SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 15 – Our Environment Solutions & Summary
Looking for accurate solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 15 – “Our Environment”? Ospin Academy provides comprehensive NCERT solutions for SEBA Assam students.
📖 Chapter Overview:
This chapter explores the components of the environment, their interconnections, and the effects of human activities on ecological balance.
📌 Key Topics Covered:
- Components of the Ecosystem
- Food Chains and Food Webs
- Biodegradable and Non-Biodegradable Substances
- Energy Flow in the Ecosystem
- Waste Management and Environmental Conservation
📌 Important Questions for Exams:
- What is an ecosystem? Explain its major components.
- Describe the energy flow in an ecosystem with a diagram.
- What is a food chain? Give an example of a terrestrial food chain.
- How do human activities disturb the ecological balance?
- Why is waste management important for the environment?
📝 How Ospin Academy Helps:
- Step-by-Step NCERT Solutions for SEBA Syllabus
- Conceptual Clarity with Diagrams and Examples
- Easy-to-Understand Chapter Notes for Quick Revision
- Practice Questions and Exam-Oriented Solutions
Access the best solutions for SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 15 – “Our Environment” only on Ospin Academy!
Class 10 Science (English Medium) PDF Solutions 2025-26 | SEBA Assam
Download Class 10 Science (English Medium) PDF with detailed solutions, MCQs, and extra practice questions for SEBA Assam 2025-26.
Textual Questions and Answers:
Page – 257
1. Why are some substances biodegradable and some non- biodegradable?
Answer: Substances are classified as biodegradable or non-biodegradable based on their ability to be broken down by microorganisms such as bacteria and decomposers like fungi. Natural materials such as wood, paper, and food waste can be decomposed by these organisms. However, synthetic materials like plastics and metals are resistant to this process. This distinction determines why some substances are biodegradable and others are not.
2. Give any two ways in which biodegradable substances would affect the environment.
Answer:
(i) Biodegradable substances break down through the action of microorganisms, and the nutrients released are returned to the soil via natural cycles, maintaining ecological balance.
(ii) Biodegradable waste like kitchen scraps and plant materials can be composted to produce organic fertilizer, enriching the soil and promoting plant growth.
3. Give any two ways in which non-biodegradable substances would affect the environment.
Answer: Non-biodegradable substances affect the environment in the following ways:
1. They contaminate soil and water resources as they cannot be decomposed by micro-organisms.
2. These substances, when accidentally eaten by stray animals, can harm them and can even cause their death.
Page – 261
1. What are trophic levels? Give an example of a good chain and state the different trophic levels in it.
Answer: Trophic level is the fundamental level occupied by an organism in food chain. Trophic literally means feeding, so trophic levels are the levels or positions at which species feed. Examples of trophic Levels include ‘herbivores’ and ‘decomposers’
An example of a food chain depicting various trophic levels is as follows:
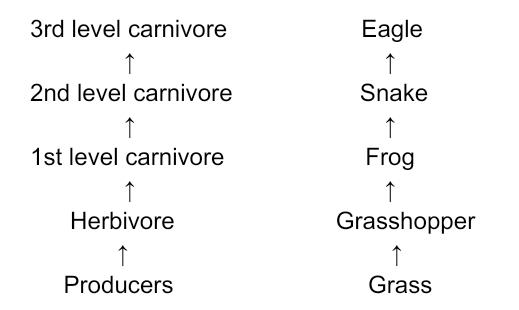
2. What is the role of decomposers in an ecosystem?
Answer: Following is the role of a decomposer in the ecosystem:
(i) They act as a cleansing agent of the environment by decomposing the dead plants and animals.
(ii) They help in recycling the nutrients.
(iii) They provide space for new beings in the biosphere by decomposing the dead.
(iv) They help in putting back the various elements into water, soil and air for the reuse of producers like crop plants.
Page – 264
1. What is ozone and how does it affect any ecosystem?
Answer: The stratospheric layer of the atmosphere contains an ozone layer
1. It acts as a protective shield to the earth from harmful UV- radiation.
2. Excess exposure to UV rays can lead to skin cancer and cataract.
3. Thus the presence of ozone layer is essential to block the entry of harmful UV rays.
2. How can you help in reducing the problem of waste disposal? Give any two methods.
Answer: The excessive waste material disposal due to modern industrialisation is becoming the major reason behind the current pollutions which is ruining our environment.
We have to control this excessive amount of waste material disposal, in order to save our environment.
Some of the prevention measures are:
1. Using recyclable objects to generate the minimum possible waste materials.
Recyclable materials are also eco-friendly, that’s why it also reduces the pollution.
2. We can use biodegradable waste materials for the biogas production which can be used as our domestic fuel. This will also save our money which we generally spend for purchasing household fuel substances such as LPG, Kerosine etc.
EXERCISES:
1. Which of the following groups contain only biodegradable items?
(a) Grass, flowers and leather.
(b) Grass, wood and plastic.
(c) Fruit-peels, cake and lime-juice.
(d) Cake, wood and grass.
Answer: (c) fruit-peels, cake and lime-juice.
2. Which of the following constitute a food-chain?
(a) Grass, wheat and mango.
(b) Grass, goat and human.
(c) Goat, cow and elephant.
(d) Grass, fish and goat.
Answer: (b) Grass, goat and human.
3. Which of the following are environment-friendly practices?
(a) Carrying cloth-bags to put purchases in while shopping.
(b) Switching off unnecessary lights and fans.
(c) Walking to school instead of getting your mother to drop you on her scooter.
(d) All of the above.
Answer: (d) All of the above.
4. What will happen if we kill all the organisms in one trophic level?
Answer: If all organisms in a trophic level are eliminated, energy transfer to the next level will cease. This would lead to overpopulation of species in the previous trophic level, while organisms in higher trophic levels would face starvation and eventually die. This disruption would cause an imbalance in the entire ecosystem.
5. Will the impact of removing all the organisms in a trophic level be different for different trophic levels? Can the Jun organisms of any trophic level be removed without causing any damage to the ecosystem?
Answer:
1. If we remove producers from ecosystem, herbivores will not survive and the entire ecosystem collapse.
2. Removing herbivores result in increase number of producers and carnivores would not get food.
3. Removing carnivores result in increase of herbivores to unsustainable levels.
4. If we remove decomposers from ecosystem waste material and animal dead remains would pile up and nutrients would not be available to the producers.
5. Some or the other damage would be caused to the ecosystem if the organisms of any trophic level is removed.
6. However impact of removing producers or decomposers would be serve as the whole ecosystem would collapse.
7. Without plants sun’s energy cannot be converted to chemical energy which is the basis of life on earth.
8. Without decomposers the nutrients cannot be recycled and made available to producers.
6. What is biological magnification? Will the level of this magnification be different at different levels of the y ecosystem?
Answer: Biological Magnification is a phenomenon which explains the increasing concentration of harmful chemicals like DDT with each increase in trophic level. From the soil the chemicals are absorbed by the plants. The primary consumers eat these plants and the harmful chemicals come to reside in their bodies. As these chemicals are not degradable, they accumulate in the bodies of the organisms and the top level of the food chain gets the highest concentration of these harmful chemicals.
Most of the plants products which we eat are grown in fields in which pesticides and fertilisers have been used. These are absorbed by the plants and cannot be removed by washing or other means. As humans are at the top level of the food chain these chemicals get accumulated in our bodies and cause various disorders.
The level of biological magnification is different for different trophic levels of an eco system.
7. What are the problems caused by the non-biodegradable wastes that we generate?
Answer: The non-biodegradable waste that we generate has the following problems on environment:
1. Biological magnification- Non biodegradable wastes like pesticides enter into the food chain and accumulate with increase in trophic levels and thus harm the organisms.
2. These pesticides and chemicals also reduce the soil fertility when they penetrate into it, the soil either becomes too acidic or too alkaline.
3. Non-biodegradable materials like plastics/polythene bags when burned by Incineration also release toxic chemicals into the environment thus causing air pollution.
8. If all the waste we generate is biodegradable, will this have no impact on the environment?
Ans: Even if all the waste we generate is biodegradable, it will have an impact on the environment. This is because too much biodegradable waste can not be broken
down into harmless simpler substances by the decomposes like micro-organisms at the right time.
9. Why is damage to the ozone layer a cause for concern? What steps are being taken to limit this damage?
Answer: Damage to the ozone layer is a major concern because:
1. It increases exposure to harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays, leading to skin cancer, premature ageing, and eye problems like cataracts in humans.
2. It disrupts aquatic ecosystems by harming phytoplankton, contributing to global warming.
To address this issue, efforts are being made to:
1. Reduce the use of CFCs by replacing them with eco-friendly alternatives in refrigerants and fire extinguishers.
2. Implement regulations to control industrial emissions of ozone-depleting substances.
.
SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 15 – Our Environment FAQs
Get Free NCERT PDFs
If you want to download free PDFs of any chapter, click the link below and join our WhatsApp group:

