SEBA Class 9 Social Science (Economics) Chapter 2 – Basic Economic Problems Solutions & Summary
Looking for SEBA Class 9 Social Science (Economics) Chapter 2 – “Basic Economic Problems” solutions? At Ospin Academy, you will get NCERT-based textbook answers, multiple-choice questions (MCQs), and a detailed chapter summary to help you prepare for exams effectively.
📖 Chapter Overview:
This chapter focuses on the fundamental problems of an economy, including scarcity, choice, and resource allocation. It explains how societies make economic decisions based on limited resources.
📌 Key Topics Covered:
- ⭐ What are basic economic problems?
- ⭐ The problem of scarcity and choice
- ⭐ Factors affecting resource allocation
- ⭐ Production possibilities curve
- ⭐ Types of economic systems and how they address basic economic problems
📌 Important Concepts:
- ⭐ What is the main economic problem?
- ⭐ How does scarcity influence decision-making?
- ⭐ What is opportunity cost?
- ⭐ How do different economies solve basic economic problems?
- ⭐ Why is resource allocation important in economics?
📝 How Ospin Academy Helps:
- ✅ Exam-Oriented Solutions: Fully NCERT-based Class 9 Social Science solutions.
- ✅ MCQs and Extra Questions: Important multiple-choice questions for better revision.
- ✅ Concept Clarity: Explanation with real-life examples.
- ✅ Quick Revision Notes: Key points summarized for last-minute preparation.
Access complete SEBA Class 9 Social Science (Economics) Chapter 2 – “Basic Economic Problems” solutions at Ospin Academy and improve your understanding today!
Class 9 Social Science (English Medium) PDF Solutions 2025-26 | SEBA Assam
Download Class 9 Social Science (English Medium) PDF with chapter-wise MCQs, textbook solutions, and extra questions for SEBA Assam 2025-26.
Class 9 Social Science
Chapter – 2 (Ospin Academy)
Basic Economic Problems
ECONOMICS
Give Very Short Answer:
1. Define.
(a) Poverty
Answer:- Poverty: Poverty is about not having enough money to meet basic needs including food, clothing and shelter. However, poverty is more, much more than just not having enough money.
(b) Unemployment
Answer:- Unemployment is when an individual who is not employed and is seeking employment, cannot find work. Unemployment is a key indicator of the health of an economy.
(c) Density of population
Answer:- Population density is the number of people per unit of area, usually transcribed as “per square kilometer” or square mile, and which may include or exclude, for example, areas of water or glaciers.
(d) Sex ratio
Answer:- Sex ratio: Sex ratio is defined as the number of females per thousand (1000) males.
(e) Absolute poverty
Answer:- Absolute poverty can be defined as the state in which a subject lacks the means to meet his or her basic needs. Such basic needs are often listed in international poverty reduction programs, and usually include food, water, shelter, basic education, and basic medical care.
(f) Relative poverty
Answer:- Relative poverty is a condition wherein an individual is deprived of minimum amount of income required for maintaining average standard of living in the society.
(g) Sustainable development
Answer:- Sustainable development is an organizing principle that aims to meet human development goals while also enabling natural systems to provide necessary natural resources and ecosystem services to humans. The desired result is a society where living conditions and resources meet human needs without undermining the planetary integrity and stability of the natural system.
(h) Green economy
Answer:- Green economy is the practice of sustainable development through the support of public and private investment to create infrastructure that fosters social and environmental sustainability.
2. What is poverty line? What is the poverty line in rural and urban areas?
Answer:- Poverty line is the amount of money needed for a person to meet his basic needs. It is defined as the money value of the goods and services needed to provide basic welfare to an individual.
In rural areas it is 2400 calories and in urban areas it is 2100 calories.
3. What is the population of India and Assam according to the 2011 census?
Answer:- According to the census 2011 census, the population of India is 121 crores and that of Assam is about 3 crores and 12 lakhs.
4. What percentage of the total land area of the world is in India?
Answer:- 2.4% of the total land area of the world is in India.
5. Which state of India has the highest sex ratio with how much is it?
Answer:- In India has the highest sex ratio in Kerala and it is 1084.
6. What is the density of population of Assam?
Answer:- According to the 2011 census, the density of population of Assam is 397 per sq km.
7. What is disguised unemployment?
Answer:- Disguised unemployment exists when part of the labor force is either left without work or is working in a redundant manner such that worker productivity is essentially zero. It is unemployment that does not affect aggregate output. An economy demonstrates disguised unemployment when productivity is low and too many workers are filling too few jobs.
8. What are the causes of inflation?
Answer:- The main causes of inflation are:
(i) Demand pull inflation.
(ii) Cost push inflation.
(iii) Increased money supply.
(iv) Devaluation.
(v) Rising wages.
9. What is known as suppressed inflation?
Answer:- Suppressed inflation occurs when the government prevents the price rise through direct methods like public distribution system, fixation of prices by the government, etc. which keeps the price level below the price level of open inflation.
11. Complete the following:
Worker-population ratio = 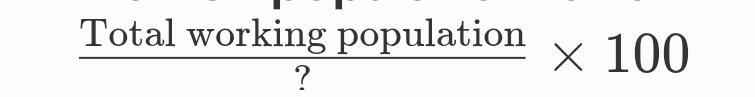
Answer:- 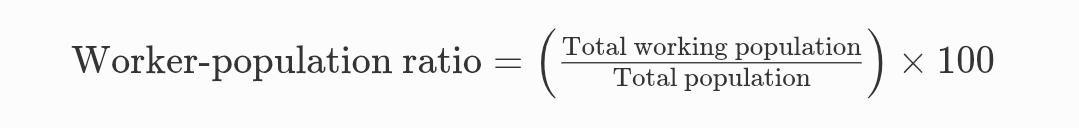
12. Which committee put forward the definition of sustainable development and in which year did it do so?
Answer:- Sustainable development was defined in the World Commission on Environment and Development’s 1987 Brundtland report Our Common Future as development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs’.
13. What is the motto of environmental thinkers?
Answer:- ‘Think globally, act locally’.
Give Very Long Answer:
1. Discuss the main causes for the problem of rapid growth of population in India.
Answer:- The main causes for the problem of rapid growth of population in India are:
(i) Increased Life Expectancy: While the average annual birth rate in India, which was 42 per thousand in 1951-61, decreased to 24.8 per thousand in 2011, the country has seen its decadal death rate decline to 8.5 in 2001-2011 from 42.6 in 1901-1911.
(ii) Lack of family planning: If we add the number of miscarriages (6.20 lakh in 2010-11) in the country with an estimated number of births (2.05 crore in 2010-11) in one year, even in this age of family planning, one woman, on an average, is pregnant at any time in the age group of 15-45 years.
(iii) Early marriage: Child marriage is one of the major social problems of our country. Even today, a large number of boys and girls are married at an age when they are not prepared for family responsibilities either socially, emotionally, physically and mentally. Marriage at unripe age also leads to higher mortality rate of infants.
(iv) Lack of social consciousness: In India, the concept of early marriage still prevails which increases the child bearing age.
(v) Lack of education: The failure of family planning is directly related to large-scale illiteracy that also contributes to early age of marriage, low status of women, high child-mortality rate etc mentioned above. Uneducated families cannot grasp the issues and problems caused by the increasing population rate.
(vi) Migration: Illegal migration is continuously taking place from the neighbouring states and countries leading to increased population density of Assam.
(vii) Problem of mind-set: Generally, illiterate and uneducated children inherit their father’s behaviour and choose to give birth to as many children as is necessary to increase the income of their family.
2. What is poverty? Explain how the poverty line determines poverty.
Answer:- Poverty line is the amount of money needed for a person to meet his basic needs. It is defined as the money value of the goods and services needed to provide basic welfare to an individual.
The poverty line of a country create a low point in the distribution line and divides a country’s population into poor.
Through several definitions of India’s poverty line have been put forward, the definition based on calories is the most widely accepted. According to the definition based on calories given by the Planning Commision of India, the minimum calorie consumption should be 2400 calories in rural areas and 2100 calories in urban areas, failing which, an individual can be defined as ‘poor’.
People in rural areas require more calories as they have to do more physical labour then the people in the urban areas. In order to consume the minimum amount of calories, the monthly per capita expenditure at current prices were as flows:
|
YEAR |
RURAL AREAS |
URBAN AREAS |
|---|---|---|
|
2000-2001 |
Rs.328 |
Rs. 454 |
|
2005-2006 |
Rs. 368 |
Rs. 558 |
3. What is inflation? Discuss the main methods of controlling inflation.
Answer:- Inflation is a rise in prices, which can be translated as the decline of purchasing power over time. The rate at which purchasing power drops can be reflected in the average price increase of a basket of selected goods and services over some period of time. The rise in prices, which is often expressed as a percentage, means that a unit of currency effectively buys less than it did in prior periods. Inflation can be contrasted with deflation, which occurs when prices decline and purchasing power increases.
The main methods of controlling inflation are:
(i) Monetary Measures: Among the monetary measures adopted by the government, the measure of Bank Rate is worthy of mentioned. The rate at which the Central Bank gives loans to the Commercial Banks is known as the Bank Rate.
During inflation, the Bank Rate is increased as a result of which the commercial banks increase the market rate of interest. This discourages the people to take loans which leads to decrease in money in circulation and thus to the control of inflation.
(ii) Fiscal Measures: This is also known as the income and expenditure method. Reduction in government expenditure leads to reduction in aggregate demand in the country and this helps in the control of inflation. Moreover, by levying different taxes, the excess disposable income in the hands of the people can be transferred to the government. This will lead to decrease in the aggregate demand and control of inflation. The government can also control inflation by taking loans from the general public.
(iii) Increase in Production: The government can accelerate the process of production by the proper utilisation of unutilised resources. This will help increase production, and the increased aggregate demand can be met with the increased supply of goods. This will help in the control of prices.
Q4. What is unemployment? What are its different types? Mention the main causes of this problem?
Answer:- Unemployment is a situation when the able-blood persons, who are willing and capable to work under the prevailing wage rate do not get suitable jobs. In other words, it is a situation when a person is not gainfully employed in any productive activity. Thus it is a situation in which number of jobseekers exceeds the number of job providers.
Types of unemployment: Generally unemployment is two types- (i) rural unemployment and (ii) urban unemployment.
(i) Rural unemployment has two categories– (a) seasonal unemployment and (b) disguised unemployment.
(a) Seasonal unemployment: The seasonal unemployed are unemployed during a season: they are employed for the rest of the year. For example, people involved in agricultural activities are seasonal unemployed.
(b) Disguised unemployment: Disguised or hidden unemployed are those who look as if they are employed but they do not have any role in the total production. For example, if a job can be carried out by two people and if five people are employed for the same, then the extra three people are said to be disguised unemployed.
(ii) Urban unemployment is also two types- (a) industrial unemoployment and (b) educated unemployment.
(a) Industrial unemployment: People who do not find employment in the industries are known as industrial unemployed.
(b) Educated unemployment: People who do not find job opportunities despite having the required educational qualifications are known as the educated unemployed.
Causes of unemployment: There are many causes of unemployment. The following causes are worth mentioning-
1. High rate of population growth: The high rate of population growth is adding to the problem of unemployment. The unemployment problem has taken an alarming form as the rate of growth of employment opportunities have not been able to keep pace with the rate of increase in population.
2. Jobless growth: The gap between the rate of growth of national income and the rate of employment is increasing. Such a situation is called jobless growth. This leads to the increase in the problem of unemployment.
3. Stagnant agricultural development: For a predominantly agricultural country like India, the rate of growth of agriculture is not up to expectations.
As a result, unemployment occurs among the people engaged in agriculture.
4. Slow rate of industrialisation: Industrial unemployment occurs as the rate of industrialisation is not up to expectations.
5. Faulty educational system: Educational unemployment is been unable to make the population fit for employment. The lack of Assuming alarming proportions as the prevailing educational system has vocational and technical education has made the population unfit for self employment.
5. Write short notes:
(a) Seasonal unemployment.
Answer:- Seasonal unemployment occurs when certain industries or job sectors experience fluctuations in demand due to seasonal variations or weather conditions. For example, agricultural workers may face unemployment during off-seasons when there is no need for planting or harvesting crops.
Answer:- Demand-Pull Inflation: This type of inflation occurs when there is an increase in consumer demand for goods and services. As demand rises, businesses struggle to meet the supply, leading to higher prices. It is one of the most common causes of inflation in an economy.
Cost-Push Inflation: This occurs when the cost of production increases, leading businesses to raise the prices of goods and services. Factors such as rising wages, increased raw material costs, and higher transportation expenses contribute to cost-push inflation. Since production costs increase, businesses pass these costs on to consumers in the form of higher prices.
(c) Sustainable development.
Answer:- In the present times, the competition that has started among the countries for economic growth has had an adverse effect on the environment. The deterioration of the environment has become a threat to the existence of the world. The temperature of the earth has been increasing over every decade. This has led to the problem of global warming. Problems like deterioration of bio-diversity, climate change etc. lead to the deterioration of the environment.
With the objective of protecting the environment from the adverse effects of economic development and growth, in 1987, the Brundtland Commission put forward the concept of incessant or sustainable development. This commission is also known as the World Commission on Environment and Development. According to the commission, sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
(d) Green economy.
Answer:- A green economy is defined as low carbon, resource efficient and socially inclusive. In a green economy, growth in employment and income are driven by public and private investment into such economic activities, infrastructure and assets that allow reduced carbon emissions and pollution, enhanced energy and resource efficiency, and prevention of the loss of biodiversity and ecosystem services.
(e) Open and suppressed inflation.
Answer:- In a free market economy, prices go up freely due to supply-demand imbalances leading to open inflation. Suppressed Inflation Suppressed inflation occurs in a controlled economy where the upward pressure on prices is not allowed to influence the quoted or managed prices.
SEBA Assam Class 9 Social Science Chapter 2 – Basic Economic Problems FAQs
Get Free NCERT PDFs
If you want to download free PDFs of any chapter, click the link below and join our WhatsApp group:

