SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 2 – Acids-Bases and Salts Solutions & Summary
Struggling with Class 10 Science Chapter 2 – “Acids-Bases and Salts”? At Ospin Academy, we provide NCERT-aligned solutions, practice MCQs, and clear explanations to help you excel in your exams.
📖 Chapter Overview:
This chapter covers the properties, reactions, and uses of acids, bases, and salts, along with pH and its significance.
📌 Key Topics Covered:
- Properties of acids and bases
- Chemical reactions of acids and bases
- pH scale and its importance
- Formation and uses of salts
- Common indicators like litmus and phenolphthalein
📌 Important Questions for Exams:
- What are the properties of acids and bases?
- How is pH measured, and why is it important?
- What happens when an acid reacts with a base?
- What are salts, and how are they formed?
- What are the uses of common salts in daily life?
📝 How Ospin Academy Helps:
- Step-by-step NCERT-based answers for SEBA Class 10 Science
- Exam-focused MCQs and practice questions
- Simple explanations with practical examples
- Concise revision notes for quick study
Unlock SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 2 – “Acids-Bases and Salts” solutions at Ospin Academy now!
Class 10 Science (English Medium) PDF Solutions 2025-26 | SEBA Assam
Download Class 10 Science (English Medium) PDF with detailed solutions, MCQs, and extra practice questions for SEBA Assam 2025-26.
Textual Questions and Answers :
Page -18
Q.1. You have been provided with three test tubes. One of them contains distilled water and the other two contain an acidic solution and a basic solution, respectively. If you are given only red litmus paper. How will you identify the contents of each test tube?
Answer: Using red litmus paper, we can determine the contents of each test tube.
This can be accomplished by observing the color shift of the red litmus paper:
(a). A few drops of each of the 3 samples in the test tubes are added separately to the litmus paper.
(b). A basic solution in one of the test tubes turns red litmus paper blue.
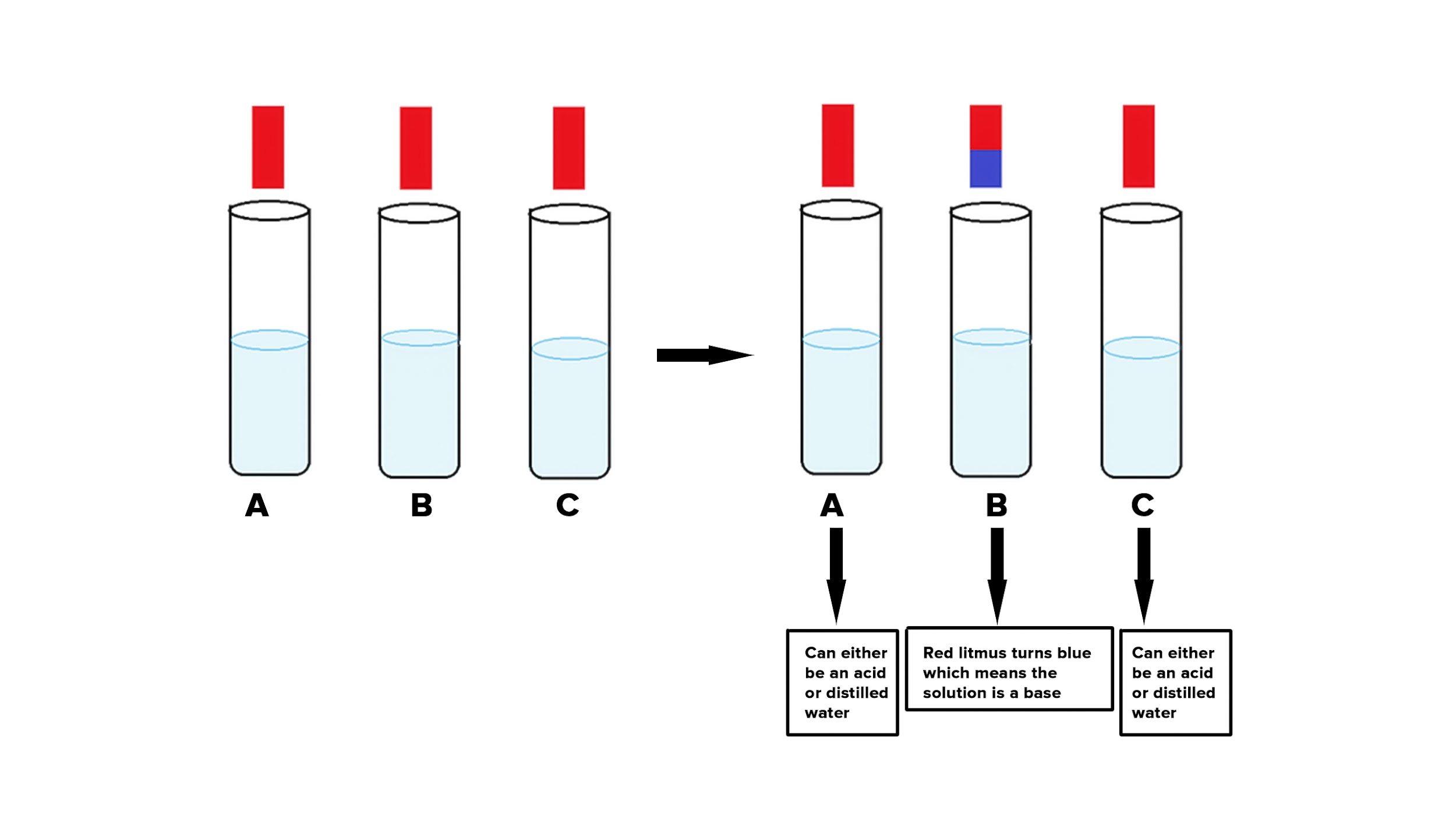
(c). Separate the blue litmus paper into two halves and a few drops of each of the remaining 2 samples in the test tubes should be added separately to the blue litmus paper.
(d). Now, the acidic solution will be the solution in the test tube that turns blue litmus paper red.
(e). Distilled water is present in test-tube solutions that do not change the colour of either red or blue litmus paper.
Page – 22
1. Why should curd and sour substances not be kept in a brass and copper vessels?
Answer: Brass and copper are metallic substances.
(a) Curd and other sour substances contain lactic acid (C₃H₆O₃).
(b) Metals react with acids to form salt and release hydrogen gas.
(c) When sour substances like curd are stored in brass or copper vessels, the lactic acid present reacts with the metal, causing corrosion of the vessels and producing harmful salts that are unsafe for consumption.
2. Which gas is usually liberated when an acid react with a metal. Illustrate with an example. How will you test for the presence of the gas?
Answer: (i) H2 gas is liberated when an acid reacts with a metal.
(ii) Illustration: Set up an apparatus. Take some Zinc granules in the test tube. Add about 5 ml dilute hydrochloric acid slowly. Soon the reaction between Zinc and hydrochloric acid starts and hydrogen gas is evolved.
(iii) Test for H2 gas: H2 gas is not soluble in water. When passed through soap solution, it gets trapped into bubbles which burn with explosion.
3. Metal compound a reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to produce effervescence. The gas evolved extinguishes a burning candle. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction if one of the compounds formed is calcium chloride.
Answer: Since the end product is calcium chloride and the gas formed extinguishes a burning candle, it is CO2 . The metal compound must be calcium carbonate.
Hence, the reaction between calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid is as follows:
CaCO3 + 2HCI → CaCl2 + CO2 + H2O
Page -25
1. Why do HCI, HNO3 etc., show acidic characters in aqueous solutions while solutions of compounds like alcohol and glucose do not show acidic character?
Answer: Solutions like HCl, HNO3 etc. get ionised in aqueous solutions and due to the presence of Hz ions they show acidic characters. While solutions of compounds like alcohol and glucose do not form any such ions so they do not show acidic characters.
2. Why does an aqueous solution of an acid conduct electricity?
Answer: In the liquid state, pure acids are terrible conductors of electricity. The presence of ions in aqueous solutions of acids is demonstrated by the fact that they conduct electricity. In an aqueous solution, acids dissociate to create H2 ions.
H+ ions reach the cathode when electricity is transmitted through an aqueous solution of an acid, and each H+ ion picks up one electron from the cathode to generate H2 gas. An aqueous acid solution conducts electricity as a result of this reaction.
HCl(aq) → H+(aq) + Cl–(aq)
In an aqueous solution with water as the solvent, the solute to be dissolved by the solvent contains fewer particles, causing the particles to move randomly. Simply said, the aqueous solution of acid conducts electricity due to the presence of ions.
3. Why does dry Hcl gas not change the colour of the dry litmus paper?
Answer: The colour of litmus paper is changed by the hydrogen ions. Dry HCl does not contain hydrogen ions (H+). Acid (For example; HCl) dissociates only in aqueous solution to give ions. since, in this case, neither HCl is in the aqueous form nor litmus paper is wet.
Therefore, the colour of litmus paper does not change.
4. While diluting an acid, why is it recommended that the acid should be added to water and not water to the acid?
Answer: Acid should always be added gradually to water while stirring continuously. If water is poured into a concentrated acid, the heat released can cause the mixture to splash out, leading to burns. Additionally, the intense local heating may cause the glass container to break.
5. How is the concentration of hydronium ions (H3O+) affected when a solution of an acid is diluted?
Answer: Mixing an acid with water results in decrease in the concentration of H3O+ ions per unit volume.
6. How is the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH–) affected when excess base is dissolved in a solution of sodium hydroxide?
Answer: When excess base is added to a sodium hydroxide solution, the concentration of hydroxide ions increases as the number of hydroxide ions per unit volume rises. However, this occurs only if the added base is soluble in water. If the base is insoluble, the hydroxide ion concentration remains unchanged.
Page -28
1. You have two solutions, A and B. The Pᴴ of solution A is 6 and Pᴴ of solution B is 8. Which solution has more hydrogen ion concentration? Which of this is acidic and which one is basic?
Answer: A solution of pH value less than 7 is acidic in nature, while greater than 7 indicates a basic solution. Therefore, the solution with pH = 6 is acidic and has more hydrogen ion concentration than the solution of pH = 8, which is basic.
2. What effect does the concentration of H+ (aq) ions have on the nature of the solution?
Answer: Acids that give rise to more H+ ions are strong acids and acids that give less H+ ions are weak acids.
3. Do basic solutions also have H+ (aq) ions ? If yes, then why are these basic?
Answer: Yes, H+ ions can be found in all basic solutions. But these are farless in number than OH– ions. For more number of OH– ions the solution is basic.
4. Under what soil condition do you think a farmer would treat the soil of his fields with quick lime (calcium oxide) or slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) or chalk (calcium carbonate)?
Answer: If the soil becomes acidic, it negatively impacts crop growth. To neutralize the acidity, farmers apply basic substances such as quick lime, slaked lime, or chalk to restore the soil’s pH balance.
Page -33
1. What is the common name of the compound CaOCl2?
Answer: Bleaching powder.
2. Name the substance which on treatment with chlorine yields bleaching powder.
Answer: Calcium Hydroxide.
3. Name the sodium compound which is used for softening hard water.
Answer: Sodium Carbonate.
4. What will happen if a solution of sodium hydrocarbonate is heated? Give the equation of the reaction involved.
Answer: When sodium hydrogen carbonate is heated, sodium carbonate and water are formed along with the evolution of carbon dioxide gas.
The reaction involved is: 2NaHCO3 → Na2CO3 + CO2+ H2O
5. Write an equation to show the reaction between plaster of paris and water.
Answer:
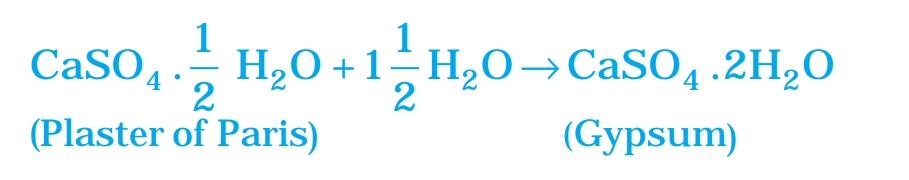
Plaster of Paris when reacts with water liberating heat through crystallisation. Gypsum is produced by heating plaster of paris to about 150-degree Celsius. When the dry plaster of paris powder is mixed with water it reforms into gypsum.
Depending upon the temperature gypsum converts to hemihydrate or anhydrous form.
EXERCISES
1. A solution turns red litmus blue, its Pᴴ is likely to be
(a) 1
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) 10
Answer: (d) 10.
2. A solution reacts with crushed egg- shells to give a gas that turns lime water milk. The solution contains.
(a) Nacl
(b) Hcl
(c) Licl
(d) Kcl
Answer: (b) Hcl.
3.10 ml of solution of NaOH is found to be completely neutralised by 8 ml of a given solution of Hcl. If we take 20 ml of the same solution of NaOH, the amount Hcl solution (the solution as before) required to neutralise it will be
(a) 4 ml
(b) 8 ml
(c) 12 ml
(d) 16 ml
Answer: (d) 16 ml.
4. Which one of the following types of medicines is used for treating indigestion?
(a) antibiotic.
(b) Analgesic.
(c) Antacid.
(d) Antiseptic.
Answer: (c) Antacid.
5. Write word equations and then balanced equations for the reaction taking place when:
(a) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with zinc granules.
(b) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium.
(c) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with aluminium powder.
(d) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with iron filings.
Answer:
a) Dilute sulphuric acid reacts with zinc granules
Word Equation: Zinc + Sulphuric Acid → Zinc Sulphate + Hydrogen
Balanced Chemical Equation: Zn + H₂SO₄ → ZnSO₄ + H₂
b) Dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium
Word Equation: Magnesium + Hydrochloric Acid → Magnesium Chloride + Hydrogen
Balanced Chemical Equation: Mg + 2HCl → MgCl₂ + H₂
c) Dilute sulphuric acid reacts with aluminium powder
Word Equation: Aluminium + Sulphuric Acid → Aluminium Sulphate + Hydrogen
Balanced Chemical Equation: 2Al + 3H₂SO₄ → Al₂(SO₄)₃ + 3H₂
b) Dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with iron filings
Word Equation: Iron + Hydrochloric Acid → Iron(II) Chloride + Hydrogen
Balanced Chemical Equation: Fe + 2HCl → FeCl₂ + H₂
6. Compounds such as alcohols and glucose also contain hydrogen beet are not categorised as acids. Describe an activity to prove it.
Answer: Take solutions of glucose and alcohols in a beaker. Fix two nails on a cork and place the cork in the beaker. connect the nails to the two terminals of a 6 volt battery through a bulb and a switch. Switch on the current. The bulb does not glow. That means current does not pass through the circuit. This show that no H+ ions are present in the solution. This experiment shows that alcohol and glucose are not acid.
7. Why does distilled water not conduct electricity, whereas rain water does?
Answer: Distilled water is pure form of water which do not contain any solute in it. Therefore it cannot conduct electricity because it does not contain ions while rain water contains dissolved salts and acids which dissociates in ions and conducts electricity.
8. Why do acids not show acidic behaviour in the absence of water?
Answer: Acids form hydrogen ions H+ (aq) ions in its aqueous solution which are responsible for their acidic characters. Therefore acids cannot show acidic behaviour in the absence of water.
9. Five solutions A, B, C, D and E when tested with universal indicator showed Pᴴ as 4, 1, 11, 7 and 9 respectively. Which solution is
(a) Neutral?
(b) Strongly alkaline?
(c) Strongly acidic?
(d) Weakly acidic?
(e) Weakly alkaline?
Arrange the Pᴴ in increasing order of hydrogen ion concentration.
Answer: (a) Neutral solution is D
(b) Strongly alkaline is C
(c) Strongly acidic is B
(d) Weakly acidic is A
(e) Weakly alkaline is E
Pᴴ values in increasing order of hydrogen ion concentration 11<9<7<4<1
10. Equal lengths of magnesium ribbons are taken in test tubes A and B. Hydrochloric acid (Hcl) is added to test tube A. while acetic acid (CH3COOH) is added to test tube B. Amount and concentration taken for both the acids are same. In which test tube will be fizzing occur more vigorously and why?
Answer: Hydrochloric acid is stronger acid than acetic acid and reaction between magnesium ribbon and Hcl is faster than between magnesium ribbon and
CH3COOH. So fizzing will occur more vigorously in test tube A. containing hydrochloric acid.
11. Fresh milk has a pH of 6. How do you think the pH will change as it turns into curd? Explain your answer.
Answer: The Pᴴ value of fresh milk falls below 6 when it turns into curd due to the formation of lactic acid during the process.
12. A milkman adds a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk.
(a) Why does the shift the Pᴴ of the fresh milk from 6 to slightly alkaline?
(b) Why does this milk take a long time to set as curd?
Answer: (a) The milkman adds a little baking soda to fresh milk to make it slightly alkaline so that milk can be preserved for a longer time.
(b) The lactic acid is used for neutralise the base initially and when more lactic acid is formed then the milk sets as curd.
13. Plaster of paris should be stored in a moisture-proof container. Explain why?
Answer: Plaster of Paris (POP) should be stored in a moisture-proof container because it reacts with moisture. POP is chemically calcium sulfate hemihydrate (CaSO₄·½H₂O), and when exposed to moisture or water, it absorbs water and turns into gypsum (CaSO₄·2H₂O), which is a hard, solid substance.
The reaction is:
CaSO₄·½H₂O + 1½H₂O → CaSO₄·2H₂O
This process makes POP hard and unusable for molding. Storing it in a moisture-proof container prevents it from reacting with air or water, ensuring it remains usable.
14. What is a neutralisation reaction? Give two example.
Answer: A neutralization reaction occurs when an acid reacts with a base to produce salt and water. It involves the combination of hydrogen ions (H⁺) from the acid and hydroxide ions (OH⁻) from the base to form water (H₂O). The neutralization of a strong acid and a strong base results in a pH of 7.
Example: When sodium hydroxide reacts with hydrochloric acid, it forms sodium chloride and water.
Reaction:
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H₂O
(Acid) (Base) (Salt) (Water)
15. Give two important uses of washing soda and baking soda.
Answer:
|
Uses of washing soda |
Uses of baking soda |
|---|---|
|
(i) Washing soda is used in glass, soap and paper paper industries. |
(i) For making baking powder, which is a mixture of baking soda and a mild edible acid such as tartaric acid. |
|
(ii) It is used for removing permanent hardness of water. |
(ii) It is used in soda-acid fire extinguishers. |
SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 2 – Acids-Bases and Salts FAQs
Get Free NCERT PDFs
If you want to download free PDFs of any chapter, click the link below and join our WhatsApp group:

