Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 – Resources and Development Solutions | NCERT | CBSE Board (English Medium)
Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 – Resources and Development (NCERT Solutions for CBSE Board – English Medium)
This chapter from Contemporary India – II (Geography) explains the importance of resources, their classification, land use patterns, and the need for resource conservation. It also covers India’s soil types, issues of land degradation, and sustainable development measures.
✅ What You Will Learn:
- Meaning and classification of natural resources
- Renewable and non-renewable resources
- Land use patterns and land degradation in India
- Types of soils in India and their distribution
- Conservation methods for resources and sustainable development
🎯 Ospin Academy Advantages:
- Complete NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography Chapter 1
- Prepared as per CBSE Board Exam /b> pattern
- Detailed answers for short questions, long answers, and map-based questions
- Inclusion of previous year CBSE Board important questions
- Clear and easy explanations to support quick revision
Class 10 Social Science (CBSE 2025) | English Medium Chapter-wise Solutions PDF
Board Exam Special!
(For CBSE Class 10, 2025)
Master Class 10 Social Science (English Medium) with this chapter‑wise solutions PDF.
Covers History, Geography, Civics & Economics as per latest NCERT syllabus.
Perfect for self-study, revision, and CBSE 2025 exam preparation.
Chapter 1 – Resources & Development
Q.1A Which one of the following is the main cause of land degradation in Punjab?
A. Intensive cultivation
B. Deforestation
C. Over irrigation
D. Overgrazing
Ans.: Over Irrigation. Over irrigation causes water logging in the fields. Punjab as we all know, is called as the bread basket of India. Due to water logging in the fields, the salinity/alkalinity increases and leads to loss in fertility.
Q.1B
In which one of the following states is terrace cultivation
practised?
A. Punjab
B. Plains of Uttar Pradesh
C. Haryana
D. Uttarakhand
Ans.: Uttaranchal. Uttaranchal is a hilly area. Whenever there is rainfall, the speed of water increases in the slopes. Due to this, it carries the top soil with it and leads to soil erosion. To prevent this, Terrace farming is practiced.
Q.1 C In which of the following states is black soil found? A. Jammu and Kashmir
B. Gujarat
C. Rajasthan
D. Jharkhand
Ans.: Black soil is formed by cooling and solidification of lava. It is found in the Deccan tract which consists of the sates Maharashtra, Chhatisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Gujrat, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu. Black soil is ideal for the cultivation of Cotton.
Q.2A Answer the following questions in about 30 words.
Name three states having black soil and the crop which is mainly grown in it.
Ans.: 1) Black soil is found in the Deccan trap region. This comprises of the states of Maharashtra, Chhatisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
2) The soil has a high water retaining capacity which makes it ideal for cotton cultivation.
3) Black soil is also called Regur( from the Telugu word Reguda meaning cotton).
Q.2B Answer the following questions in about 30 words.
What type of soil is found in the river deltas of the eastern coast? Give three main features of this type of soil.
Ans.: The soil found in the river deltas of the eastern coast is alluvial soil. The main characteristics of the soil are as follows: –
1. These soils have an adequate proportion of potash, phosphoric acid and lime. This makes the soil ideal for the growth of sugarcane, paddy, wheat and other cereal and pulse crops.
2. Alluvial soil has high fertility. Due to this characteristic, there in intense cultivation and thus, the areas with these soils are densely populated.
3. Drier areas have more alkaline content in the soil. It can be made productive after proper treatment.
Q.2C Answer the following questions in about 30 words. What steps can be taken to control soil erosion in the hilly areas? Ans.: In the hilly areas soil erosion can be controlled by
1. Ploughing across contour lines can slow down the water flow in the slopes. This is known as Contour ploughing.
2. Making use of terrace farming techniques to prevent the water take away the top soil and cause erosion.
3. Using strips of grass to check erosion by wind and water. This divides the wind force and causes less damage.
Q.3A
Answer the following questions in about 120 words.
Explain land use pattern in India and why has the land under forest not increased much since 1960-61?
Ans.: India has a total geographical area of 32.87 lakh sq. km. As per the land use data, only 93% is available to us. Of this 93%, 43.4% is sown area, 22.6% is forest cover,4.4% is culturable waste, 7.3% is current fallow, 4% is pasture cover and 1% is tree cover.
The net sown area pattern varies greatly from one state to another. The forest cover in the country is lower than the ideal 33% as outlined in the National Forest Policy formulated in the year 1952. The percentage of forests is needed to increase in order to maintain the ecological balance.
The forest cover did not increase since 1960-61 due to the following reasons: –
1. Improper use of land has caused degradation and loss of forests.
2. Ever increasing deforestation to meet the needs of the increasing population.
3. Large scale development projects, industrialization and urbanization have reduced the forest cover.
Q.3B Answer the following questions in about 120 words.
How have technical and economic development led to more consumption of resources?
Ans.: Technical and economic development has led to more consumption resources because of the following reasons:
1). Technology has led to the development of various types of industries which led to increase in use of resources.
2). Goods become outdated very fast and development of advanced goods with the latest technology require more resources.
3). Increase in population and improvement in medical facilities has also increased demands for more resources
Q.1 1Make a project showing consumption and conservation of resources in your locality.
Ans.: → Doing car pool with around 5-6 members together will save the fuel. → using public transport facilities for transportation. → using electricity only when need and not wasting it by just running fan’s, A.C all day long. By following many such ways we will be able to conserve resources in our locality.
Q.2 Have a discussion in the class-how to conserve various resources used in your school.
Ans.: Conservation methods to conserve various resources:
(i) Useful commodities should be used cautiously so that they are not wasted.
(ii) Paper is made of trees so we should not waste it.
(iii) We should switch off unnecessary electrical equipment when not in use.
(iv) Water should not be wasted. Instead we can use it water plants. (v) Whenever you see a tap open, close it. Wastage should be minimized.
(vi) Leaking taps should be repaired immediately in order to stop water wastage.
Q.3 Imagine if oil supplies get exhausted, how will this affect our lifestyle?
Ans.: Oil is a basic necessity of the economy today. It is used in almost everything. If it get exhausted, it can affect the economy and living in the worst of the ways. Some of them are:
(i) Electricity, which is the basic necessity of today’s world, will come to a halt. If there is no electricity, no refrigerator, no air conditioners, no phones etc.
(ii) Production would completely stop. We would be deprived of almost everything. Even vegetables will not be available.
(iii) All transportation would come to a halt. Roadways or railways, everything will stop.
(iv) Technology advancement will also slow down.
(v) Without electricity, we will go back in the Stone Age. Industries will halt, growth in agricultural areas will stop completely.
(vi) If there is no oil, there will be no transportation, if there is no transportation, then we will be deprived of food and supplies.
Q.4
Solve the puzzle by following your search horizontally and vertically
to find the hidden answers.
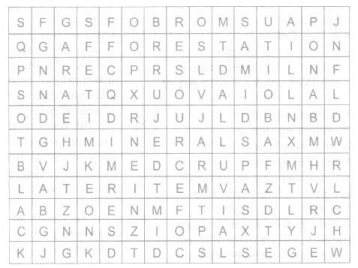
(i) Natural endowments in the form of land, water, vegetation and minerals.
(ii) A type of non-renewable resource.
(iii) Soil with high water retaining capacity.
(iv) Intensively leached soils of the monsoon climate.
(v) Plantation of trees on a large scale to check soil erosion.
(vi) The Great Plains of India are made up of these soils.
Ans.:
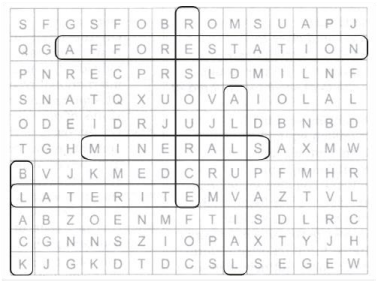
(i) Natural endowments in the form of land, water, vegetation and minerals.
(ii) A type of non-renewable resource.
(iii) Soil with high water retaining capacity.
(iv) Intensively leached soils of the monsoon climate. (v) Plantation of trees on a large scale to check soil erosion.
(i) Resource: These natural endowments in the aforesaid forms are called resources.
(ii) Minerals: Minerals are found naturally and are utilized in a greater speed than it can renew. So it falls under the non-renewable category.
(iii) Black: It has the highest water retaining capacity.
(iv) Laterite: The Laterite Soil develops in areas with high temperature and heavy rainfall.
(v) Afforestation: Plantation of trees on a large scale to check soil erosion.
(vi) Alluvial: This is the most widely spread and important soil. The entire northern plains are made of alluvial soil. These soils contain adequate proportion of potash, phosphoric acid and lime.
Class 10 Social Science Chapter 6 – Frequently Asked Questions
Get Free NCERT PDFs
If you want to download free PDFs of any chapter, click the link below and join our WhatsApp group:


