SEBA Class 7 Science Chapter 3 Heat – Textbook Solutions & MCQ (Part I)
Get Class 7 Science Chapter 3 “Heat” Solutions for SEBA Assam (English Medium) students. This chapter, from Part I of the Science book, explains the concepts of heat, temperature, transfer of heat, conductors and insulators, and the working of a thermometer. Our solutions include detailed NCERT/SCERT textbook answers, multiple-choice questions (MCQs), and key explanations, helping students understand the fundamental principles of heat transfer and measurement. These solutions are designed to assist students in exam preparation and conceptual learning.
Class 7 Science
Chapter – 3 (Part I) Ospin Academy
Heat
EXERCISE
Q.1. State similarities and differences between the laboratory thermometer and the clinical thermometer.
Ans: Similarities:
(i) Both thermometers consist of long narrow uniform glass tubes.
(ii) Both have a bulb at one end.
(iii) Both contain mercury in bulb.
(iv) Both contain Celsius scale on the glass tube.
Differences:
(i) A clinical thermometer reads tempera- tures 35°C to 42°C while the range of laboratory thermometer is-10°C to 110°C.
(ii) Clinical thermometer has a kink near the bulb while there is no kink in the laboratory thermometer.
2. Give two examples each of conductors and insulators of heat.
Ans: Conductors: aluminum, iron.
Insulators: plastic, wood.
Q.3. Fill in the blanks:
(a) The hotness of an object is determined by its ________.
Ans: Touching.
(b) Temperatures of boiling water cannot be measured by a ________ thermometer.
Ans: Clinical.
(c) Temperature is measured in degree ___________.
Ans: Celsius.
(d) No medium is required for transfer of heat by the process of ________.
Ans: Radiation.
(e) A cold steel spoon is dipped in a cup of hot milk. It transfers heat to its other end by the process of __________.
Ans: Conduction.
(f) Clothes of _________ colors absorb heat better than clothes of light colors.
Ans: Dark.
Q. 4. Match the following:
|
(i) Land breeze blows during |
(a) summer |
|---|---|
|
(ii) Sea breeze blows during |
(b) winter |
|
(iii) Dark coloured clothes are preferred during |
(c) day |
|
(iv) Light coloured clothes are preferred during |
(d) night |
Ans:
|
(i) Land breeze blows during |
(d) night |
|---|---|
|
(ii) Sea breeze blows during |
(c) day |
|
(iii) Dark coloured clothes are preferred during |
(b) winter |
|
(iv) Light coloured clothes are preferred during |
(a) summer |
Q. 5. Discuss why wearing more layers of clothing during winter keeps us warmer than wearing just one thick piece of clothing?
Ans: More layers of clothing keep us warm in winters as they have a lot of space between them. This space gets filled up with air. As air is a bad conductor, it does not allow the body heat to space out.
Q. 6. Look at Fig. 4.13. Mark where the heat is being transferred by conduction, by convection and by radiation.
Ans:
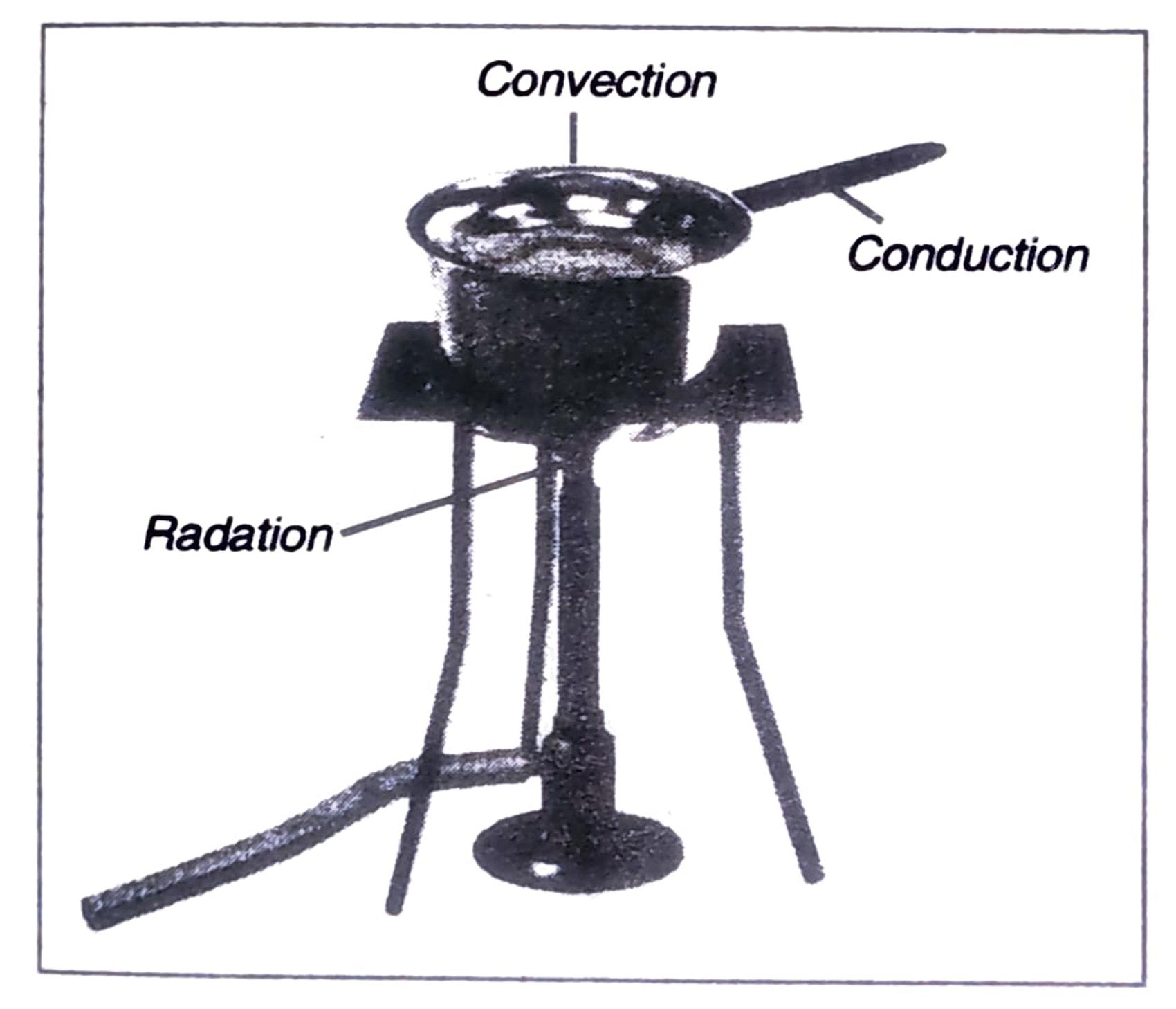
Q. 7. In places of hot climate it is advised that the outer walls of houses be painted white. Explain.
Ans: In places of hot climate it is advised that the outer wall of houses be painted white because white color absorbs very little sun’s heat rays, it reflects most of the sun’s heat rays. This keeps the house cool in the hot days of summer.
Q. 8. One liter of water at 30°C is mixed with one liter of water at 50°C. The temperature of the mixture will be:
(a) 80°C
(b) More than 50°C but less than 80°C
(c) 20°C
(d) Between 30°C and 50°C
Ans: (b) More than 50°C but less than 80°C.
Q. 9. An iron ball at 40°C is dropped in a mug containing water at 40°C. The heat will:
(a) Flows from iron ball to water.
(b) Not flows from iron ball to water or from water to iron ball.
(c) Flows from water to iron ball.
(d) Increases the temperature of both.
Ans: (a) Flows from iron ball to water.
Q. 10. A wooden spoon is dipped in a cup of ice-cream. Its other end:
(a) Becomes cold by the process of conduction.
(b) Becomes cold by the process of convection.
(c) Becomes cold by the process of radiation.
(d) Does not become cold.
Ans: (d) Does not become cold.
Q. 11. Stainless steel pans are usually provided with copper bottoms.
The reason for this could be that:
(a) Copper bottom makes the pan more durable.
(b) Such pans appear colourful.
(c) Copper is a better conductor of heat than the stainless steel.
(d) Copper is easier to clean than the stainless steel.
Ans: (c) Copper is a better conductor of heat than the stainless steel.
Q1: What is heat and how is it measured?
Heat is a form of energy that flows from a hotter object to a colder one. It is measured in joules (J) or calories (cal) using instruments like a thermometer.
Q2: What is the difference between heat and temperature?
Heat is the total energy of molecular motion, while temperature measures the intensity of heat. Temperature is measured in degrees Celsius (°C) or Fahrenheit (°F).
Q3: What are the different modes of heat transfer?
Heat is transferred by conduction, convection, and radiation.
Conduction occurs in solids,
Convection in liquids and gases,
Radiation transfers heat without a medium.
Q4: Where can I find Class 7 Science Chapter 3 solutions for SEBA Assam?
You can find detailed textbook solutions, MCQs, and explanations for SEBA Assam Class 7 Science Chapter 3 on this page.
Q5: Where can I find solutions for all Class 7 Science chapters?
To get solutions for all Class 7 Science chapters, Click Here
