SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 1 – Chemical Reactions and Equations Solutions & Summary
Looking for SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 1 – “Chemical Reactions and Equations” solutions? At Ospin Academy, we provide NCERT-based solutions, important MCQs, and exam-focused explanations to enhance your preparation.
📖 Chapter Overview:
This chapter introduces the fundamental concepts of chemical reactions, types of reactions, and the process of balancing chemical equations. Understanding these topics is essential for mastering the subject and performing well in exams.
📌 Key Topics Covered:
- What is a Chemical Reaction?
- Types of Chemical Reactions (Combination, Decomposition, Displacement, Double Displacement, Redox)
- Balancing Chemical Equations
- Law of Conservation of Mass
- Applications of Chemical Reactions in Daily Life
📌 Important Questions for Exams:
- What are the different types of chemical reactions?
- How do you balance a chemical equation?
- Explain the Law of Conservation of Mass with examples.
- What is a redox reaction? Provide examples.
- What are the applications of chemical reactions in daily life?
📝 How Ospin Academy Helps:
- Detailed NCERT-based answers for SEBA Class 10 Science
- Exam-focused MCQs and extra questions for practice
- Step-by-step explanations to understand reaction balancing
- Concise revision notes to ensure quick preparation
Access complete SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 1 – “Chemical Reactions and Equations” solutions at Ospin Academy now!
Class 10 Science (English Medium) PDF Solutions 2025-26 | SEBA Assam
Download Class 10 Science (English Medium) PDF with detailed solutions, MCQs, and extra practice questions for SEBA Assam 2025-26.
Textual Questions and Answers :
1. Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air?
Answer: Because it quickly forms the white layer of magnesium oxide, which does not burn.
2. Write the balanced equation for the following chemical reactions.
(i) Hydrogen + chloride → Hydrogen chloride
(ii) Barium chloride + Aluminium sulphate → Barium sulphate + Aluminium chloride
(iii) Sodium + water → Sodium hydroxide + Hydrogen.
Answer:
(i) H2+ Cl2 → 2HCl
(ii) 3BaCl2+ AI2(SO4)3 → 3BaSO4 + 2AICl3
(ii) 2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2
3. Write a balanced chemical equation with state symbols for the following reactions.
(i) Solutions of barium chloride and sodium sulphate in water react to give insoluble barium sulphate and the solution of sodium chloride.
(ii) Sodium hydrochloric acid solution (in water) to produce sodium chloride solution an water.
Answer:
(i) Bacl2 (aq) + Na2SO4 (aq) → BaSO4 (s) + 2Nacl (aq)
(ii) NaOH (aq) + Hcl(aq) → Nacl(aq) + H2O
Page – 10
1. A solution of substance ‘x’ is used for white-washing.
(i) Name the substance ‘x’ and write its formula.
(ii) Write the reaction of the substance ‘x’ named in (i) above with water.
Answer:
(i) X is quick lime; CaO
(ii) CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2
2. Why is the amount of gas collected in one of the test tubes in Activity 1.7 double of the amount collected in the other? Name this gas.
Answer: Activity 1.7 depicts the process of electrolysis of water.
The decomposition of H2O compounds into H2 and O2 with the help of electricity is known as electrolysis of water.
The chemical equation for the electrolysis of water can be written as:
2H2O → 2H2 + O2
The equation implies that water consists of two parts of hydrogen and one part of oxygen. It is evident that the amount of hydrogen gas collected in one test tube is double that of the oxygen collected in the other test tube. Therefore, the required name of the gas is hydrogen.
Page -13
1. Why does the colour of copper sulphate solution change when an iron nail is is kept immersed in it?
Answer: When an iron nail is placed in a copper sulphate solution, iron displaces copper from copper sulphate solution forming iron sulphate, which is green in colour.
Therefore, the blue colour of copper sulphate solution fades and green colour appears.
CuSO4 + Fe ⟶ FeSO4 + Cu
2. Give an example of a double displacement reaction other than the one given in Activity 1.10.
Answer: When sodium carbonate reacts with calcium chloride, it forms a precipitate of calcium carbonate and sodium chloride. In this reaction, exchange of carbonate and chloride ions form two new compounds.

This is double displacement reaction.
3. Identify the substances that are oxidised and the substances that are reduced in the following reactions:
(i) 4Na(s) + O2 (g) → 2Na2O (s)
(ii) CuO (s) + H2 (g) → Cu (s) + H2O (l)
Answer: (i) Oxidised: Na(s), H2(g)
(ii) Reduced: O2(g), CuO(s)
Exercises:
1. Which of the statements about the reaction below are incorrect?
2PbO(s)+C(s) → 2Pb(s) + Co2(g)
(a). Lead is getting reduced.
(b). Carbon dioxide is getting oxidised.
(c). Carbon is getting oxidised.
(d). Lead oxide is getting reduced.
(i) (a) and (b)
(ii) (a) and (c)
(iii) (a), (b) and (c)
(iv) all
Answer: (i) (a) and (b)
2. Fe2O3+ 2Al → Al2O3+ 2Fe The above reaction is an example of a
(a). combination reaction.
(b). double displacement reaction .
(c). decomposition reaction.
(d). displacement reaction.
Answer: (d) displacement reaction.
3. What happens when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to iron filling? Tick the correct answer.
(a). Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced.
(b). Chlorine gas and iron hydroxide are produced.
(c). No reaction takes place.
(d). Iron salt and water are produced.
Answer: (a) Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced.
4. What is a balanced chemical equation? Why should chemical equations be balanced?
Answer: A chemical equations is balanced so that the numbers of atoms of each type involved in a chemical reaction are the same on the reactant and product sides of the equation.
The chemical equations must be balanced because the number of atoms of each element remains the same, before and after a chemical reaction.
5. Translate the following statements into chemical equations and then balance them:
(a). Hydrogen gas combines with nitrogen to form ammonia-
(b). Hydrogen sulphide gas burns in air to give water and sulphur dioxide.
(c). Barium chloride reacts with aluminium sulphate to give aluminium chloride and a precipitate of barium sulphate.
(d). Potassium metal reacts with water to give potassium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
Answer:
(a). 3H2(g) + N2(g) → 2NH3(g)
(b). 2H2s(g) + 3O2 → 2SO2(g) + 2H2O(e)
(c). 3BaCl2(aq) + Al2(SO4)3(aq) → 2AlCI3(aq) + 3BaSO4(s)
(d). 2K(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2KOH (aq) + H2(g)
6. Balance the following chemical equations –
- HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 → Ca(NO3)2 + H2O
- NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O
- Nacl + AgNO3 → Agcl + NaNO3
- Bacl2 + H2SO4 → BaSo4 + HCI
Answer: (a) 2HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 → Ca(NO3)2 + 2H2O
- 2NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2H2O
- Nacl + AgNO3 → Agcl + NaNO3
- Bacl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2Hcl
7. Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions:
(a). Calcium hydroxide + Carbon dioxide → Calcium Carbonate + water
(b). Zinc + Silver nitrate → Zinc nitrate + Silver
(c). Aluminium + Copper chloride → Aluminium Chloride + copper
(d). Barium chloride + Potassium sulphate → Barium sulphate + Potassium chloride.
Answer:
(a). Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
(b). Zn + 2AgNO3 → Zn(NO3)2 + 2Ag
(c). 2Al + 3CuCl2 → 2AICI3 + 3Cu
(d). BaCl2 + K2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2KCl
8. Write the balanced chemical equation for the following mule and identify the type of reaction in each case.
(a). Potassium bromide (aq) + Barium iodide (ag) → Potassium iodide (aq) + Barium bromide(s)
(b). Zinc carbonate (s) → Zinc oxide(s) + carbon di-oxide(g)
(c). Hydrogen(g) + chloringe(g) → Hydrogen chloride(g)
(d). Magnesium(s) + Hydrochloric acid(aq) → Magnesium chloride(aq) + Hydrogen (g)
Answer: (a) 2KBr (aq) + Bal2 (aq) → KI(aq) + BaBr2 (s)
Type: Double displacement reaction.
- ZnCO3(s) → ZnO(s) + CO2(g)
Type: Decomposition reaction.
- H2(g) + Cl2 (g) → 2HcI(g)
Type: Combination reaction.
- Mg(s) + 2Hcl(aq) → Mgcl2 (aq) + H2(g)
Type: Displacement reaction.
9. What does one mean by exothermic and endothermic reactions? Give examples.
Answer: The chemical reactions that release heat energy are called exothermic reactions.
Example: C(g) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + Heat Energy
The chemical reactions in which heat energy is absorbed are called endothermic reactions.
Example: CaCO3 Heat → CaO + CO2 ![]()
10. Why is respiration considered an exothermic reactions? Explain.
Answer: During digestion, food is broken down into simpler substances. For example- rice, potatoes and bread contain carbohydrates. These carbohydrates are broken down to form glucose. This glucose combines with oxygen in the cells of our body
and provides energy. This reaction is known as respiration. The chemical equation is-
C₆H12 O₆ (aq) + 6O2 (aq) → 6CO2 (aq) + 6H2O(e) + energy Thus respiration is an exothermic reaction.
11. Why are decomposition reactions called the opposite of combination reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Answer: Decomposition reactions are opposite of combination reactions. In a decomposition reaction, a single substance decomposes to give two or more substances.
For example:
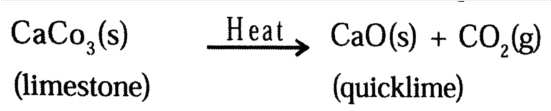
In a combination reaction two or more substances combine to form a new single substance.
For example: C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g)
12. Write one equation each for decomposition reactions where energy is supplied in the form of heat, light or electricity.
Answer:
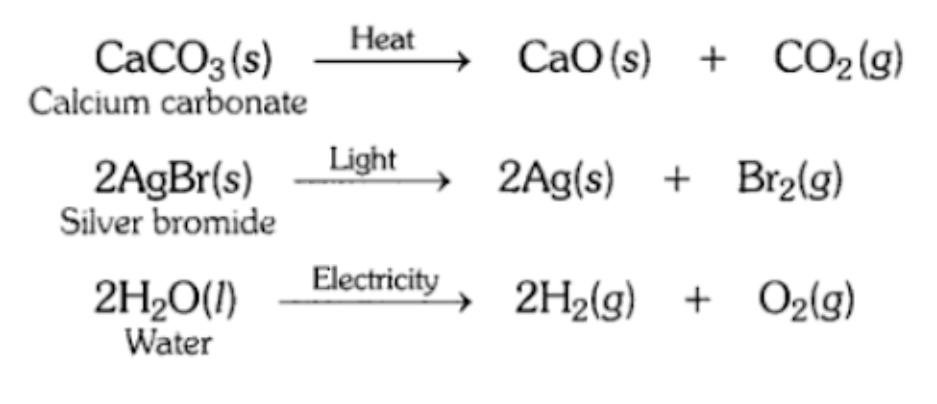
13. What is the difference between displacement and double displacement reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Answer: Displacement reaction: A displacement reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from its compound or salt solution.
Example: When Zinc(Zn) metal is dipped in the Copper sulphate(CuSO4) solution, Zinc displaces the copper metal from its salt solution and forms Zinc sulphate (ZnSO4) and Copper is deposited at the bottom. CuSO4 (aq) + Zn(s) → ZnSO4(aq)
+ Cu(s)
Double displacement reaction: A double displacement reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which two compounds react by exchanging their ions to form new compounds. It is typically identified by the formation of a product that is a precipitate.
Example: When Sodium sulphate (Na2SO4) is treated with Barium chloride (BaCl2), it will lead to the formation of Barium sulphate(BaSO4) and Sodium chloride (NaCl).
Na2SO4(aq)+BaCl2(aq) → BaSO4(s)+2NaCl(aq)
14. In the refining of silver, recovery of silver from silver nitrate solution involved displacement by copper metal. Write down the reaction involved.
Answer: AgNO3 (aq) + Cu(s) → CuNO3 (aq) + Ag (s)
15. What do you mean by a precipitation reaction? Explain by giving examples.
Answer: A precipitate is an insoluble substance.
A reaction in which any insoluble solid precipitate is formed is called Precipitation Reaction.
For example:
1. When Sodium Sulphate solution is mixed with Barium Chloride solution It forms Barium Sulphate and Sodium Chloride solution.
In this reaction, a white precipitate of Barium Sulphate is formed.
For example: Na2SO4 (aq) + Bacl2 (aq) → BaSO4 (s) + 2Nacl(aq)
2. When Potassium Iodide solution is added to Lead Nitrate solution A yellow precipitate of Lead Iodide is formed along with Potassium Nitrate solution
KI + Pb(NO3 )2 → KNO3 + PbI2
16. Explain the following in terms of gain or logs of oxygen with two example reach –
(a) Oxidation.
(b) Reduction.
Answer: (a) Oxidation: Oxidation is a process in which a chemical substance changes because of the addition of oxygen.
Example:
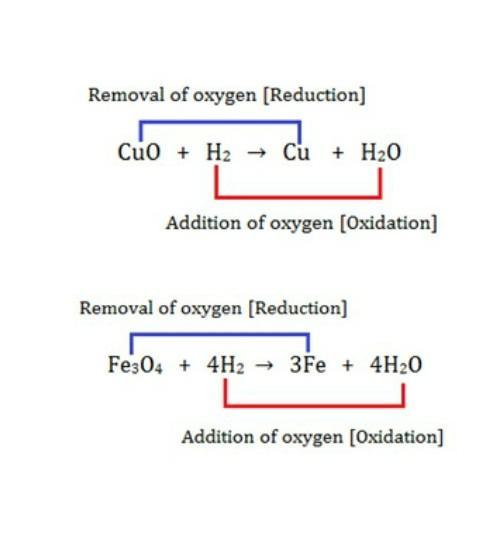
(b) Reduction: The chemical reactions in which a substance losses oxygen is called reduction.
Example: ZnO + C → Zn + CO
Cuo + H2 → Cu + H2O
17. A shiny brown coloured element ‘x’ on heating in air becomes black in colour. Name the element ‘x’ and black coloured compound formed.
Answer: The shiny elements are metals. The brown coloured metal is copper. Hence ′X′ is copper and the black coloured compound formed is Copper oxide.
The reaction involved is:
2Cu(s)+O2(g)→CuO(s)
18. Why do we apply paint on iron articles?
Answer: Iron articles are coated with paint to prevent air and moisture from coming in contact with iron and hence, to protect it from rusting.
19. Oil and fat containing food items are flushed with nitrogen. Why?
Answer: Nitrogen is flushed into food packets containing oil and fat to prevent rancidity. Rancidity occurs when oils and fats react with oxygen, producing an unpleasant smell and taste. Nitrogen, being an inert gas, creates an unreactive atmosphere, preventing the oils and fats from coming into contact with oxygen, thus keeping the food fresh.
20. Explain the following terms with an example each:
(a) corrosion.
(b) Rancidity.
Answer:
(a) Corrosion: Corrosion is a natural process in which pure metals are gradually transformed into undesirable substances by reacting with environmental factors like water, air, or other chemicals. This reaction leads to the weakening or destruction of the metal. Over time, corrosion spreads to the entire metal surface, causing significant damage.
Example: The formation of rust on iron when it reacts with moisture and oxygen in the air.
(b) Rancidity: Rancidity occurs when fats or oils in food undergo oxidation due to exposure to air, light, or moisture, resulting in unpleasant odors and tastes. This happens because the unsaturated parts of the fats react with oxygen, forming compounds such as aldehydes and ketones that cause the foul smell.
Example: The bad smell of butter or oil when left exposed to air for a long time.
Rancidity can be prevented by storing food in airtight containers and keeping it away from heat and light.
SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 1 – Chemical Reactions and Equations FAQs
Get Free NCERT PDFs
If you want to download free PDFs of any chapter, click the link below and join our WhatsApp group:

