(ii) Spirogyra |
|
(d) Wings |
(i) Maple |
|
(e) Spores |
(vi) Rose |
Q. 10. Tick (✔) the correct answer:
(a) The reproductive part of a plant is the:
(i) Leaf
(ii) Stem
(iii) Root
(iv) Flower
Ans: (iv) Flower.
(b) The process of fusion of the male and the female gametes is called:
(i) Fertilization
(ii) Pollination
(iii) Reproduction
(iv) Seed formation
Ans: (i) Fertilization.
(c) Mature ovary forms the:
(i) Seed
(ii) Pistil
(iii) Stamen
(iv) Fruit
Ans: (iv) Fruit.
(d) A spore producing plant is:
(i) Rose
(ii) Bread mold
(iii) Potato
(iv) Ginger
Ans: (ii) Bread mold.
(e) Bryophyllum can reproduce by its:
(i) Stem
(ii) Leaves
(iii) Roots
(iv) Flower
Ans: (ii) Leaves.
Q1: What are the different types of reproduction in plants?
Plants reproduce through asexual reproduction (budding, fragmentation, spore formation, vegetative propagation) and sexual reproduction (pollination, fertilization, seed formation).
Q2: What is the role of pollination in plant reproduction?
Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma, leading to fertilization and seed formation in flowering plants.
Q3: How does vegetative propagation work?
Vegetative propagation is a form of asexual reproduction where new plants grow from roots, stems, or leaves, such as in potatoes, onions, and bryophyllum.
Q4: Where can I find Class 7 Science Chapter 4 solutions for SEBA Assam?
You can find detailed textbook solutions, MCQs, and explanations for SEBA Assam Class 7 Science Chapter 4 (Part II) on this page.
Q5: Where can I find solutions for all Class 7 Science chapters?
To get solutions for all Class 7 Science chapters, Click Here
