Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4– Agriculture Solutions | NCERT | CBSE Board (English Medium)
Class 10 Social Science Chapter 4 – Agriculture (NCERT Solutions for CBSE Board – English Medium)
This chapter from Contemporary India – II (Geography) explains the importance of agriculture in India, types of farming, and cropping patterns. It provides detailed insights into major food crops like rice, wheat, millets, pulses, as well as commercial crops like cotton, sugarcane, tea, and coffee. It also covers agricultural development strategies and challenges.
✅ What You Will Learn:
- Types of farming in India – primitive, subsistence, and commercial
- Kharif, Rabi, and Zaid cropping seasons
- Major food crops – Rice, Wheat, Millets, Pulses
- Important cash crops – Cotton, Jute, Sugarcane, Tea, Coffee
- Agricultural challenges and technological development (Green Revolution, White Revolution)
🎯 Ospin Academy Advantages:
- Complete NCERT Solutions for Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture
- Prepared as per CBSE Class 10 Board Exam
- Answers for long questions, short notes, and map-based questions
- Coverage of sample questions from CBSE previous year exams
- Concise notes for last-minute exam revision
Class 10 Social Science (CBSE 2025) | English Medium Chapter-wise Solutions PDF
Board Exam Special!
(For CBSE Class 10, 2025)
Master Class 10 Social Science (English Medium) with this chapter‑wise solutions PDF.
Covers History, Geography, Civics & Economics as per latest NCERT syllabus.
Perfect for self-study, revision, and CBSE 2025 exam preparation.
Chapter 4
Agriculture
Q.1(i) Which one of the following describes a system of agriculture where a single crop is grown on a large area?
A. Shifting agriculture
B. Plantation agriculture
C. Horticulture
D. Intensive agriculture
Ans.: Plantation agriculture is a process in which the same kind of crop is grown in a large area. This disturbs the soil fertility.
Q.1(ii)Which one of the following is a rabi crop?
(a) Rice(b) Gram(c) Millets(d) Cotton
Ans.:On the other hand, crops grown during the winter season are called rabi crops. Rabi crops include wheat, gram, and mustard.
Q.1C Which one of the following is a leguminous crop?
A. Pulses
B. Jowar
C. Millets
D. Sesame
Ans.: Leguminous plants are a member of the pea family. The seeds are in pods, they have distinctive flowers and these plants are able to provide Nitrogen to the soil due to the symbiotic bacteria in the roots.
Q.2(i) Answer the following questions in 30 words:
Name one important beverage crop and specify the geographical conditions required for its growth.
Ans.: Tea is an important beverage crop. It is used almost all across the country. The geographical conditions for its growth are: –
(a) There is good growth of tea plants in tropical and sub-tropical climates.
(b) The soil required for its growth should be fertile and well-drained, rich in humus and organic matter.
(c) Tea plants require constant warm and moist climate throughout the year.
(d) The tender leaf growth is ensured by evenly distributed annual rainfall.
Q.2(ii) Answer the following questions in 30 words:
Name one staple crop of India and the regions where it is produced.
Ans.: Rice is the staple food crop of majority people in India. It is cultivated in the plains of north and north-eastern India, coastal areas and the deltaic regions. The growth of rice has been made possible with the dense network of canals and tube wells. These tube wells and canals have made the cultivation of rice possible in areas with low rainfall such as Punjab, Haryana, Western Uttar Pradesh and parts of Rajasthan.
Q.2(iii) Answer the following questions in 30 words:
Enlist the various institutional reform programmes introduced by the government in the interest of farmers.
Ans.: The various institutional reform programmes introduced by the government for the benefits of farmers are: –
1. Crop insurance against drought, floods, fire, etc.
2. Minimum support price to encourage farmers for farming.
3. Subsidy on various agricultural inputs and resources such as power and fertilisers.
4. Kissan credit card and personal accident insurance scheme have been introduced which help the farmers even more.
5. Abolition of zamindari system also helped farmers to get more money and more produce.
Q.3(i) Answer the following questions in about 120 words.
Suggest the initiative taken by the government to ensure the increase in agricultural production.
Ans.: various initiatives have been taken by the Govt of India to ensure increase in the agricultural production. They are: –
1. Collectivisation, consolidation of holdings, cooperation and removal of zamindari system, etc. were given priority to bring about the institutional reforms in the country post-independence.
2. Land reform was the prime focus of the ‘First Five Year Plan’.
3. The Green Revolution was based on the use of package technology and White Revolution were some of the strategies initiated to improve the lot of Indian agriculture.
4. Minimum Support Price policy, provision for crop insurance , subsidy on agricultural inputs and resources such as power and fertilizers , Grameen Banks, Kissan Credit Card and Personal Accident Insurance Scheme are also some of the reforms brought about by the Indian Government.
Q.3(ii) Answer the following questions in about 120 words. Describe the geographical conditions required for the growth of rice. Ans.:
Rice is the staple food crop of a major portion of people in India. Our country is the second largest producer of rice in the world after China. It is kharif crop .
the geographical conditions required for it’s growth are: – 1. It requires high temperature (above 25 degrees celcius)
2. It requires high humidity with annual rainfall above 100 cm. 3. In the areas of low rainfall, it is cultivated with the help of irrigation.
4. It is grown in the plains of north and north-eastern India, coastal areas and the deltaic regions.
5. Development of dense network of canal irrigation and tube-wells have made it possible to cultivate rice in areas of less rainfall such as Punjab, Haryana, Western Uttar Pradesh and parts of Rajasthan.
Project work:
Q.1 Group discussion on the necessity of literacy among farmers Ans.: In a country like India, educating and training farmers is very essential. The farmers of India need proper guidance about the quality of their land and the decision about the growth of crops. A proper guidance is needed for the farmers about using fertilisers, insecticides and pesticides. Still, today, most of the farmers use the old method of agriculture. It not only takes more time, but also more effort. This is the main reason for the farmers are still so poor. It is very important to provide these farmers to provide them with the modern technologies to cultivate the land.
If they are educated, they will get to know about many important things which otherwise they were unaware of, like the following: –
1. How to run the equipment and machines to improve agricultural. 2. Right kind of fertilisers, pesticides, seeds, climate, etc. required for the growth of particular type of crop.
3. The condition of the soil, or if it requires ore nutrients and in what quantity.
4. They also will know about how to deal with bankers and loans and grants and subsidies if there is any.
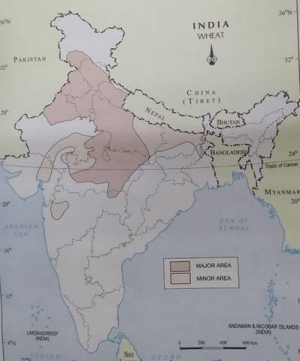
Q.2 On an outline map of India, show wheat-producing areas. Ans.: See the given map.
Activity:
Q.1 Solve the puzzle by following your search horizontally and vertically to find the hidden answers.
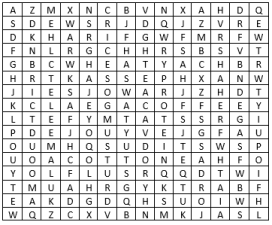
(i) The two staple food crops of India.
(ii) This is the summer -cropping season of India.
(iii) Pulses like arhar, moong, gram, urad contain……….
(iv) It is a coarse grain.
(v) The two important beverages in India are……….
(vi) One of the four major fibres grown on black soils.
Ans.:
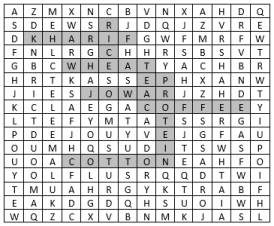
(i) Wheat and rice
(ii) Kharif
(iii) Protein
(iv) Jowar
(v) Tea and Coffee
(vi) Cotton
Class 10 Social Science Chapter 9 – Frequently Asked Questions
Get Free NCERT PDFs
If you want to download free PDFs of any chapter, click the link below and join our WhatsApp group:


