Class 10 Geography Chapter 2 – Environmental Geography All Exercise Solutions | SEBA Assam (English Medium)
Class 10 Geography Chapter 2 – Environmental Geography (SEBA Assam – English Medium)
The second chapter of SEBA Class 10 Geography, Environmental Geography, explains the close relationship between the natural environment and human society. It highlights how human activities affect natural systems and how environmental changes impact human lives. The chapter focuses on issues like deforestation, air and water pollution, population pressure, climate change, and sustainable development. Understanding this chapter is crucial for HSLC exam preparation since it includes both theoretical and application-based questions.
✅ What You Will Learn in Chapter 2:
- Meaning and scope of Environmental Geography
- Man-environment relationship
- Major environmental issues – deforestation, soil erosion, wasteland, global warming, and pollution
- Impact of population growth on environment
- Concept of sustainable development and conservation practices
🎯 Why Choose Ospin Academy Solutions:
- Complete Class 10 Environmental Geography solutions (English Medium)
- Prepared as per SEBA Assam syllabus
- Answers explained in simple, exam-friendly language
- Important notes and MCQs for HSLC exam
- Helpful for project work, assignments, and board exam preparation
Class 10 Geography (English Medium) HSLC 2026 Textual Solutions PDF | SEBA Assam Syllabus
Limited Time Offer!
(For HSLC Exam 2026)
Get complete preparation for Class 10 Geography (English Medium) with this all-in-one SEBA textual solution PDF.
Covers chapter-wise solutions, definitions, map work, diagrams and practical geography – fully updated for HSLC 2026 syllabus.
Perfectly designed for revision, practice and boosting exam scores!
Class 10th Geography(E)
Chapter: 2 Ospin Academy
Environmental Geography
TEXTUAL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
1. What is meant by environment? Why is environment considered to be a system?
Answer: The term environment refers to the physical conditions that exist around an organism. In simple terms, it includes all the elements that surround an object or living being. In geography, the environment refers to the region around the earth comprising the lithosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere, and biosphere. It is a natural arrangement where living and non-living elements coexist in a balanced manner.
The concept of environment has a broad meaning. It functions as a system that contains various interconnected sub-systems. These include the biotic and abiotic environments as well as natural cycles such as the hydrological cycle, carbon cycle, water cycle, and energy cycle. The unique aspect of this system is the close interaction and interdependence among these sub-systems, ensuring that they remain balanced and interconnected.
2. State with examples the relationship amongst lithosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere and biosphere.
Answer: The environment is made up of four main components: the lithosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere. These components are closely connected and depend on each other for their existence. Natural cycles like the hydrological cycle, carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, and energy cycle pass through all four components. Both living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) elements are present in each of them, forming a complex web of relationships.
A change in any one of these components directly affects the others. For example, when the atmosphere experiences excessive solar radiation, it can cause the polar ice to melt, raising sea levels and changing coastal areas on the lithosphere. This submerges land and impacts many living organisms in the biosphere and hydrosphere. Another example is rainfall: clouds form due to evaporation from water bodies and plants, and rain is essential for the survival of living beings on land and in water. Similarly, deforestation in the lithosphere increases greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, causing global warming, which harms life on both land and oceAnswer:Thus, these four components are deeply interlinked and depend on each other for maintaining balance in nature.
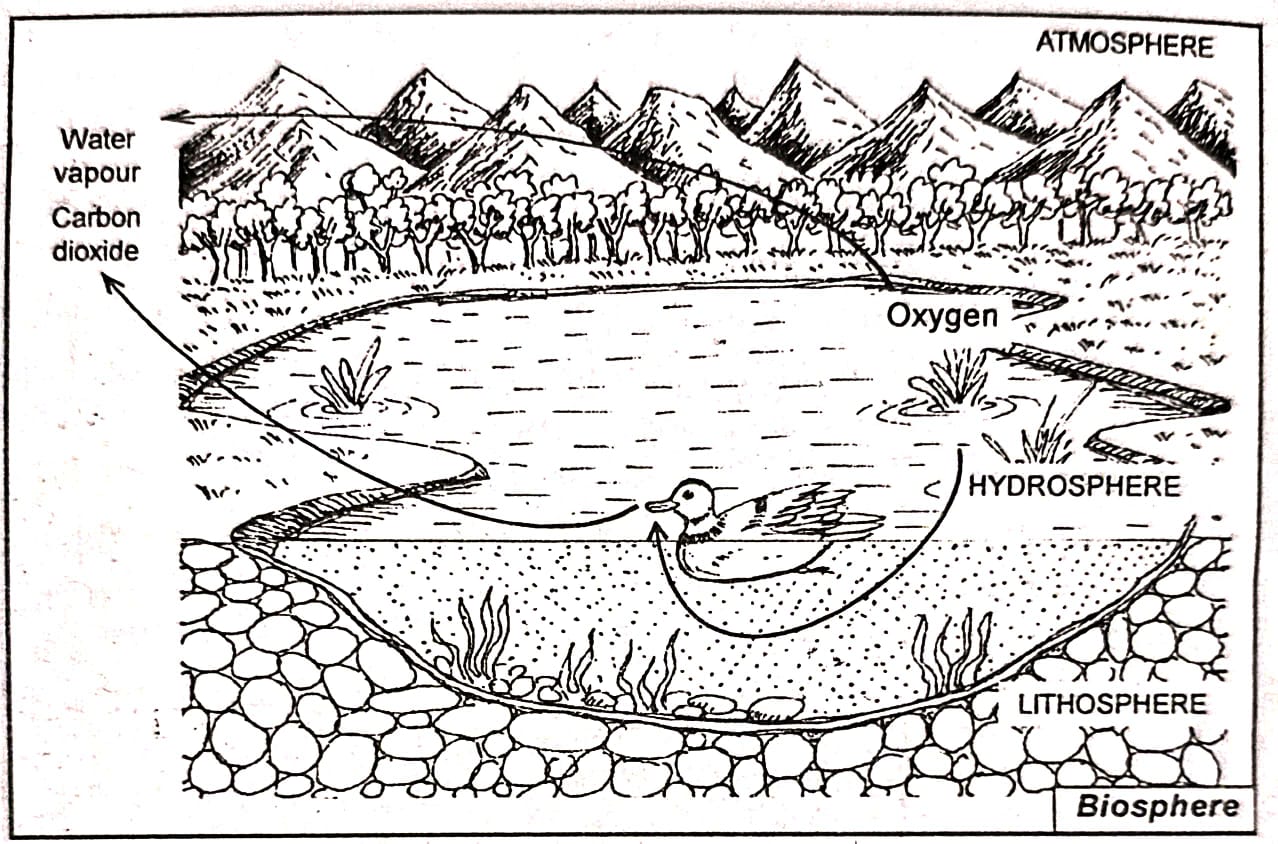
3. Write in brief as to why the environments of all the regions of the world are not same.
Answer: One of the distinct features of the environment is its variation across the world. For instance, the equatorial regions experience high temperatures and heavy rainfall throughout the year, whereas polar regions have extremely low temperatures with little or no rainfall. These differences arise due to several factors, including geographical location, topography, distance from seas or oceans, altitude, climate, and the type of vegetation and wildlife present. Since these factors vary from one place to another, the environmental conditions also differ. In fact, this variation forms the basis for identifying and classifying the different natural regions on the Earth’s surface. Hence, the environments of all regions are not the same.
4. Define Environmental Geography
Answer: Environmental Geography is a branch of geography that focuses on studying the nature of the global environment, its changes over time and space, and ways to solve environmental problems caused by human activities. In simple terms, it is a subdivision of geography that examines the interactions between humans and their environment, exploring how the environment influences human life and how human actions, in turn, affect the environment.
5. Discuss the importance of Environmental Geography as a branch of Geography.
Answer: Environmental Geography has become an important field of study in recent times due to the increasing environmental challenges faced by the world. Problems such as deforestation, global warming, air pollution, water pollution, and depletion of freshwater resources have reached alarming levels, directly affecting human health, life span, and economic well-being. These issues have also led to the emergence of new diseases and a rise in global temperatures, making life on Earth more difficult.
This branch of geography is also significant because it connects closely with other fields like Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Geology, Climatology, and Environmental Science, allowing a broader understanding of global environmental issues. Traditional approaches are often insufficient to address today’s environmental crises, hence Environmental Geography has emerged to study these problems systematically and propose practical solutions.
6. Give an account on the objective and scope of Environmental Geography.
Answer: Environmental Geography is a branch of geography that studies the nature of the global environment, its recent changes, and seeks effective solutions to existing environmental issues. Its main objective is to analyze the relationship between humans and their environment and to promote sustainable practices for a balanced coexistence.
The scope of Environmental Geography includes:
(i) Understanding the nature of the global environment.
(ii) Studying recent changes in environmental conditions.
(iii) Identifying and analyzing various environmental problems.
(iv) Promoting eco-friendly use of natural resources.
(v) Encouraging sustainable development practices.
(vi) Examining population growth and its impact on the environment.
(vii) Managing natural disasters effectively.
(viii) Using modern tools and technology for studying environmental issues.
7. What do you mean by elements of environment? Write down the meanings of biotic and abiotic elements.
Answer: Elements of environment, mean the various components that constitute the environment. The environment consists of two categories of elements, namely biotic elements and abiotic elements. 619
(i) Biotic elements: The elements that have life are called biotic elements. For example, man, plants, animals, microorganisms, marine creatures, etc. They exist within the biosphere. et ombiner of tunafan-co
(ii) Abiotic elements: The elements that do not have life are called abiotic elements. For example, soil, land, water, rocks, sand, air, sunlight, humidity, etc. Abiotic elements are found in the lithosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere and biosphere.
Both the elements of environment are characterised by two significant features. These are:
(i) Both the categories of elements are closely interlinked and are interdependent.
(ii) The characteristics of both biotic and abiotic elements vary from place to place and from region to region.
8. Complete the given list by making a division of biotic and abiotic from the following elements:
sand, mineral, bacteria, phytoplankton, grass, rainfall, humidity, soil, water, forest, insects, virus, coal, mineral oil, mangrove, solar energy.
|
Biotic elements |
Abiotic elements |
Answer:
|
Biotic elements |
Abiotic elements |
|
bacteria, phytoplankton, grass, forest, insects, virus, mangrove. |
sand, mineral, rainfall, humidity, soil, water, coal, mineral oil, solar energy. |
9. What is meant by environmental problem?
Answer: Environmental problems are issues that seriously disturb the normal functioning of different elements and components of the environment. In other words, these are challenges—either natural or man-made—that disrupt the ecological balance of nature. Most environmental problems today are caused by human activities, and hence, they can often be reduced or controlled if proper and timely measures are taken.
10. Mention the causes which are responsible for the growing environmental problems in the world.
Answer: The modern world faces numerous environmental challenges, most of which are the result of human actions. These include deforestation, global warming, pollution of air, water, and noise, as well as large-scale environmental degradation. The key causes behind these growing problems are:
(i) Rapid growth of population: Urbanisation, industrialisation, and the expansion of human settlements have led to the overuse and depletion of natural resources like forests, water, and minerals. The world’s population has risen from 6 billion in 2000 to over 7 billion today, with urban population increasing from just 2% in 1800 A.D. to about 50% now. This high population density demands greater use of resources, which disturbs the ecological balance.
(ii) Overuse of resources: Although nature provides enough resources, humans often exploit them unsustainably. From extraction to consumption, a significant portion of resources is wasted, leading to their rapid depletion and environmental imbalance.
(iii) Rapid industrial expansion: Since the Industrial Revolution, industries have multiplied at an unprecedented rate, increasing resource use and releasing pollutants into the atmosphere. Industrial production has expanded nearly 100 times over the last century. Many industries emit greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, methane, sulphur dioxide, nitrous oxide, and chlorofluorocarbons, contributing to global warming.
(iv) Increased use of vehicles: With industrial growth, urbanisation, and improved living standards, the number of vehicles has grown rapidly, emitting huge amounts of smoke and greenhouse gases. Additionally, the expansion of air travel has added harmful gases to the atmosphere, causing depletion of the ozone layer, which adversely affects all living beings on Earth.
11. What do you mean by the balance state of environment? Answer: The balance state of the environment refers to the ecological equilibrium maintained by various elements of nature. It ensures the smooth functioning of natural processes and sustains life on Earth.
- Nature maintains this ecological balance through the interaction of biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) components.
- If this balance is disturbed, it leads to serious environmental problems such as global warming, natural disasters, and resource depletion.
Some important aspects of ecological balance are:
- Forest cover: At least 33% of forest/green cover is necessary for ecological balance. In hilly or mountainous regions, it should be 60% or more; otherwise, problems like soil erosion, landslides, and water scarcity occur.
- Interdependence: There exists an ecological balance between biotic and abiotic elements. The depletion of any element disrupts the whole system.
- Balance within elements: There is also a balance among organisms themselves (biotic-biotic) and among abiotic elements (abiotic-abiotic).
- Ecological cycles: Natural cycles like the hydrological cycle, carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, and water cycle play a vital role in maintaining ecological balance.
12. “Deforestation is the cause of many problems and the result of many developmental processes”- analyse the statement with arguments. Answer: Deforestation is one of the most serious environmental problems faced by the world today. Forests, which act as the green lungs of the Earth, are disappearing rapidly due to human activities. The minimum required forest cover is 33%, but most countries, including industrially developed and developing ones, fall short of this requirement.
This statement is justified because deforestation is both:
- A cause of several environmental problems, and
- A result of developmental processes such as industrialisation, urbanisation, and agricultural expansion.
Problems caused by deforestation:
- Causes drought conditions and reduces rainfall.
- Leads to decline in agricultural production due to less rain.
- Causes landslides and soil erosion.
- Increases the presence of carbon dioxide, as fewer trees absorb it.
- Contributes to the rise in Earth’s temperature (global warming).
- Destroys biodiversity, leading to the extinction of various species.
- Disturbs ecological balance, creating a chain of environmental crises.
Benefits or reasons behind deforestation:
- Provides more space for human settlement and habitation.
- Facilitates industrial expansion and urban growth.
- Supplies timber and raw materials for industries like construction, paper, and chemicals.
- Assists in the development of transport infrastructure (e.g., railways).
- Increases cultivable land area, leading to higher food production.
Thus, while deforestation fuels development, it also creates long-term environmental challenges, making sustainable forest management crucial.
13. What is global warming? Discuss its main causes.
The main causes of global warming are:
(i) Use of fossil fuels: One of the primary causes for the increase of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere is the burning of fossil fuels such as petroleum, diesel, kerosene, coal, etc. The use of these fuels in vehicles, factories, homes, etc. results in the release of gases such as carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, sulphur oxide, etc.
(ii) Deforestation: Rampant deforestation increases the presence of greenhouse gases particularly carbon dioxide. Trees normally absorb the carbon dioxide given out by human beings and convert it into oxygen. But, today the green cover is shrinking at an alarming rate and the population is increasing rapidly leading to great increase in the presence of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere which in turn causes an increase in the temperature of the atmosphere.
(iii) Increased presence of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs): As a result of the use of air conditioners, refrigerators, evaporation of industrial solvents, production of plastic foams, aerosols, propellants, etc. the presence of chlorofluorocarbons has increased in the atmosphere. These gases keep the earth warmer and reduce the extent of the ozone layer.
(iv) Increased production of methane: Methane is produced when bacteria breaks down dead matter in moist places that lack oxygen such as swamps, wetlands, etc. Production and use of oil, natural gas and incomplete burning of organic matter are also sources of methane. Decaying of dead animals and dumping of animal and human excreta in the open increase the presence of methane in the atmosphere.
(v) Nitrogen gases: The increased presence of nitrogen gases such as nitrogen dioxide and nitrous oxide has also been responsible for increased global warming. These type of gases are released by aircraft, from burning of biomass and nitrogen rich fuels, from nitrogen fertilizers, etc.
(vi) Volcanic activity: During volcanic eruption many gases are released into the atmosphere. Volcanic activity often leads to an increase in the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Among the greenhouse gases, carbon dioxide contributes the most to the rise of temperature over the earth.
14. Give an account of the problems that may occur as a result of global warming. Answer: Global warming has far-reaching and multi-dimensional impacts on the earth’s climate, ecosystems, and human life. It is caused primarily by increased greenhouse gas emissions, leading to a gradual rise in the earth’s temperature. The following problems may arise as a result:
- Rise in Sea Levels:
Melting of polar ice caps and glaciers due to global warming would increase sea levels. A temperature rise of even 2°C–3°C could cause significant ice melt, submerging around 5 million sq. km of coastal regions, affecting deltaic areas, low-lying lands, and island nations. - Expansion of Arid Regions:
Many fertile areas may turn into semi-arid or desert-like zones. Forest regions may shrink into grasslands, and glaciated mountain areas will recede, reducing natural freshwater sources. - Impact on Agriculture:
Rising temperatures would negatively affect crop productivity as many crops cannot tolerate excessive heat. This may cause food shortages, famine, and poverty. Agricultural exports would decline, leading to reduced trade, and rural populations may migrate to urban areas, creating socio-economic challenges. - Disturbance in Ecological Balance:
Global warming disturbs the delicate ecological balance of nature. Certain plants and microorganisms may not survive higher temperatures, leading to biodiversity loss, disrupted ecosystems, and increased vulnerability to natural calamities. - Extreme Weather Events:
Increased heat may result in unpredictable climatic conditions such as droughts, floods, heatwaves, and cyclones, threatening both natural and human systems. - Methane Emissions:
Improper disposal of dead animals and organic waste in open areas can increase methane emissions, further contributing to global warming.
16. What do you mean by air pollution? What are the causes of air pollution? Answer: Air pollution refers to the contamination of the atmosphere by harmful substances that disturb its natural composition. When pure air gets mixed with pollutants such as carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, smoke, lead particles, and other toxic gases, it becomes harmful to humans, animals, and plants.
The causes of air pollution can be broadly classified into two categories:
- Natural Causes:
- Volcanic Eruptions: Release of ash, gases, and fine particles into the air.
- Forest Fires: Natural wildfires emit large amounts of smoke and carbon monoxide.
- Biological Decay: Decomposition of organic matter produces methane and other gases.
- Radioactive Minerals: Naturally occurring radioactive materials in the earth’s crust release radiation into the atmosphere.
- Man-Made Causes:
- Thermal Power Plants: Use of coal and fossil fuels releases pollutants like sulphur dioxide and carbon dioxide.
- Industrial Activities: Factories emit smoke, toxic gases, and particulate matter.
- Vehicular Emissions: Automobiles produce nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, and hydrocarbons.
- Deforestation: Reduces the natural ability of trees to absorb carbon dioxide.
- Urbanisation and Rapid Industrial Growth: Increase in construction, transport, and waste burning adds to air pollution.
- Burning of Fossil Fuels: Use of petrol, diesel, and coal for energy generation and transportation.
- Atomic and Nuclear Activities: Release of radioactive substances during nuclear experiments or accidents.
17. Write the names of some greenhouse gases.
Answer: Some of the main greenhouse gases are:
carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane (CH), nitrous oxide (N₂O), chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), water vapour, etc.
18. What kinds of problems may be created by air pollution?
Answer: Air pollution has adverse effects on living organisms and materials. The pollution in air may result in the occurrence of the following problems:
(i) Long exposure to air pollutants (including cigarette smoke) can result in lung cancer, asthma, chronic bronchitis and several other diseases.
(ii) Air pollutants enter plants through stomata, destroy chlorophyll and affect photosynthesis.
(iii) When rain water comes down through the polluted atmosphere, it may become laden with sulphuric acid and nitric acid. This acid rain may be injurious to plants and animals. It is also harmful for the buildings made of marbles.
(iv) Air pollutants mixing up with rain can cause high acidity in fresh water lakes. This adversely affects the aquatic life.
(v) Because of their corrosiveness, particulates can cause damage to exposed surfaces. Presence of sulphur dioxide (SO₂) and moisture can accelerate corrosion of metallic surfaces.
19. How is water polluted? How can it harm?
Answer: The deterioration of the chemical, physical, and biological properties of water is called water pollution. There are several factors responsible for water pollution. Some of the major causes are:
(i) Discharge of untreated sewage into rivers, lakes, and other freshwater bodies through drains and sewers.
(ii) Release of industrial wastes containing toxic chemicals, acids, alkalis, metallic salts, phenols, cyanides, ammonia, and radioactive substances into water bodies.
(iii) Excessive use of agrochemicals like fertilizers and pesticides, which get washed away by rainwater and surface run-off.
(iv) Use of synthetic detergents for washing and cleaning.
(v) Spillage of oil during drilling, transportation, and shipment in seas and oceans.
The polluted water can harm the environment and living beings in various ways. Some of the major effects of water pollution are:
(i) Decomposition of organic matter by microorganisms depletes the dissolved oxygen in water, which is harmful to aquatic life, especially fish.
(ii) Contaminated water spreads waterborne diseases like cholera, dysentery, typhoid, and jaundice.
(iii) Polluted water, when used for irrigation, may reduce soil fertility and agricultural productivity.
(iv) Harmful substances such as heavy metals, pesticides, and cyanides damage or kill aquatic organisms.
(v) Pesticides and toxins present in drinking water can enter the human body and cause serious health problems.
20. What kinds of steps may be taken by the people for the solution of environmental problems? Answer: Today, our planet is facing several critical environmental problems such as deforestation, global warming, air pollution, water pollution, soil degradation, noise pollution, and overall environmental deterioration. These issues mainly arise from rapid population growth, industrialisation, urban expansion, excessive use of vehicles, overexploitation of minerals, and burning of fossil fuels.
The people, as responsible citizens, can play a major role in addressing these issues by taking the following steps:
- Population Control: Reducing the growth of population to keep the demand for natural resources within sustainable limits.
- Forest Conservation: Enforcing strict laws to prevent indiscriminate cutting of trees and promoting afforestation.
- Promotion of Green Cover: Expanding forested areas and encouraging tree plantation drives.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Minimising the use of chemical fertilisers and pesticides while encouraging organic farming practices.
- Renewable Energy Use: Promoting the use of solar, wind, and biomass energy instead of conventional fossil fuels.
- Avoiding Non-Biodegradable Materials: Reducing the use of plastic, nylon, and other non-degradable substances.
- Waste Recycling: Recycling and proper management of industrial and urban wastes to minimise environmental damage.
- Protecting the Ozone Layer: Avoiding products that emit chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs).
- Minimising Fossil Fuel Dependency: Reducing excessive use of coal, petrol, and diesel to cut down greenhouse gas emissions.
- Energy Conservation: Saving electricity by switching off unused appliances and adopting energy-efficient technologies.
- Industrial Regulation: Restricting industries from releasing untreated waste into rivers and other water bodies.
- Public Awareness: Educating people about environmental conservation through campaigns and community initiatives.
By adopting these measures, individuals and communities can contribute significantly to protecting and preserving the environment for future generations.
Class 10 Geography Chapter 2 – Environmental Geography FAQs
Get Free NCERT PDFs
If you want to download free PDFs of any chapter, click the link below and join our WhatsApp group:


