Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 – Regional Geography of the USA All Exercise Solutions | SEBA Assam (English Medium)
Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 – Regional Geography of the USA (SEBA Assam – English Medium)
The fourth chapter of SEBA Class 10 Geography, Regional Geography of the USA, introduces students to the geographical features and economic development of the United States of America. This chapter covers the country’s enormous natural resources, varied climate, agriculture, industries, transport systems, and its role as an advanced economy. Being one of the world’s leading nations, the USA serves as a model of regional study for HSLC students.
✅ What You Will Learn in Chapter 4:
- Location, area, and physical features of the USA
- Climate and population distribution
- Major agricultural activities (wheat belt, corn belt, cotton belt)
- Mineral resources, industries, and manufacturing centers
- Transport and trade development in the USA
- Contribution of the USA in world economy
🎯 Why Choose Ospin Academy Solutions:
- Complete SEBA Assam Class 10 Geography solutions with clear explanations
- All textbook exercises solved in English Medium
- Extra notes covering HSLC-focused short and long questions
- Exam-oriented summaries for quick revision
- Helpful for classroom tests, assignments, and HSLC board exam preparation
Class 10 Geography (English Medium) HSLC 2026 Textual Solutions PDF | SEBA Assam Syllabus
Limited Time Offer!
(For HSLC Exam 2026)
Get complete preparation for Class 10 Geography (English Medium) with this all-in-one SEBA textual solution PDF.
Covers chapter-wise solutions, definitions, map work, diagrams and practical geography – fully updated for HSLC 2026 syllabus.
Perfectly designed for revision, practice and boosting exam scores!
Class 10th Geography(E)
Chapter: 4 Ospin Academy
Regional Geography of the USA
TEXTUAL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
1. Write in short the locational and geographical characteristics of the USA.
Answer: The USA is located in North America. It is bordered by Canada to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Mexico and the Gulf of Mexico to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. The mainland stretches from 25°N to 43°N latitudes and 66°W to 125°W longitudes. Key geographical features include:
- The total geographical area is about 96 lakh sq. km, making up around 6.37% of the Earth’s total area.
- It is the fourth largest country in the world.
- Despite its size, it has only about 4.6% of the world’s population, estimated at 302 million in 2007.
- The entire country lies in the temperate climatic zone.
- Its geographical position and climate are highly suitable for agriculture, industries, trade, and commerce, which have contributed significantly to its industrial and agricultural development.
- In terms of population, it ranks third globally.
The USA can be divided into several physical divisions.
2. Give a comprehensive description of each of them.
Answer: The USA is located in the continent of North America and possesses some distinct physical and geographical features. Based on its geophysical structure, the USA can be divided into the following major physical divisions:
1. The Appalachian Highlands:
These highlands are situated in the eastern part of the USA and run almost parallel to the Atlantic Ocean. This region stretches from the Hudson Valley and the Erie–Ontario Lakes in the north to Alabama in the south. The key features of this region are:
(a) It consists of mountains, plateaus, hills, and plains with a complex structure. Major parts include the Allegheny Mountains in the west, Cumberland Plateau in the southwest, Appalachian Mountain system and valleys in the east, Bloris Mountain in the south, and the Coastal lowlands in the east.
(b) These mountains are much older than the Rockies and hence are more eroded and weathered.
(c) The average elevation does not exceed 2,000 metres above sea level.
(d) Many rivers flow through this region, such as the Ohio, Tennessee, Hudson, and Alabama.
(e) The Atlantic coastal plain located to the east and south of the Appalachian Highlands is narrow in the north and widens towards the south.
(f) This area is rich in mineral deposits like coal, petroleum, and iron, leading to the growth of several industrial cities such as New York, Boston, Philadelphia, Baltimore, Atlanta, and Washington D.C. It is one of the most economically developed regions in the USA.
2. The Central Plain:
This vast plain lies between the Rockies in the west and the Appalachian Highlands in the east. It stretches from the Great Lakes region in the north to the Gulf of Mexico in the south and forms a part of the Mississippi–Missouri basin. These rivers and their tributaries have made this one of the most fertile agricultural regions of the USA. The Central Plain can be divided into four parts:
(a) The Highland Plain region: Comprising the foothill lowlands lying east of the Rockies.
(b) The Mississippi Plain: Situated between the Highland Plain and the Appalachian Highlands, this region has an average elevation of about 300 m above sea level with very few hillocks.
(c) The Great Lake Region: Covering the areas around the Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario lakes, which were formed due to glacial activities.
(d) The Mexico Coastal Lowlands: Located in the southern part of the Central Plain with an elevation below 200 m. This lowland is prone to frequent flooding, and the Mississippi delta lies here.
Major cities in this region include Minneapolis, Chicago, Kansas, St. Louis, Birmingham, New Orleans, Miami, and Houston.
3. The Rocky Mountains or the Cordillera:
This division lies between the Central Plains in the east and the Pacific coastal lowlands in the west, consisting of mountains, plateaus, valleys, and lakes. The Rockies are young fold mountains running north–south, with some peaks rising above 4,200 m. Important mountain ranges west of the Cordillera include Sierra Nevada, Cascade, and Coast Range, while major plateaus include Columbia Plateau, Great Basin, and Colorado Plateau. The region contains many lakes like the Great Salt Lake and rivers such as Columbia, Snake, and Colorado flowing westward into the Pacific Ocean, while the Missouri, Arkansas, and Red rivers join the Mississippi and flow southward. The Rio Grande flows southeast into the Gulf of Mexico. Fertile valleys such as Puget Sound, Willamette, and California are also found here.
The famous Grand Canyon of Colorado and Death Valley are located in this region. The Cordillera is rich in minerals such as gold, silver, copper, coal, and petroleum. The California coast is agriculturally productive due to the Mediterranean climate with winter rainfall. Major cities include Seattle, Portland, San Francisco, Los Angeles, and Las Vegas.
3. Show on a sketch the physical divisions of USA.
Ans:
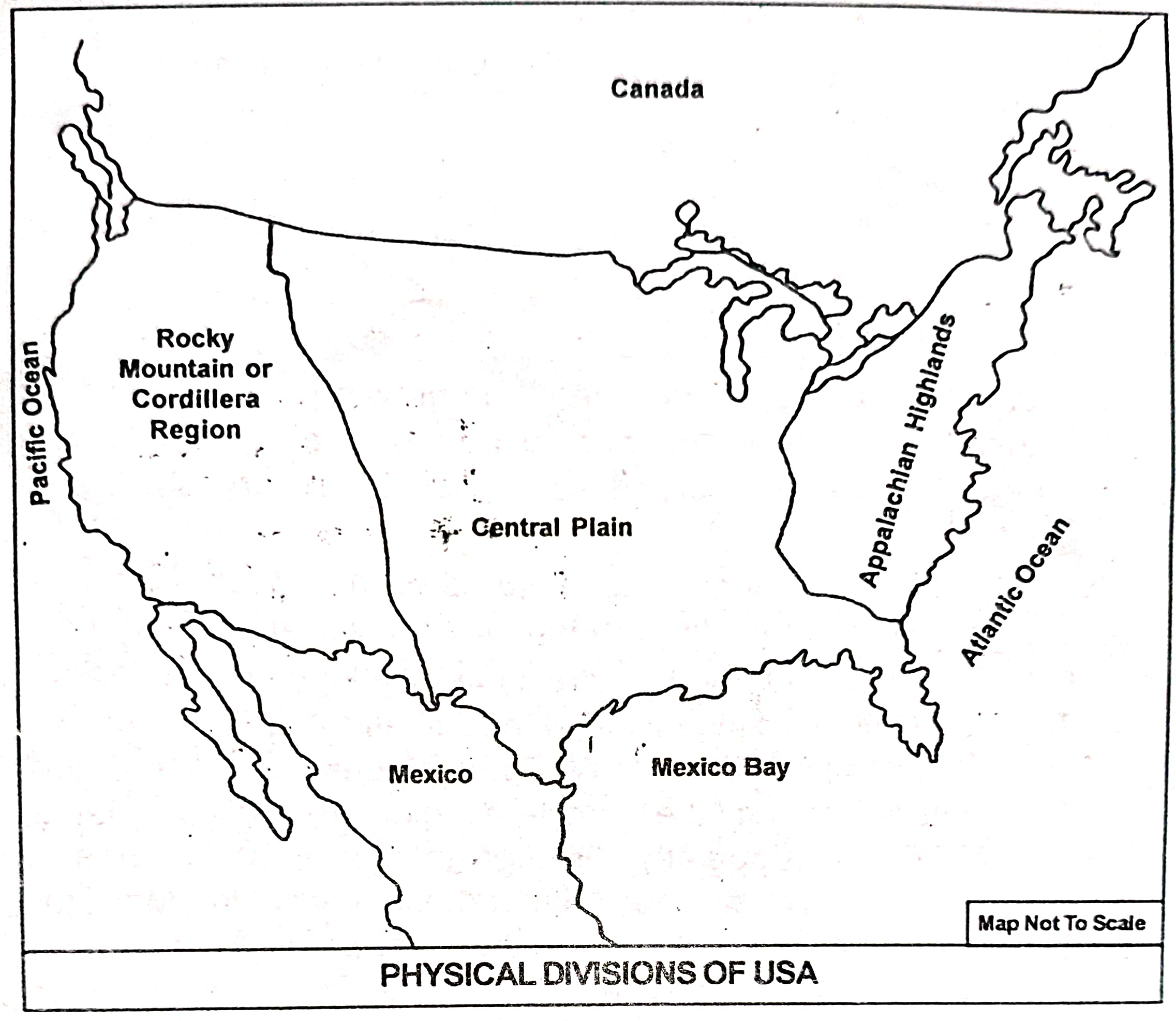
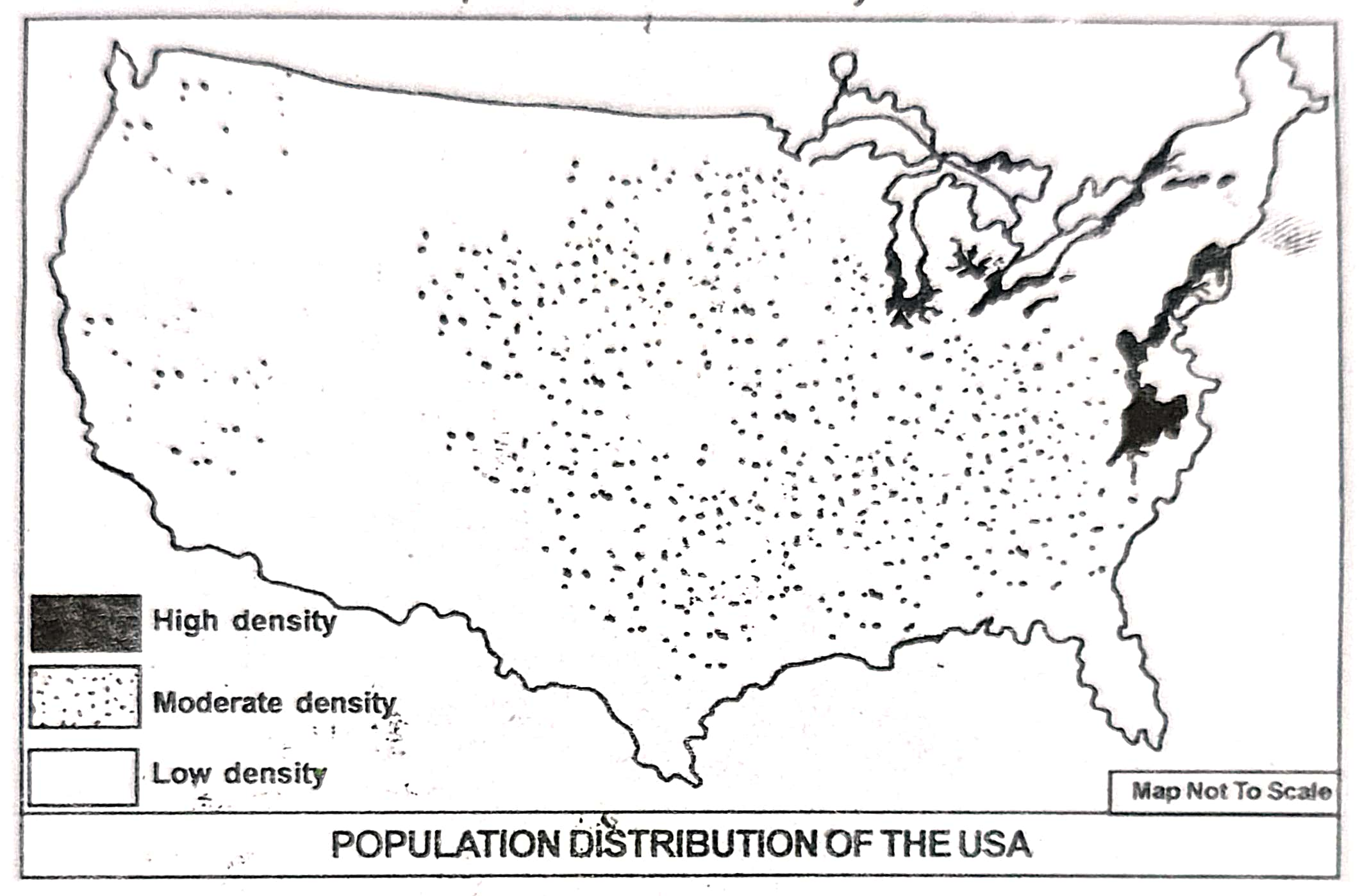
4. Discuss with the help of a sketch the growth and the distribution of population in the USA.
Answer: During the independence of the United States of America in 1776, the country had only 13 states with a total population of about 3 million. However, soon after independence, the population began to rise rapidly due to migration from Europe and the addition of 37 more states over time. By 1800, the population reached 5 million, and by 1900 it had increased to 76 million. In the 20th century, population growth became even faster because of improved living standards and advanced medical facilities. From 76 million in 1900, it rose to 281 million in 2000, and as per the 2007 estimate, the population stood at 302 million. Today, the USA is the third most populous country in the world.
Population Growth in the USA:
|
Census year |
Population (in million) |
|
1776 1800 1900 2000 2007 |
3 5 76 281 302 |
At present, the population growth rate in the USA has slowed down considerably to around 0.60%, compared to the global average of 1.20%.
A notable feature of the USA’s population is its uneven distribution, caused by differences in natural conditions, transport facilities, and economic development. The Appalachian Highlands and Atlantic Sea Board in the east are densely populated, while the Central Plain and Cordillera region are sparsely populated. Population density is also high in California’s coastal region in the west. About one-fourth of the country’s area, mainly in the south and east of Michigan State, accommodates nearly two-thirds of the total population, with a density of 85 persons per sq. km compared to the national average of 32 persons per sq. km. Massachusetts, New Jersey, and Rhode Island have a density of 300 persons per sq. km, and the District of Columbia, where Washington D.C. is located, has 3,600 persons per sq. km.
On the other hand, the Central Plain and Cordillera region have a low density of about 15 persons per sq. km, with states like Montana, Nevada, North Dakota, and Wyoming having less than 5 persons per sq. km. These areas remain sparsely populated due to rugged terrain and low rainfall, though the Cordillera region is partly inhabited because of its mineral resources.
Nearly three-fourths of the population of the USA now lives in urban areas, largely due to the high level of industrialization in the country.
5. Discuss the role of agriculture in the economy of the USA.
Answer: The USA is one of the leading developed countries of the world. It holds a top position in terms of natural resources, agriculture, industrial output, and standard of living. Agriculture has been an important factor behind the economic growth and overall progress of the nation. Although only about 5% of the population is engaged directly in agriculture, its contribution to the economy is remarkable.
(i) Provides employment: Agriculture in the USA generates employment for a large number of people. Even though only 5% of the total population works directly in this sector, many agriculture-based industries like paper, pulp, sugar, and rubber provide jobs to millions.
(ii) Earns foreign exchange: The USA ranks among the leading producers of major agricultural products in the world. It is the largest producer of corn, cotton, and tobacco, and the second largest producer of wheat and barley. The country produces about 46% of the world’s corn and 18% of its wheat. A significant share of these products is exported, earning valuable foreign exchange.
(iii) Meets domestic food needs: The USA is almost self-reliant in food production. While many developed nations import food items to feed their people, the USA is able to fulfil its own food requirements through its local production, reducing dependence on other nations.
(iv) Supplies food to other countries: The surplus agricultural production of the USA is exported to many nations. Several countries rely heavily on these supplies. Because of its vast wheat production, especially from the central plains, the USA is often called the “wheat bowl” of the world. This has strengthened its economic position globally.
(v) Boosts industrial growth: The USA is among the most industrially advanced nations. Its agriculture is highly mechanised, with extensive use of modern equipment for farming activities. This growth of agriculture has supported and expanded industrial production, with many industries benefiting from the modern farming practices developed in the USA.
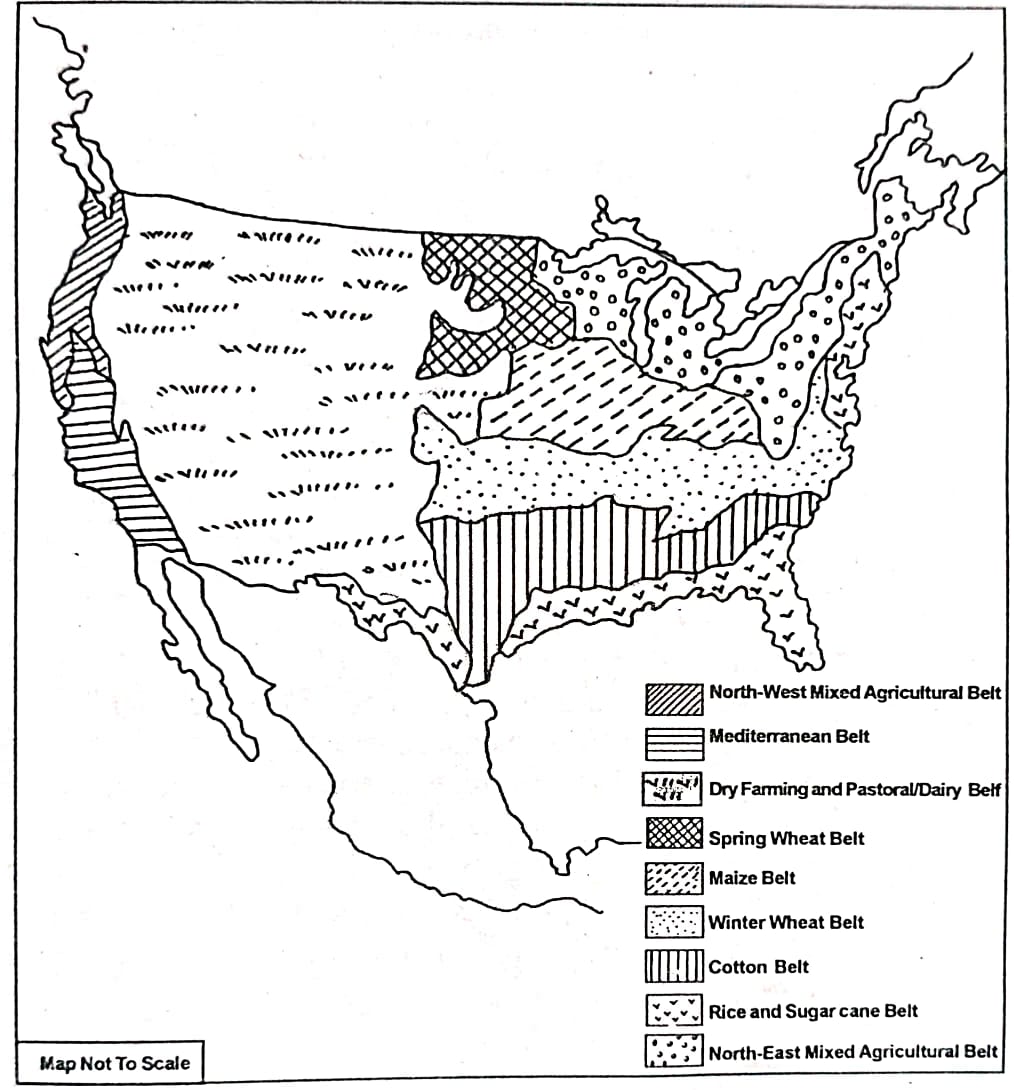
6. What do you mean by agricultural belt? How many agricultural belts have been recognised in the USA? Show them on a sketch and describe each of them briefly.
Answer: By the term ‘agricultural belt’ we mean the division of the country on the basis of the cultivation of crops or on the basis of certain agricultural characteristics.
On the basis of factors like physiography, climate, and soil, nine major agricultural belts have been identified in the USA. A brief description of each belt is given below:
(i) Rice and sugar cane belt: This belt is located along the Mexican coast and includes Florida, Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi, and the southern part of Louisiana. The area has a sub-tropical climate with high temperatures and heavy rainfall. The alluvial soil found here is well suited for growing rice and sugar cane. Banana and pineapple are also widely cultivated in this region.
(ii) The cotton belt: Situated north of the rice and sugar cane belt, this zone covers the southern part of the Mississippi valley, with its northern boundary marked by the 36°N latitude. Nearly half of the USA’s cotton is produced in Texas, Mississippi, and Arkansas.
(iii) Winter wheat and tobacco belt: Located to the north of the cotton belt, this zone stretches from the Atlantic coast in the east to Colorado in the west. The eastern section, including North Carolina, Kentucky, Virginia, and Maryland, is well known for tobacco production, while the western portion—comprising Nebraska, Kansas, East Colorado, Oklahoma, and Texas—grows winter wheat. A large share of this wheat is exported abroad.
(iv) Maize belt: This belt lies north of the winter wheat zone and stretches from mid-Ohio to mid-Nebraska. Major maize-producing states include Iowa, Illinois, Indiana, Minnesota, Pennsylvania, and Nebraska.
(v) Spring wheat belt: Found north of the Prairies, this belt has extremely cold winters, so wheat is grown during spring. It mainly includes eastern Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, and western Minnesota. The wheat produced here is of high quality, and a significant amount is exported.
(vi) Mixed agriculture of the north-east: Covering the southern and eastern states of the Great Lake Region—Minnesota, Wisconsin, Michigan, Pennsylvania, and the New England states—this belt is also called the dairy farming region. Livestock rearing is common in its new grasslands, and crops like rye and barley are also grown.
(vii) Dry farming and dairy belt: Situated mostly in the western central plain and the eastern Cordillera region, this area receives low rainfall, which supports natural grass growth and promotes dairy farming. Sheep and cattle are widely reared here. Key states include western Texas, New Mexico, Utah, Colorado, Nevada, Wyoming, Idaho, and Montana. Major crops include jowar and bajra under dry farming, while barley and maize are often cultivated with irrigation. Dairy products include milk, meat, beef, and wool.
(viii) The Mediterranean agricultural belt: Found in California along the Pacific coast, this belt produces wheat, cotton, and a variety of fruits such as oranges, grapes, and apples.
(ix) Mixed farming belt of the north-west margin: Covering Washington, Idaho, and Oregon in the north-west, this region is known for wheat and maize cultivation along with animal rearing for milk and meat, making it a prominent mixed farming area.On the basis of physiography, climate, soil, etc. there are nine recognised agricultural belts in the USA. A detailed description of each of them is given below:
7. Name the major industries of the USA and show them on a map. Describe any one of them.
Alternate Question:
Name the major industrial regions of the USA and show them on a map. Describe any one of them.
Answer: The USA is one of the most industrially advanced nations in the world, with a wide variety of industries spread across different regions. Some of the major industries of the USA include:
- Iron and steel industry
- Automobile industry
- Textile industry
- Chemical industry
- Shipbuilding industry
- Food processing industry
- Aircraft industry
- Electronic and machinery industry
The major industrial regions of the USA are:
- The North-Eastern Industrial Region
- The Great Lakes Region
- The Southern Industrial Region
- The Western Industrial Region (California)
Description of one major industrial region:
The North-Eastern Industrial Region:
This is the oldest and most important industrial region of the USA. It covers parts of New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Massachusetts, and Connecticut. This region has a well-developed transport network, abundant skilled labour, and easy access to raw materials and markets. Industries like iron and steel, textiles, shipbuilding, chemicals, and electrical goods are highly concentrated here. Major cities in this region include New York, Boston, Philadelphia, and Baltimore.
8. Write short notes on the following:
(a) Physiography of the Rocky mountaineous region.
(b) Physiography of Appalachian highlands.
(c) Drainages of central plain.
(d) Urbanisation of the the USA and the principal urban centres.
(e) Economic characteristics of the USA.
(f) Agricultural belts of the USA.
(g) North-eastern industrial region of the USA.
(h) Pacific coastal industries of the USA.
(i) Dry agriculture and dairy farming belt of the USA.
(j) Mineral resources of the USA.
Answer:
(a) Physiography of the Rocky Mountainous Region
The Rocky Mountains form a major physical feature of western USA, extending from Alaska in the north to Mexico in the south. They are young fold mountains with rugged peaks, steep slopes, and deep valleys. The region also has high plateaus and volcanic features in some areas. It is rich in minerals like copper, gold, and silver, and contains extensive forests, national parks, and rivers originating from snow-fed peaks.
(b) Physiography of Appalachian Highlands
The Appalachian Highlands are located in the eastern part of the USA and are among the oldest mountain systems in the world. Over millions of years, erosion has worn them down into low, rounded peaks and broad valleys. This region is rich in coal, iron, and forest resources, making it an early centre for industries such as coal mining, iron and steel, and timber processing.
(c) Drainages of Central Plain
The Central Plain is one of the most fertile regions of the USA and is drained by the Mississippi River system, including major tributaries like the Missouri, Ohio, and Arkansas rivers. These rivers deposit alluvial soil, making the land highly productive for crops like wheat, maize, and soybean. The river network also supports inland waterways, providing cheap transportation and boosting trade and agriculture.
(d) Urbanisation of the USA and the Principal Urban Centres
The USA is one of the most urbanised nations in the world, with more than four-fifths of its population living in urban areas. Rapid industrialisation, trade, and transport development have encouraged city growth. Major urban centres include New York (financial hub), Los Angeles (film and trade), Chicago (transport and industry), Houston (oil and space), and San Francisco (technology and ports). These cities are centres of culture, employment, and economic activities.
(e) Economic Characteristics of the USA
The economy of the USA is highly developed and diversified. It has an advanced industrial sector, highly mechanised agriculture, strong service industries, and leading technology-based enterprises. Abundant natural resources like coal, oil, and minerals, combined with skilled labour and developed infrastructure, make it one of the largest economies in the world. It is also a major exporter of manufactured goods, food grains, and technological products.
(f) Agricultural Belts of the USA
Agriculture in the USA is organised into different belts based on crop type and climate. The Corn Belt lies in the Midwest and produces maize on a large scale. The Wheat Belt covers parts of the Great Plains, producing wheat for domestic use and export. The Cotton Belt is located in the southern states, while the Dairy Belt around the Great Lakes produces milk and milk products. These belts are characterised by mechanised and scientific farming.
(g) North-Eastern Industrial Region of the USA
This is the oldest and most significant industrial region of the country, stretching from Boston to Washington D.C. It includes important cities like New York, Philadelphia, and Pittsburgh. Rich coal and iron deposits from the Appalachian region, access to waterways, skilled labour, and a large market contributed to its growth. Industries here include iron and steel, textiles, shipbuilding, and machinery.
(h) Pacific Coastal Industries of the USA
The Pacific coastal region includes the states of California, Oregon, and Washington. It has developed industries like aircraft manufacturing (Boeing in Seattle), shipbuilding, electronics, and film production (Hollywood in Los Angeles). Its ports, including Los Angeles and San Francisco, facilitate trade with Asian countries. The region is also known for its agricultural products like fruits, vegetables, and wine.
(i) Dry Agriculture and Dairy Farming Belt of the USA
Dry agriculture is practised mainly in the central and western parts where rainfall is low, and irrigation facilities are limited. Crops such as wheat, barley, sorghum, and millet are commonly grown here. The Dairy Farming Belt is concentrated around the Great Lakes region, where cool climate and rich pastures support large-scale milk, cheese, and butter production.
(j) Mineral Resources of the USA
The USA is one of the richest countries in terms of mineral resources. Coal is abundantly found in the Appalachian region; petroleum and natural gas are majorly produced in Texas, Alaska, and the Gulf Coast; iron ore is mined in Minnesota; copper in Arizona; and gold in California and Nevada. These resources provide raw materials for industries and contribute significantly to exports and energy production.
Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 – Regional Geography of the USA FAQs
Get Free NCERT PDFs
If you want to download free PDFs of any chapter, click the link below and join our WhatsApp group:




