Embark on a journey to understand the fundamentals of measurement and movement with Class 6 *Amar Bigyan* Chapter 9 – Measurement of Length and Motion, designed as per the new SCERT Assam syllabus 2025-26 for English Medium students. This chapter introduces students to the concepts of measuring length accurately and exploring the principles of motion in everyday life. Aligned with the updated Assam board curriculum, it encourages hands-on learning and scientific curiosity, making physical science accessible and engaging for young learners.
The new syllabus 2025-26 emphasizes practical skills and inquiry-based learning, and this chapter provides a perfect platform to master measurement techniques and understand motion. Students will learn about standard units of length, tools for measurement, and the types of motion observed in their surroundings. From rulers to real-world examples of motion, this chapter connects theory to practice. Scan the QR code X3W9A6 to access interactive resources and deepen your understanding of measurement and motion as per the SCERT Assam English Medium curriculum.
✅ What You’ll Learn in Chapter 9:
- Introduction to measurement of length in the new SCERT Assam syllabus
- Standard units of length: centimeters, meters, and kilometers
- Tools for measuring length, such as rulers and measuring tapes
- Types of motion: linear, circular, and periodic motion
- Differences between rest and motion with practical examples
- Importance of accurate measurement in scientific experiments
- Real-world applications of measurement and motion in Assam’s context
- Inquiry-based activities to practice measurement and observe motion, as per the 2025-26 curriculum
- Simple experiments to explore length and motion concepts
🎯 Why Choose Ospin Academy for Class 6 Amar Bigyan?
- 100% aligned with the SCERT Assam English Medium new syllabus 2025-26
- Clear, concise explanations, accurate Q&A, and exam-ready notes
- Ideal for Assam board students preparing for the updated curriculum
- Engaging video lessons available on Ospin Academy’s YouTube channel
- Downloadable resources, including chapter notes, MCQs, and QR code X3W9A6 content
- Focus on conceptual clarity and practical applications as per new syllabus guidelines
With the new SCERT Assam syllabus 2025-26, learning about measurement and motion is both practical and exciting! Ospin Academy’s resources make Chapter 9 – Measurement of Length and Motion engaging, accessible, and easy to master. Use the QR code X3W9A6 to unlock additional study materials and join Ospin Academy to excel in the updated Class 6 Amar Bigyan curriculum while discovering the science behind everyday measurements and movements!
SCERT Assam Class 6 Science (Amar Bijnan) – English Medium Chapter-wise Solutions PDF
Special Combo Offer!
(For SCERT Assam Class 6, 2025)
Get complete chapter-wise Science (Amar Bijnan) solutions in English Medium prepared by expert teachers.
Covers all textbook exercises, key concepts, definitions, and diagrams as per the latest SCERT Assam syllabus.
Ideal for concept clarity, homework assistance, and exam preparation.

Class 6th Science
MEASUREMENT OF LENGTH AND MOTION
Exercise
Q.1. Match each item in coloumn I with most appropriate units of column II
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(a) Height of building |
(i) cm |
|
(b) Distance between two cities |
(ii) m |
|
(c) Length of pencil |
(iii) mm |
|
(d) Thickness of your note book |
(iv) km |
Answer:
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(a) Height of building |
(ii) m |
|
(b) Distance between two cities |
(iv) km |
|
(c) Length of pencil |
(i) cm |
|
(d) Thickness of your note book |
(iii) mm |
Q.2. Classify the following objects based on the most appropriate measuring instrument: i.e. scale and measuring tape.
(a) Height of a building
Answer: measuring tape
(b) Length of a pencil
Answer: scale
(c) Length of a paper clip
Answer: scale
(d) Circumference of the stem of a tree
Answer: measuring tape
(e) Width of an eraser
Answer: scale
(f) Length of football field.
Answer: measuring tape
Q.3. True or false?
(a) 1m-100cm
Answer: True
(b) 5000m 5 cm
Answer: false
(c) 2000 mm = 2 cm
Answer: false
(d) Movement of a clock hand is an example of linear motion
Answer: false
(e) Motion in a straight line is called as oscillatory motion.
Answer: false
Q.4. Darken the circle of correct answer.
(i) Which of the following is an example of periodic motion?
(A) A bus moving in the road
(B) A swing pendulum
(C) A falling ball
(D) A walking person
Answer:(b)
(ii) Which of the following is an example of circular motion?
(A) A swing in motion
(B) A moving train
(C) A ceiling fan’s blade in motion
(D) A moving cycle
Answer:(c)
5. Convert the followings:
(a) 250 mm to m
Answer: 250 mm = 250/ 1000 m = 0.25m
(b) 7.5 km to m
Answer: we know that. 1km = 1000m
∴ 7.5 km = 7.5 × 1000m
= 7500m
(c) 3m to cm
Answer:
3m = 3 x 100 cm
= 300 cm
(d) 1.25m to mm
Answer: we know that,
1m = 1000mm
.:. 1.25m = 1.25 × 1000mm
= 1250mm
Q.6. Distance between your home and school is 2000m, convert it into kilometer
Answer: We know that,
1 km = 1000 m
∴ The Distance between home and school = 2000m
= 2 × 1000m
= 2.x 1km
= 2km
Q.7. With the help of a thread measure the length of different objects around you, such as pencil, pen, geometry box etc. Express each length in milimeter, centimeter and record your findings in a table. Here an example is given below
|
Object |
Length in cm |
Length in mm |
|
Pencil Pen Geometry box |
15 14 20 |
150 140 200 |
Q.8. Observe different objects in your classroom and classify them based on their length less then 10 cm, between 10cm and Im and more than 1m. Record your observations in appropriate table.
Answer:
|
Object length |
Example |
|
Less than 10 cm Between 10 cm and 1m More than 1m |
Eraser, Sharpener Pen, notebook Classroom board, table |
Q.9. Ask three of your friends to stand against a wall. Mark their height on the wall. Now measure their height and express each measurment in meter and centimeter.
Let’s assume your measured the height of your three friends as follows-(
|
Name |
Height in cm |
Height in meter |
|
Riya |
142 cm |
1.42m |
|
Abhijit |
156 cm |
1.56 m |
|
Deepa |
140 cm |
1.40 m |
Q.10. Identify different type of motion in your surrounding: lin-ear, circular and oscillatory. Give two examples for each type of motion.
Answer:
Two examples for each type of motion are
(1) Linear motion: Car moving on a straight road, A person walking in a straight line.
(2) Circular motion: Blades of a fan, a merry-go-round
(3) Oscillatory motion: A swing, a pendulum clock
11. (a)
|
Reference point |
Distance |
Distance |
|
Pritam |
To Bikash——m |
To Anima——m |
|
Ankur |
To Gargi——m |
To Pritam——m |
|
Anima |
To Pritam——m |
To Bikash——m |
|
Gargi |
To Bikash——m |
To Ankur——m |
Answer:
|
Reference point |
Distance |
Distance |
|
Pritam |
To Bikash 3 m |
To Anima 6 m |
|
Ankur |
To Gargi 3 m |
To Pritam 6 m |
|
Anima |
To Pritam 3 m |
To Bikash 6 m |
|
Gargi |
To Bikash 6 m |
To Ankur 3 m |
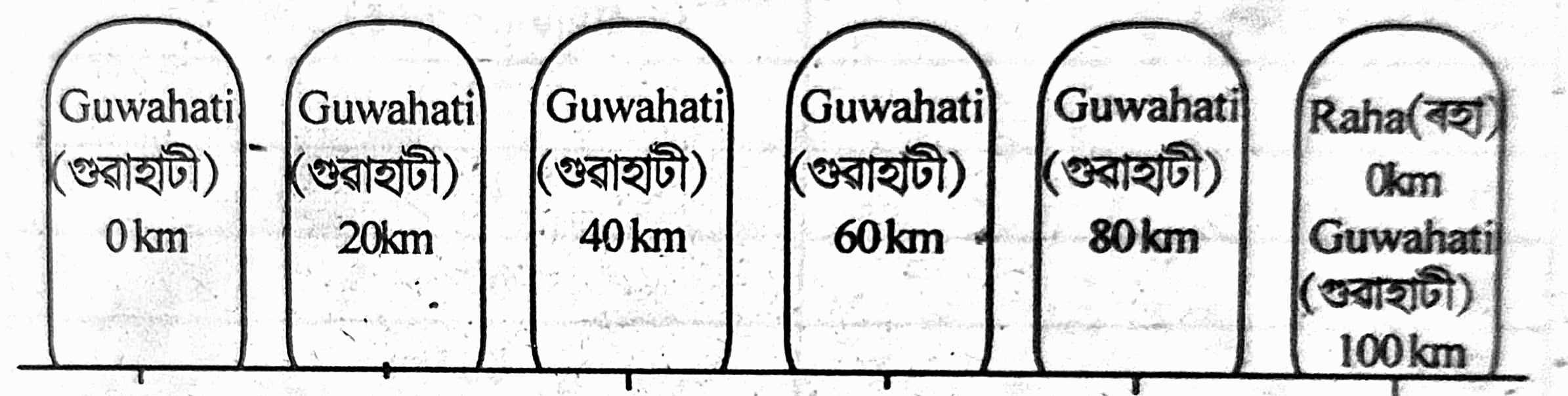
|
Reference point (প্রসংগ বিন্দু) |
Distance to Guwahati |
|
A |
|
|
B |
|
|
C |
|
|
D |
|
|
Distance to Raha |
|
|
A |
|
|
B |
|
|
C |
|
|
D |
|
|
From Guwhati (গুৱাহাটীৰ পৰা) |
Answer:
|
Reference point |
Distance to Guwahati |
|
A |
20 |
|
B |
40 |
|
C |
60 |
|
D |
80 |
|
Distance to Raha |
|
|
A |
80 |
|
B |
60 |
|
C |
40 |
|
D |
20 |
|
From Guwhati |
100 |
Class 6 Amar Bigyan Chapter 9 – Measurement of Length and Motion FAQs
Get Free NCERT PDFs
If you want to download free PDFs of any chapter, click the link below and join our WhatsApp group:




