SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 13 – Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Solutions & Summary
Looking for accurate solutions to Class 10 Science Chapter 13 – “Magnetic Effects of Electric Current”? Ospin Academy provides complete NCERT solutions for SEBA students.
📖 Chapter Overview:
This chapter explains the magnetic field around current-carrying conductors, electromagnetic induction, the working of electric motors and generators, and the domestic electric circuit.
📌 Key Topics Covered:
- Magnetic Field and Its Properties
- Magnetic Field Due to a Current-Carrying Conductor
- Right-Hand Thumb Rule
- Electromagnetic Induction
- Working of Electric Motor and Generator
- Domestic Electric Circuit
📌 Important Questions for Exams:
- What is a magnetic field? Describe its properties.
- State and explain the right-hand thumb rule.
- Explain the working principle of an electric motor.
- Define electromagnetic induction with examples.
- Describe the structure of a domestic electric circuit.
📝 How Ospin Academy Helps:
- Detailed NCERT Solutions for SEBA Syllabus
- Step-by-Step Problem Solving
- Interactive Diagrams and Explanations
- Quick Notes for Revision
Access the best solutions for SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 13 – “Magnetic Effects of Electric Current” only on Ospin Academy!
Class 10 Science (English Medium) PDF Solutions 2025-26 | SEBA Assam
Download Class 10 Science (English Medium) PDF with detailed solutions, MCQs, and extra practice questions for SEBA Assam 2025-26.
Textual Questions and Answers:
Page – 224
1. Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet?
Answer: The needle of a compass is itself a small magnet. When it is brought near a bar magnet, the magnetic field of the bar magnet interacts with the magnetic field of the needle. This interaction causes the needle to experience a force, leading to its deflection in response to the bar magnet’s field.
Page – 228
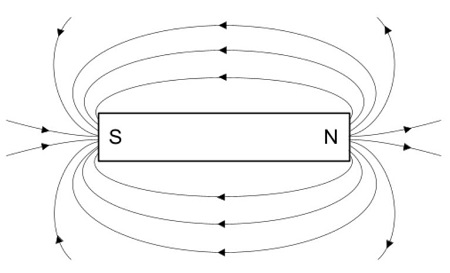
1. Draw a magnetic field lines around a bar magnet.
Answer:
2. List the properties of magnetic lines of force.
Answer: General Properties of Magnetic Lines of Force:
(a) Magnetic lines of force (or magnetic field lines) are closed continuous curves. They start from the North Pole and end at the South Pole.
(b) The two magnetic lines of force never intersect each other.
(c) Magnetic lines of force are crowded where the magnetic field is strong, and they are far from each other where the field is weak.
3. Why don’t two magnetic lines of force intersect each other?
Answer: The two magnetic lines of force do not intersect each other because net force acting at any point on a magnetic line of force will be in one direction only. If the two magnetic lines of force intersect with each other, then the compass needle would point in two directions at the same time at that point, which is not possible at all.
1. Consider a circular loop of wire lying in the plane of the table. Let the current pass through the loop clockwise. Apply the right-hand rule to find out the direction of the magnetic field inside and out side the loop.
Answer: In the following diagram the current is flowing clockwise. If we are applying right hand thumb rule to the left side of the loop then the direction of magnetic field lines inside the loop are going into the table while outside the loop they are coming out of the table.
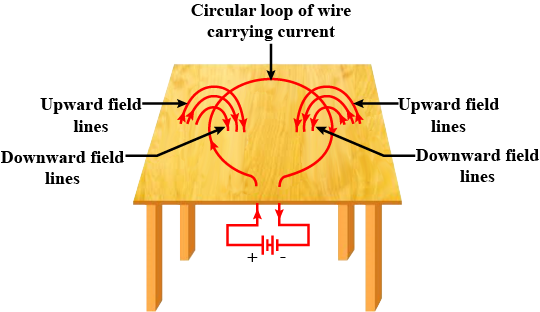
2. The magnetic field in a given region is uniform. Draw a diagram to represent it.
Answer:
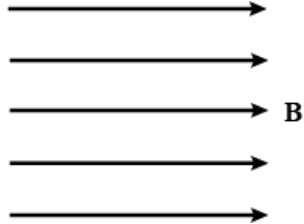
Uniform magnetic field is represented by equidistant and parallel lines as shown. The parallel lines are close to each other, if the field is strong. Stronger the field, closer are the lines.
Page – 230
Choose the correct option.
1. The magnetic field inside a long straight solenoid carrying current.
(a) Is zero.
(b) Decreases as we move to wards end.
(c) Increases as we move towards end.
(d) Is same at all the points.
Answer: (d) Is same at all the points.
Page – 231
1. Which of the following property of porton can change which it moves freely in a magnetic field? (There may be more than one correct answer)
(a) Mass.
(b) Speed.
(c) Velocity.
(d) Momentum.
Answer: (c) and (d)
Page – 232
1. In activity 13.7, how do we think the displacement of rod AB will be affected if
(i) Current in rod AB is increased.
Answer: If current in rod AB will increases, the force will also increase. Since force increases, displacement will also increase.
(ii) A stronger horse-shoe magnet is used.
Answer: When a stronger horse-shoe magnet is used, the magnitude of the magnetic field increases and this increases the force exerted on the rod and the displacement of the rod.
(iii) Lengths of the rod AB is increased?
Answer: When the length of the rod AB is increased, force exerted on the conductor increases, so the displacement of the rod increases.
2. A positively charged particle (a particle) emitted from a nucleus and projected towards west is deflected towards north by a magnetic field. The direction of the magnetic field is
(a) Towards south.
(b) Towards east.
(c) Down ward.
(d) Upward.
Answer: (d) Upward.
Page – 233
1. State Fleming’s left hand rule.
Answer: Fleming’s left hand rule can be stated as: Stretch the forefinger, the middle finger and the thumb of the right hand, such that they are mutually perpendicular to each other. If the forefinger indicates the
direction of the magnetic field, the middle finger indicates the direction of current in the conductor then thumb indicates the direction of force exerted on the conductor.
2. What is the principle of an electric motor?
Answer: An electric motor is not a generator, but a device that converts electricity into mechanical energy. They work on the principle of electromagnetism, which indicates that a force is applied when an electric current is present in a magnetic field.
Motors have a variety of moving components that allow them to rotate continuously and power as needed. The motor can be operated by direct current (DC) or alternating current (AC). The principle of an electric motor is based on a conducting conductor that creates a magnetic field around it. Conductors that carry current are placed perpendicular to the magnetic field so that forces are applied.
3. What is the role of the split ring in an electric motor?
Answer: The split ring is used to reverse the coil’s current direction. The coil’s current must be reversed in order for it to continue rotating in the same direction. As a result, the direction of the couple rotating the coil remains the same after every half rotation, and the coil continues to rotate in the same direction.
Page – 236
1. Explain different ways to induce current in a coil.
Answer: Different ways to induce a current in a coil:
(i) By rotating the coil between the poles of a U-shaped magnet in a magnetic field.
(ii) By holding the coil still and moving a magnet within it.
(iii) By continuously changing the current in another coil kept nearby.
Page – 237
1. State the principle of an electric generator.
Answer: Based on the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction, electric generator are prepared. In an electric generator, Mechanical energy is used to rotate a conductor in a magnetic field to produce electricity. This is the principle of an electric generator.
2. Name some source of direct current.
Answer: In direct current, the current flows in One Direction only. Direct current is written in short form D.C. The current which we get from a cell or a battery is direct current because it always flows in the same direction. The positive(+) and negative (-) terminal of a direct current is fixed. Some of the sources of direct current(D.C) are: Dry cell, dry cell battery, car battery and DC generator, radio and television works only with D.C they have a device in them which convert A.C supplied to them into D.C.
3. Which sources produce Alternating current?
Answer: The sources are hydroelectric power plants, thermal power generators,nuclear power generators, AC generators produce alternating current.
Choose the correct option:
1. A rectangular coil of copper wires is rotated in magnetic field. The direction of induced current changes once in each:
(a) Two revolutions.
(b) One revolutions.
(c) Half revolution.
(d) One forth revolution.
Answer: (c) Half revolution.
Page – 238
1. Name two safety measures commonly used in electric circuits and appliances.
Answer:
(i) Electric fuse.
(ii) Earthing.
2. An electric oven of 2kw power rating is operated in a domestic electric circuit (220v) that has a current ratting of 5A. What result do you except? Explain.
Answer: Given that,
P = 2kw = 2000w
v = 220 volt
I = ? P = VI
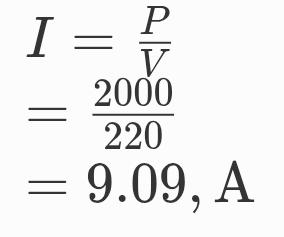
A current of 9.09A will flow in the circuit. Since the current rating of circuit is 5A, the fuse rating if inserted in circuit will burn up. If no fuse has been put in the circuit, there may be a fire.
3. What precaution should be taken to avoid the overloading of domestic electric circuits?
Answer: The fuse should be always be connected in the circuit to protect overloading and short-circuiting. Do not connect too many appliances in a single socket as it may lead to a fire. Always use the appliances in the safe limit of an electric circuit. Always use the single appliance at a time.
EXERCISES
1. Which of the following correctly describes the magnetic field near a long straight wire?
(a) The field consists of straight lines perpendicular to the wire.
(b) The field consists of straight lines parallel to the wire.
(c) The field consists of radial lines originating from the wire.
(d) The field consists of concentric circles centred on the wire.
Answer: (d) The field consists of concentric circles centred on the wire.
2. The phenomenon of electromagnetic induction is
(a) The process of charging a body.
(b) The process of generating magnetic field due to a current passing through a coil.
(c) Producing induced current in a coil due to relative motion between a magnet and the coil.
(d) The process of rotating a coil of an electric motor.
Answer: (c) Producing induced current in a coil due to relative motion between a magnet and the coil.
3. The device used for producing electric current is called a
(a) Generator.
(b) Galvanometer.
(c) Ammeter.
(d) Motor.
Answer: (a) Generator.
4. The essential difference between AC generator and a DC generator is that
(a) AC generator has an electromagnet while a DC generator has permanent magnet.
(b) DC generator will generate a higher voltage .
(c) AC generator will generate a higher voltage.
(d) AC generator has slip rings while the DC generator has a connector.
Answer:
(d) AC generator has slip rings while the DC generator has a connector.
5. At the time of short circuit, the current in the circuit.
(a) Reduces substantially.
(b) Does not change.
(c) Increases heavily.
(d) Vary continuously.
Answer: (c) Increases heavily.
6. State whether the following statement are true or false-
(a) An electric motor converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Answer: False.
(b) An electric generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
Answer: True.
(c) The field at the centre of a long circular coil carrying current will be parallel straight lines.
Answer: True.
(d) A wire with a green insulation is usually the live wire of an electric supply.
Answer: False.
7. List two methods of producing magnetic fields.
Answer: Magnetic field can be produced by any of the following methods:
(i) Any magnet-bar magnet, horse-shoe magnet or round magnet can be used.
(ii) A wire carrying current produces a field around it.
8. How does a solenoid behave like a magnet? Can you determine the north and south poles of a current carrying solenoid with the help of a bar magnet? Explain.
Answer: It has a soft iron core with insulated copper wire covering it, the solenoid acts like a magnet.
Solenoid behaves as a magnet in the following ways:
(i) magnetic field produced by a solenoid is similar to the magnetic field of a bar magnet.
(ii) one end of the solenoid behaves as north seeking pole and another end behaves as a south seeking pole as in magnet.
9. When is the force experienced by a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field largest?
Answer: The force experienced by a current–carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field is largest when the direction of current and the magnetic field are perpendicular to each other.
10. Imagine that you are sitting in a chamber with your back to one wall. An electron beam moving horizontally with back towards the front wall is defected by a strong magnetic field to your right side. what is the direction of the magnetic field?
Answer: The movement of electrons represents the direction of conventional current in the opposite direction. Since the electron beam is deflected to the right, the force (F) acting on it is towards the right side.
By applying Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule, where:
The forefinger represents the direction of the magnetic field (B),
The middle finger represents the direction of current (I, opposite to electron flow),
The thumb represents the direction of force (F, which is towards the right),
it can be concluded that the magnetic field (B) is directed vertically downward (perpendicular to the plane of motion and directed inward, represented by ⊗).
11. Draw a labelled diagram of an electric motor. Explain its principle and working. What is the function of a split ring in electric motor?
Answer: An electric motor is a device which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. The principle behind the electric motor is based on Fleming’s left hand rule.
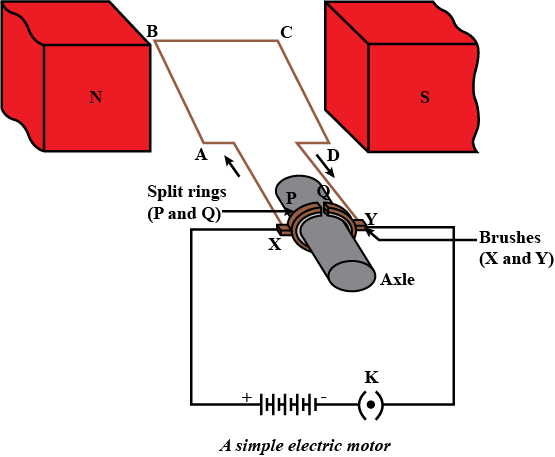
Working: Working: When a current is allowed to flow through the coil PQRS the coil starts rotating anti- clockwise. This happens because a downward force acts on length PQ and at the same time, an upward force acts on length RS. As a result, the coil rotates anti-clockwise.
Current in the length PQ flows from P to Q and the magnetic field acts from left to right, normal to length PQ. Therefore, according to Fleming’s left hand rule, a downward force acts on the length PQ. Similarly at an upward force acts on the length RS. These two forces cause the coil to rotate anti-clockwise.
When coil complete half rotation, the position of PQ and RS interchange. The half-ring D comes in contact with brush A and half-ring C comes in contact with brush B. therefore the direction of current in the coil PQRS gets reversed. Now the current flows through the coil in the direction SRQP.
12. Name some devices in which electric motors are used.
Answer: Electric motors are used in water pumps, electric fans, electric mixers and washing machines.
13. A coil of insulated copper wire is connected to galvanometer. What will happen if a bar magnet is
(a) Pushed into the coil.
Answer: An electric current is induced in the coil and the galvanometer shows a deflection.
(b) With drawn from inside the coil.
Answer: When the bar is with drawn, there will again be momentarily a deflection but in a direction opposite to that when magnet was pushed.
(c) Held stationary inside the coil?
Answer: When the magnet is held stationary in the coil, there will be no deflection in galvanometer.
14. Two circular coils A and B are placed closed to each other. If the current in the coil A is changed will some current be induced coil B? Give reason.
Answer: Because of the shift in the magnetic field caused by the placement of coils B and C in close proximity to each other, the other coil will experience some current induced into it. Electromagnetic induction is the term used to describe this phenomenon.
15. State the rule to determine the direction of a
(i) Magnetic field produced around a straight conductor carrying current.
Answer: Right hand thumb rule will determine the direction of a magnetic
field around a straight conductor carrying current.
(ii) Force experienced by a current carrying straight conductor placed in a magnetic field which is perpendicular to it.
Answer: Fleming’s left hand rule will determine the direction of a force experienced by a current carrying straight conductor placed in a magnetic field which is perpendicular to it.
(iii) Current induced in a coil due to its rotation in a magnetic field.
Answer: Fleming’s right hand rule will determine the direction of current induced in a coil due to its rotation in a magnetic field.
16. Explain the underlying principle and working of an electric generator by drawing a labelled diagram. What is the function of brushes?
Answer: The principle of electric generator is Electromagnetic Induction. The schematic is shown below
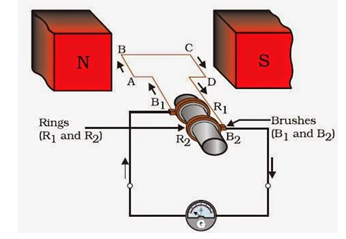
An electric generator is a device that converts mechanical energy obtained from an external source into electrical energy as the output. The flow of electric charges is induced by moving an electrical conductor, such as a wire that contains electric charges, in a magnetic field. This movement creates a voltage difference between the two ends of the wire or electrical conductor, which in turn causes the electric charges to flow, thus generating electric current.
The function of brushes is to make proper contact with the rotating rings because through them the current is supplied to the coil
17. When does an electric short circuit occur?
Answer:
A short circuit occurs when the current flows through a path of little or no resistance, bypassing the appliance. This can happen, for example, when frayed insulation exposes a wire, allowing it to touch the appliance’s frame, causing the current to flow directly to the ground.
18. What is the function of an earth wire? Why is it necessary to earth metallic appliances?
Answer: Function of an Earth Wire:
The primary function of the earth wire is to safely conduct excess or leaking current from electrical appliances to the ground.
Necessity of Earthing Metallic Appliances:
Earthing metallic appliances is essential because, in case of a fault, the earth wire provides a low-resistance path for the current to flow into the ground. This prevents the current from passing through a person who might accidentally touch the appliance, thereby protecting against electric shocks.
SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 13 – Magnetic Effects of Electric Current FAQs
Get Free NCERT PDFs
If you want to download free PDFs of any chapter, click the link below and join our WhatsApp group:

