Class 6 Science Chapter 13 Wonderful Facts of Space Complete Solutions | SCERT Assam (English Medium)
Class 6 Science Chapter 13 – Wonderful Facts of Space Complete Solutions (SCERT Assam – English Medium)
This chapter explores fascinating facts about space, including planets, satellites, asteroids, comets, the solar system, and the Milky Way Galaxy. Based on the latest SCERT Assam curriculum, these solutions cover all exercises, scientific definitions, and observational activities to prepare students for school and Board exams. The chapter connects textbook concepts to real-life space science and famous discoveries. Chapter QR Code: F7Z2Z2. Ospin Academy presents these answers in simple language for English medium students.
✅ What you will learn:
- The solar system: Sun, planets, satellites, asteroids, and comets
- The concept of stars, constellations, and galaxies
- Important facts about the Milky Way and universe
- Observing the night sky and identifying constellations
- Characteristics of different planets and other celestial objects
🎯 Benefits of Ospin Academy:
- All exercise solutions according to latest SCERT Assam syllabus
- Stepwise answers and explanations for every question
- Extra notes for Board exam preparation
- Easy-to-understand English explanations
- Application-based learning with space science examples
Book QR Codes:
- Part 1 Book Code: P4D4R9
- Part 2 Book Code: F5C4J8
SCERT Assam Class 6 Science (Amar Bijnan) – English Medium Chapter-wise Solutions PDF
Special Combo Offer!
(For SCERT Assam Class 6, 2025)
Get complete chapter-wise Science (Amar Bijnan) solutions in English Medium prepared by expert teachers.
Covers all textbook exercises, key concepts, definitions, and diagrams as per the latest SCERT Assam syllabus.
Ideal for concept clarity, homework assistance, and exam preparation.
![]() Class 6th Science
Class 6th Science
Chapter – 13 Ospin Academy
WONDERFUL FACTS OF SPACE
Exercise
(1-5) Darken the circle of correct answer
Q.1. Which of the following is an example of a constellation?
(a) Meteor
(b) Comet
(c) Ursa Major
(d) Asteroid
Answer:(c)
Q.2. Which of the following is not a member of our Solar System?
(a) Satellite
(b) Constellation
(c) Comet
(d) Asteroid
Answer:(b)
Q.3. Which of the following is a member of our Solar System?
(a) Sirius
(b) Orion
(c) Canis Major
(d) Asteroids
Answer:(d)
Q.4. Which of the following is not a planet of the Sun?
(a) Neptune
(b) Pluto
(c) Saturn
(d) Mercury
Answer:(b)
Q.5. Which is the second nearest star to the Earth? (a) Ursa Minor
(b) Sun
(c) Proxima Centauri
(d) Pole Star
Answer:(c)
Q.6. Match the following
|
Column -1. |
Column – II |
|
(i) Red Planet |
(a) Venus |
|
(ii) Planet with rings |
(b) Mars |
|
(iii) Constellation |
(c) Saturn |
|
(iv) Planet which is commonly called an evening star |
(d) Orion |
Answer:
|
Column -1. |
Column – II |
|
(i) Red Planet |
(b) Mars |
|
(ii) Planet with rings |
(c) Saturn |
|
(iii) Constellation |
(d) Orion |
|
(iv) Planet which is commonly called an evening star |
(a) Venus |
Q.7. Fill in the blanks
(i) A celestial body or object that revolves around a planet is known as ______.
(ii) Asteroids are found between the orbits of Mars and_____.
(iii) The star Sirius is located in ______ constellation.
(iv) The eight planets in order of their distance from the Sun are _____.-Venus, Earth, Mars, ______, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
Answer:
(i) Satellite
(ii) Jupiter
(iii) Canis Major
(iv) Mercury, Jupiter
Q.8. State whether the following statements are True (T) or False(F)
(i) Pluto is the ninth planet of our solar system.
Answer: False
(ii) Pole star is a member of the solar system.
Answer: False
(iii) A comet does not have a tail.
Answer: False
(iv) There are millions of stars in the Universe.
Answer: True
(v) Uranus is the farthest planet in the solar system.
Answer: False
(vi) Orion is the brightest star in the Universe.
Answer: False
Q.9. A portion of night sky with stars is shown in Fig. 13.16.
Look carefully and identify the groups of stars that form the patterns-the Big Dipper and the Little Dipper. Draw lines to connect the stars for these patterns and label them. Also,
identify and label the Pole Star. You may refer to Fig. 13.6 for help.
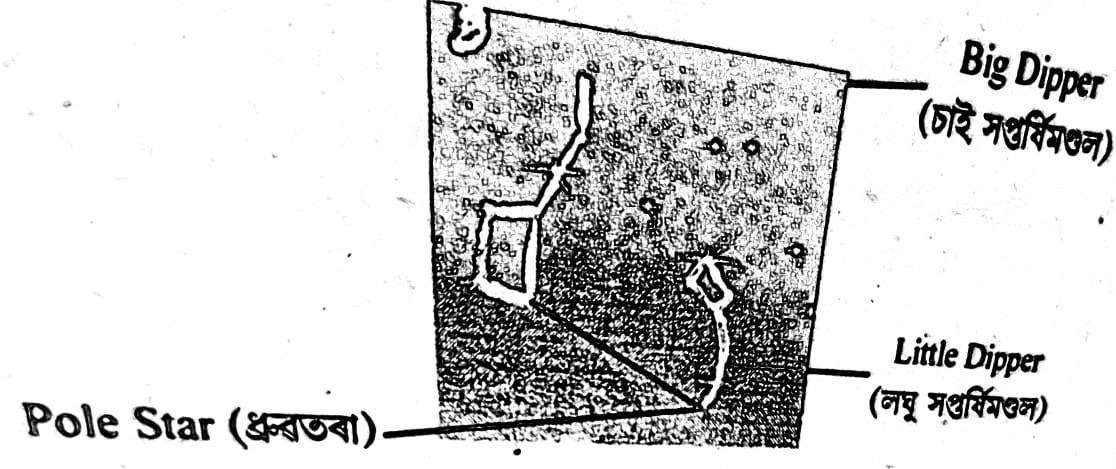 Answer:
Answer:
Q.10. A portion of the night sky is shown in Fig. 13.17. Draw line to connect the stars for Orion and label the star Sirius. You may refer to Fig. 13.5.
Answer:

Q.11. During a clear night, try to observe the Big Dipper (Ursha Major) 3-4 times at an interval of 2 to 3 hours. Try to locate the Pole Star each time. Does the Big Dipper Appear to move? Draw a rough sketch mentioning the time in each case.
Answer: During a clear night, I observed the Big Dipper (Ursa Major) four times at intervals of 2 to 3 hours. I noted the position of the Big Dipper each time and also located the pole star I found that:
(i) The pole star remained in the same position.
(ii) The Big Dipper appeared to change its position gradually over time. It seemed the rotate around the polè star in a circular motion.
Q.12. Write a poem or a story thinking about the night sky.
Answer:
The sky turns dark, the stars appear,
The moon comes out, shining clear.
Clouds float gently, passing by,
Magic fills the quiet sky.
I look above, my heart feels light,
The world sleeps under stars so bright.
Class 6 Science Chapter 13 – Frequently Asked Questions
Get Free NCERT PDFs
If you want to download free PDFs of any chapter, click the link below and join our WhatsApp group:




