SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 7 – Control and Coordination Solutions & Summary
Struggling with Class 10 Science Chapter 7 – “Control and Coordination”? Ospin Academy provides detailed NCERT solutions, key concepts, and exam-focused practice questions to help you succeed.
📖 Chapter Overview:
This chapter explains how organisms control and coordinate their actions through the nervous system, hormones, and plant responses to stimuli.
📌 Key Topics Covered:
- Human Nervous System (Structure and Functions)
- Reflex Action and Reflex Arc
- Coordination in Plants (Tropic and Nastic Movements)
- Hormonal Coordination in Animals
- Endocrine Glands and Their Functions
📌 Important Questions for Exams:
- What is the function of the nervous system in humans?
- Explain the concept of reflex action with an example.
- How do plants respond to light and gravity?
- Describe the role of hormones in human body regulation.
- What are the differences between voluntary and involuntary actions?
📝 How Ospin Academy Helps:
- Comprehensive NCERT solutions for SEBA syllabus
- Exam-oriented explanations with diagrams
- Quick revision notes and practice questions
- Clear explanations of complex topics
Access SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 7 – “Control and Coordination” solutions now on Ospin Academy!
Class 10 Science (English Medium) PDF Solutions 2025-26 | SEBA Assam
Download Class 10 Science (English Medium) PDF with detailed solutions, MCQs, and extra practice questions for SEBA Assam 2025-26.
Textual Questions and Answers:
Page – 119
1. What is the difference between a reflex action and walking?
Answer: Difference between reflex action and walking:
Reflex action: It is an involuntary, automatic response to a stimulus that occurs at an unconscious level without thinking.
Walking: It is a voluntary action that requires conscious effort and is under our control.
2. What happens at the synapse between two neurons.
Answer: A synapse is a gap between the two neurons. At the synapse, the electrical signals are converted into chemicals that can easily cross over the gap and pass on to the next neurons where it is again converted into an electrical signal.
3. Which part of the brain maintains posture and equilibrium of body?
Answer: Cerebellum. This is the back of the brain. It coordinates voluntary muscle movements and helps to maintain posture, balance, and equilibrium.
4. How do we detect the smell of an agarbatti (incense sticks)?
Answer: Smell of an incense stick is detected by the olfactory receptors present in the nose. The information is transmitted to olfactory lobe located in the fore brain which interprets the information.
5. What is the role of brain in reflex action?
Answer: In a reflex action, the brain plays no part. The spinal cord, which reacts without thinking about how to respond to stimuli, is in charge of these automatic actions.
They receive information from all parts of the body and integrate it.
Page -122
1. What are plant hormones?
Answer: Plant hormones are chemical compounds present in very low concentration in plants. Plant hormones help to co – ordinate growth, development and responses to the environment.
2. How is the movement of leaves of sensitive plant is different from movement of a short towards light?
Answer: The type of movement of leaves of the sensitive plant is known as a nastic movement. But the movement of shoot is directional towards light.
This type of movement does not depend on the direction of stimuli. The movement of the shool towards light is due to growth controlled by growth hormone.
3. Given an example of plant hormone that promotes growth.
Answer: Auxin: Auxin is a plant hormone that promotes growth.
4. How do auxins promote growth of a tendril around a support .
Answer: In plants like the pea plant, tendrils are sensitive to touch. When a tendril touches a support, auxins accumulate on the opposite side of the contact. This causes faster cell growth on that side, making the tendril bend and coil around the support, helping the plant cling to it.
5. Design an experiment to demonstrate hydrotropism.
Answer: Growth movements in response to the stimulus of moisture are termed as hydrotropic movements.
Place some ready to germinate seeds of pea in moist sawdust in a shallow box whose bottom has been replace by a wire gauze.
Keep the apparatus undisturbed for 2-3 days. keep the sawdust moist. After some time radicals will pass through the sieves. Then the radicles curve upwards again to enter into the moist sawdust. the roots are positively hydrotropic and the curvature is more than that due to entropic effect.
Page – 125
1. How does chemical coordination take place in animals?
Answer: Chemical coordination takes place in animals with the help of chemical messengers called as hormones. They are secreted by endocrine glands. The hormones are carried by the blood to the site of action. The hormones are consumed during their action. Hormones regulate the growth, development and homeostasis of the animals.
2. Why is the use of iodised salt advisable?
Answer: Iodine is essential for the thyroid gland to produce thyroxin hormone. Thyroxin regulates carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism in the body so as to provide the best balance for growth. Iodine is essential for the synthesis of thyroxin. In case iodine is deficient in our diet, there is a possibility that we might suffer from goitre.
This deficiency disease is known as goiter. Therefore iodized salt is advised.
3. How does our body respond when adrenaline is secreted into the blood?
Answer: When secreted in large amounts it speeds up the heartbeat and hence supplies more oxygen to the muscles. The breathing rate also increases due to contractions of diaphragm and rib muscles. It also increases the blood pressure. All these responses enable the body to deal with any stress or emergency.
4. What are some patients of diabetes treated by giving injections of insulin?
Answer: Insulin is a hormone which is produced by the pancreas and helps in regulating blood sugar levels. If it is not secreted in proper amounts the sugar level in the blood rises causing many harmful effects.
EXERCISES
1. Which of the following is a plant hormone?
(a) Insulin.
(b) Thyroxin.
(c) Oestrogen.
(d) Cytokinin.
Answer: (d) Cytokinin.
2. The gap between two neurons is called a
(a) Dendrite.
(b) Synapse.
(c) Axon.
(d) Impuls.
Ans. (b) Synapse.
3. The brain is responsible for
(a) Thinking.
(b) Regulating the heart beat.
(c) Balancing the body.
(d) All of the above.
Answer: (d) All of the above.
4. What is the function of receptors in our body? Think of a situation where receptors do not work properly. What problems are likely to arise?
Answer: Receptors are present in all parts of the body for example in the skin, eyes, nose tongue, etc.
The function of receptors is to detect information from the environment.
If receptors do not detect the information there will not be any co – ordination. It may lead to accidents. Body response will not be there.
5. Draw a structure of a neuron and explain its function:
Answer: Structure of neuron: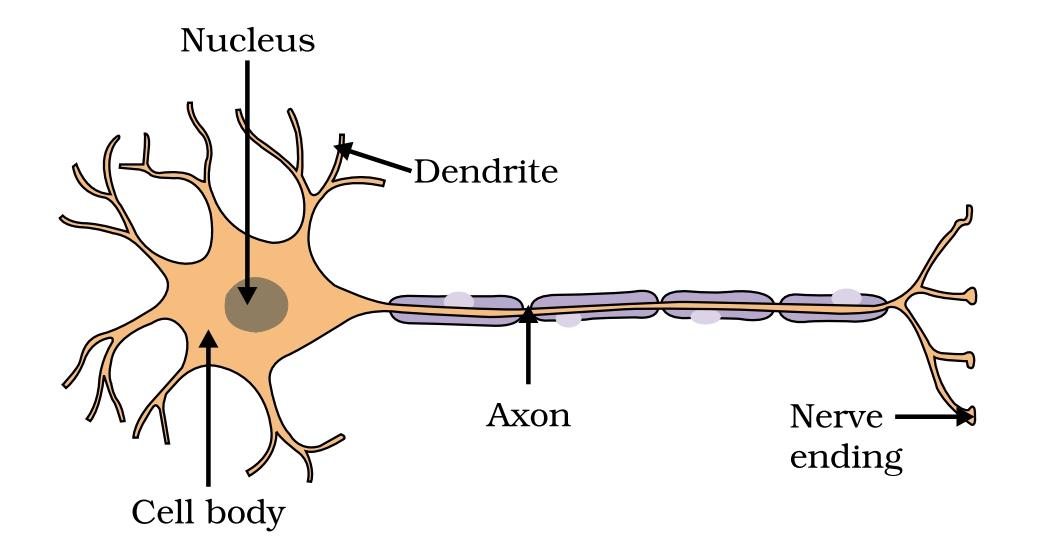
Function:
(i) Dendrites of a neuron collect information from the receptor.
(ii) Axon conducts information as electrical impulse.
(iii) Terminal arborization pass the information as chemical stimulus at synapse for on ward transmission.
6. How does phototropism occur in plants?
Answer: Phototropism is the directional response of a plant that allows the plant to grow towards or in some cases away from the light. These directional or tropic movements can be either towards the stimulus, or away from it, so, in two different kinds of phototropic movement, shoots respond by bending towards light while roots respond by bending away from it.
7. Which signals will get disrupted in case of a spinal cord injury?
Answer: Reflex action will be disturbed because reflex arcs are located in the spinal cord. So, the quick responses needed to safe guard the body will not take place. The delayed responses may cause harm to the body.
As both of these signals meet in a bundle in the spinal cord, so, if there is any spinal cord injury then both of these signals will be disrupted.
8. How does chemical coordination occur in plants?
Answer: Chemical coordination occurs in plants with the help of phytohormones or plant hormones secreted by plants. Auxin, cytokinin, gibberellin, abscisic acid are plant hormones. These hormones regulate the growth and development of the plants.
They also regulates various metabolic activities in the plants. All growth processes are regulated by one or more phytohormones acting synergistically or antagonistically.
9. What is the need for a system of control and co che ordination in an organism?
Answer: An organism needs control and coordination system for the following functions:
(i) To save the body of the organisms from the harmful changes in the environment.
(ii) To control the speed of voluntary and involuntary actions.
(iii) To have the capability to think and learn for responding to any stimuli.
10. How are involuntary actions and reflex actions different from each other?
Answer: Reflex actions are the spontaneous responses by voluntary organs but involuntary actions are by the involuntary organs
The difference between involuntary actions and reflex actions are:
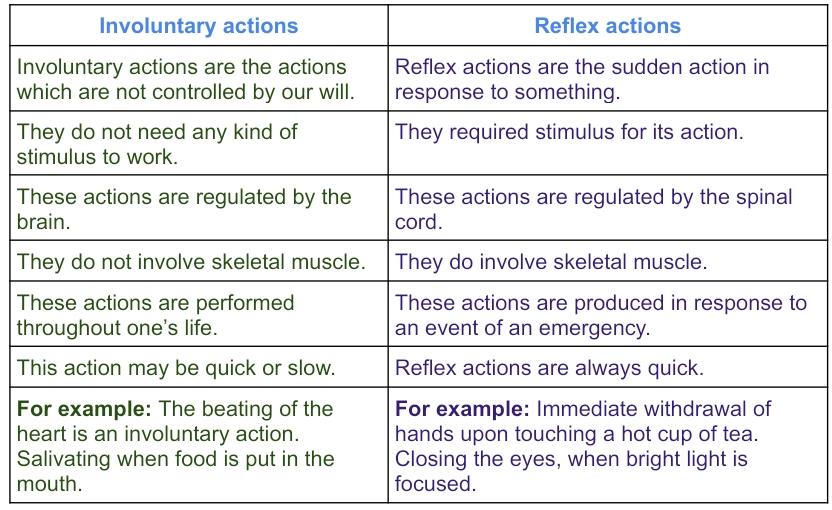
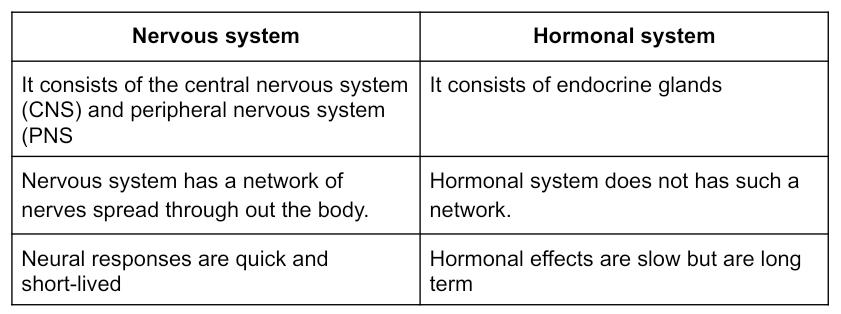
11. Compare and contrast the nervous and hormonal mechanism for control and coordination in animals.
Answer:
12. What is the difference between the manner in which movement takes place in a sensitive plant and the First movement in our legs?
Answer: 
SEBA Class 10 Science Chapter 7 – Control and Coordination FAQs
Get Free NCERT PDFs
If you want to download free PDFs of any chapter, click the link below and join our WhatsApp group:


