Class 9 Geography Chapter 2 – People on the Earth Complete Solutions | Assam Board (ASSEB) | Latest Syllabus | English Medium
Class 9 Geography Chapter 2 – People on the Earth Complete Solutions (Assam Board – ASSEB – English Medium)
This chapter provides an overview of the world’s population, exploring the distribution, density, and composition of people on Earth. It covers demographic concepts and patterns that shape human settlements and social structures. The chapter includes comprehensive solutions and exercises to help students grasp these concepts effectively.
✅ What you will learn:
- Population distribution across different continents and regions
- Factors affecting population density
- Population composition – age, sex, and occupation
- Demographic terms such as birth rate, death rate, and migration
- Patterns and trends of human population
🎯 Why choose Ospin Academy?
- Complete solutions for every question from the latest Assam Board (ASSEB) syllabus
- Easy-to-understand English medium explanations
- Helps students prepare thoroughly for exams
- Practice questions and detailed answers for better learning
- Resources aligned strictly with the latest Class 9 Geography syllabus
Class 9 Geography Elective English Medium | Latest Syllabus Chapter-wise Solutions PDF
Limited Time Offer!
(For Class 9 Geography Elective, English Medium)
Prepare thoroughly for Class 9 Geography Elective with this chapter-wise solutions PDF.
Includes complete, clear, and exam-focused textual solutions as per the latest syllabus.
Ideal for self-study, homework help, and last-minute revision.
Chapter-2
People on the Earth
1. Give a definition of ‘human geography’ and mention its major branches.
Ans. Human geography is defined as the sub-discipline of geography that undertakes the study of the interrelationship between humanity and the natural environment, alongside the analysis of the man-made (cultural) environment, all viewed from a spatial and temporal perspective. This field of study is extensive and encompasses several major and minor branches.
Some of the notable branches of human geography include:
(i) Settlement Geography
(ii) Social Geography
(iii) Economic Geography
(iv) Cultural Geography
(v) Political Geography
(vi) Urban Geography
(vii) Population Geography
(viii) Medical Geography
(ix) Historical Geography
(x) Geography of Regional Development and Planning, and others.
2. Briefly write about the subject matter of human geography.
Ans. Human geography primarily focuses on the systematic analysis of human activities within both the natural and the cultural (man-made) environment, examining the reciprocal impacts each has upon the other. Though vast and human-centric in scope, the core subject matter of human geography can be outlined as follows:
(i) Study of the link between the physical environment and humanity: Human geography investigates the complex relationship between the physical setting and human life. The physical environment significantly shapes human activities, and in turn, people modify and adjust to their environment to sustain their existence.
(ii) Study of the man-made environment and its creation by human beings: This discipline addresses the cultural landscape and the mechanisms by which humans construct this environment. The nature of the man-made environment differs across regions; for example, human settlements are typically dense in plains but notably sparse in hilly areas. A critical study area involves understanding the diverse forms of the cultural environment and the underlying reasons for these variations.
(iii) Study of various human characteristics across different locations: Human geography systematically examines the diversity in human traits across various regions, much like the physical differences observed on the Earth’s surface. Characteristics such as physical structure, religious-linguistic composition, customs, economic activities, and educational attainment vary significantly among the Earth’s population, and these variations form a key focus of the subject.
(iv) Study of ongoing changes and processes: Human geography researches the various dynamic changes and processes that continuously occur in the interaction and relationship between the natural environment and human populations.
3. Write briefly, what you mean by ‘human race’.
Ans. A human race refers to a collection of people who share largely similar physical characteristics and skin colour, and who transmit these shared traits to successive generations through natural reproduction (heredity). Biologists and anthropologists suggest that the human species, known as Homo sapiens, emerged in Central Africa approximately 500,000 to 600,000 years ago via the process of evolution.
However, the influence of diverse climatic and geographical conditions across the globe led to the appearance of people with different physical features from the earliest stages of human existence. Consequently, distinct differences arose in the body structure, skin pigmentation, nose and facial structure, and hair colour among groups settled in different locations. People sharing a common set of physical attributes are grouped together to define a human race. Biologists traditionally classify humankind into three fundamental races: Caucasoid, Negroid, and Mongoloid.
4. Write briefly the bases or criteria of division of human race.
Ans. While the global human population exhibits variations in skin colour and various aspects of physical structure, individuals with comparable physical attributes have been categorized together to form what is known as a human race. The concept of ‘human race’ therefore signifies a group of people possessing nearly identical physical features that are passed down to succeeding generations via heredity.
These groups are primarily distinguished into three broad categories—Caucasoid, Negroid, and Mongoloid—based on the following main criteria:
(i) Skin colour
(ii) Hair colour and texture
(iii) Height
(iv) Structure of the nose (nasal index)
(v) Facial features (e.g., cheekbones, eye folds)
(vi) Structure of the forehead
5. Discuss in brief the origin of human and human race.
Ans. Very little is known about the origin of human beings. According to the theory of evolution proposed by viologists and anthropologists, man seem to have originated from certain type of monkeys like ape, chimpanzee, gorilla, e’s. This supposed to have taken place during the middle of Pleistocene period (about 5-6 lakh years ago) whern the overall natural environment including climate was favourable. This newly emerged animal human species came to be called Homo sapiens. It is also presumed that this process must have taken place in central Africa and later these newly evolved man-like creatures migrated to other parts of the world.Living in different physical environment caused further biological developments in human beings. As a result of the influence of physical environment around them, different physical characteristics began to appear in Homo sapiens settled in different parts of the world. Accordingly, the human beings settled in the hot regions of Africa were identified as Negroid (i.e.dark skin colour), colder regions of earth were named as Caucasoid (i.e. while skin colour) and the colder regions of Central Asia were identified as Mongoloids (i.e. yellow skin colour). Thus, these three groups can be considered as the primary human races of the world. However over the years, a number of sub-races seemed to have emerged from these primary groups. All human beings living today belong to one of these primary groups or from a combination of primary groups or their sub-races.
6. Divide man on the earth based on the physical characteristics like hair, nose, face, height, skin, etc.
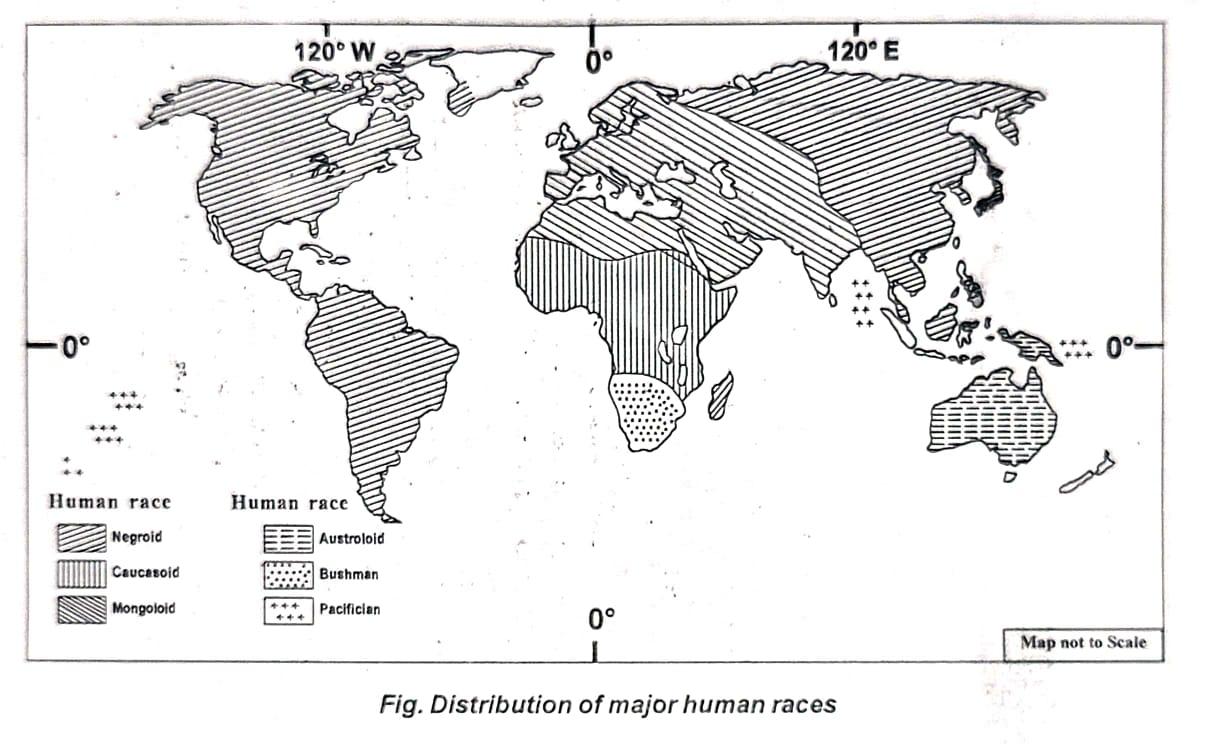
Ans. On the basis of physical features such as hair type, facial shape, nose form, height, and skin colour, human beings on the earth are broadly classified into three major racial groups — the Mongoloid, the Negroid, and the Caucasoid. Each group shows distinct physical traits that developed as an adaptation to different environmental conditions across the world.
7. Mention the characteristics of the three major human races in the world.
Ans. The major human races in the world are:
(i) Caucasoid race
(ii) Negroid race
(iii) Mongoloid raceThe main characteristics of the three major human races are:
|
Sl. No. |
Basics |
Caucasoid race |
Negroid race |
Mongoloid race |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
(i) |
Skin colour |
Pale reddish, white to olive brown. |
Black |
Saffron to yellow brown |
|
(ii) |
Eye colour |
Light blue to dark brown. |
Black to dark brown |
Brown to dark brown |
|
(iii) |
Hair colour |
Light blonde to dark brown. |
Curly |
Black, long and straight |
|
(iv) |
Face |
Narrow to medium. |
Broad to narrow |
Broad and flat |
|
(v) |
Lips |
Thin. |
Thick |
Normal |
|
(vi) |
Nose |
Sharp and narrow. |
Wide and blunt |
Flat or low |
|
(vii) |
Height |
Medium to tall. |
Short to tall |
Relatively small |
|
(viii) |
Head form |
Long to broad and short. |
Elongated |
Generally flattened |
8. Which regions of the world are considered first origin of man? With the help of sketch brir fly write about the spread and distribution of major human races in the world.
Ans. There is no definite evidence to determine the exact time or place where human life first began on Earth. However, according to modern archaeological findings, human beings first appeared in the eastern part of tropical Africa (Old World) nearly one lakh years ago. Around 25,000 to 30,000 years ago, humans began to migrate to various other regions of the world.
Over time, due to continuous migration, geographical influences, and climatic variations, noticeable differences developed in the physical characteristics of human beings. It is believed that the early human form was a blend of the three major races — Caucasoid, Negroid, and Mongoloid. Later, with the process of migration, heredity, and natural selection, distinct racial features began to evolve among populations living in different areas.
It is assumed that the first major migration started from Central Africa, which is regarded as the centre of human origin. From there, human groups gradually moved towards the north and north-eastern regions, possibly using nearby island groups as passageways, since the vast oceans acted as natural barriers.
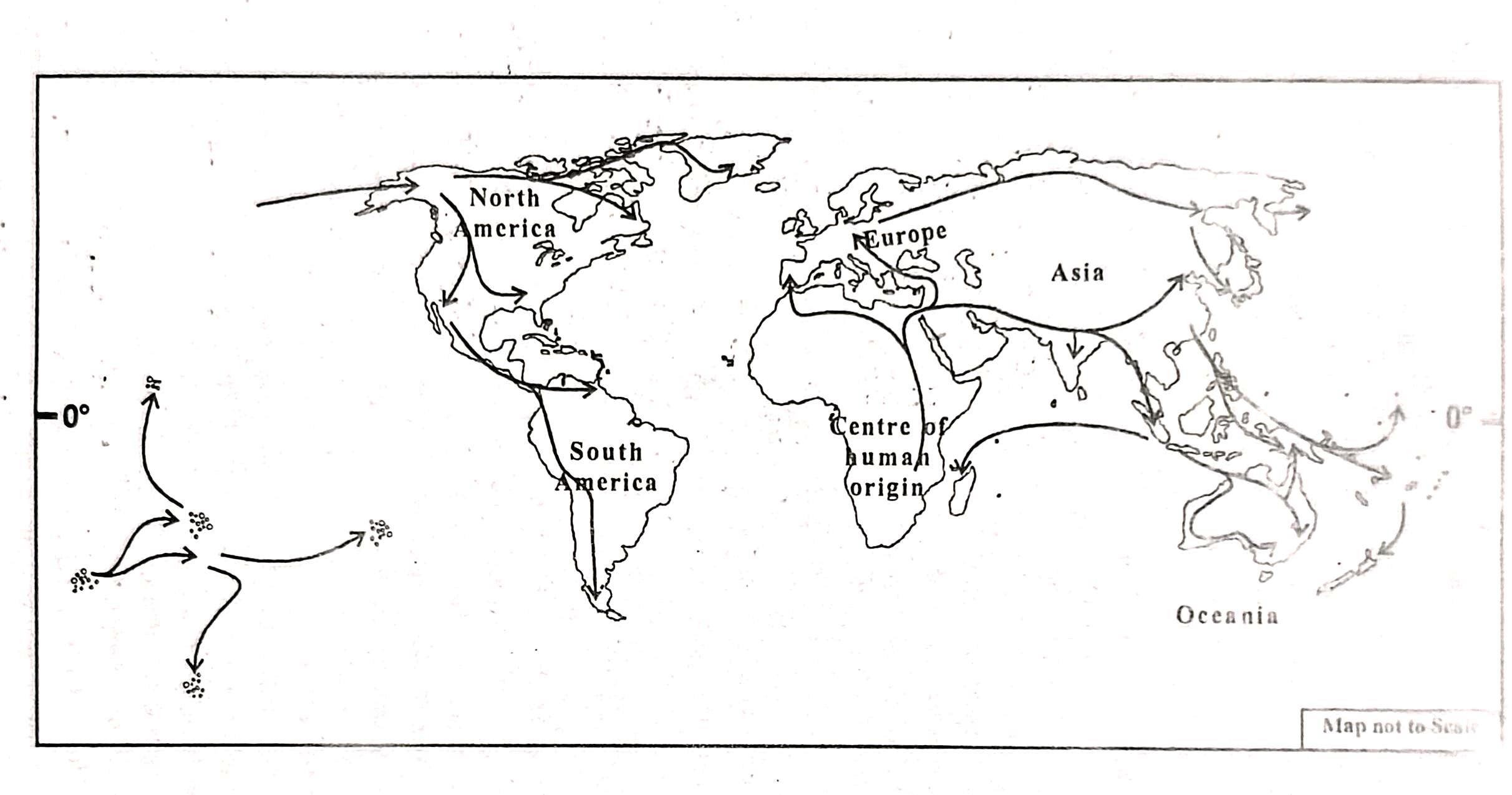
Fig:Human migration and spread
towards east and west. Besides, the snow-covered oceans during the Pleistocene ice-age acted as linkage between the landmasses. This enabled them to cross Bering Strait between Siberia and Alaska. Similarly, the people of Central Asia of Mongoloid racial origin moved towards North, Central and South America. Moreover, people of Caucasoid racial origin migrated from south-west Asia and moved to North and Western Europe and North and East Africa and from Central Africa to South and East Africa and some parts of South Asia.The people residing in India belong to sub-race called Mediterranean class of the Caucasoid racial group who migrated from Southern Europe. The white people living in south Africa, Australia and New Zeeland belong to the Nordic class of the Caucasoid racial group which migrated from Western Europe.Thus, we can say that people living in different parts of the world is a mixed population of different races.
9. What are the major religions? Discuss the salient characteristics and distribution of these religious groups along with their population size.
Ans. The major religions of the world are Christianity, Islam, Hinduism and Buddhism. These four religions constitute about 75% of the world’s population. The population size of these religions as per 2006 estimate is given below:
|
Name |
Population size (in crores |
Percentage |
|---|---|---|
|
1. Christianity 2. Islam 3. Hinduism 4. Buddhism |
213 crores 135 crores 90 crores 38 crores |
33% 21% 14% 6% |
[I] Christianity:
Christianity originated around 2000 years ago under the teachings of Jesus Christ. Although it began in ancient Israel, the religion soon expanded to various parts of the world through active missionary efforts, especially within the Roman Empire. The main characteristics of Christianity include:
(i) Christians believe in one God, making them monotheists.
(ii) It is the largest religion in the world, with nearly 213 crore followers (as per 2006 data).
(iii) Christianity is broadly divided into two main branches—Roman Catholic and Protestant.
(iv) The sacred text of Christianity is the Bible.
[II] Islam:
Islam was established by Prophet Mohammad about 1400 years ago in the desert region of the Middle East. It quickly spread to regions of Africa, South Asia, and South-East Asia. The key features of Islam are:
(i) Followers of Islam, known as Muslims, believe in one God (monotheism).
(ii) The two principal sects of Islam are Shia and Sunni.
(iii) It is the world’s second-largest religion.
(iv) The holy scripture of Islam is the Quran.
[III] Hinduism:
Hinduism is regarded as the oldest religion in the world. It developed after the Aryans settled in the Indo-Gangetic Valley nearly 5000 years ago. The main features of Hinduism are:
(i) The term “Hinduism” is derived from its place of origin—India—situated to the east of the Indus River.
(ii) It originated about 5000 years ago.
(iii) The religion is deeply connected with India’s social and cultural traditions.
(iv) It is followed primarily by the Aryans and Dravidians.
(v) The main sacred texts of Hinduism include the four Vedas, the Ramayana, and the Mahabharata.
[IV] Buddhism:
Buddhism was founded by Lord Gautama Buddha around 2500 years ago in the Bodh Gaya region of northern India. From India, it spread to nearby countries such as Bhutan, China, Sri Lanka, and several parts of South-East Asia. The significant features of Buddhism are:
(i) It has two main branches—Hinayana and Mahayana.
(ii) The principal holy book of Buddhism is the Tripitaka.
10. Write in brief about religious composition and distribution of population in India.
Ans. India is a land of many religions. India has been the birthplace of major religions such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism and Sikhism.
Religious composition: The religious compositions of India are:
|
SI NO. |
Religion |
Percentage |
|---|---|---|
|
(i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) |
Hindus Muslims Christians Sikhs Buddhists |
81.4% 12.4% 2.3% 1.9% 0.8% |
Distribution: The largest religious group in India is the Hindus who live throughout all parts of the country. The chief Islam-dominated state in India is Jammu and Kashmir. People of Islam religion are also found in Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, etc. The Sikhs mostly live in the states of Punjab and Haryana: North-eastern states such as Nagaland, Mizoram and Meghalaya have high concentration of Christians. They are also found in certain pockets in different parts of the country. The Buddhists are mostly found in Sikkim, western part of Arunachal Pradesh, northern part of West Bengal and northern part of Bihar. The Jains mostly live in Rajasthan.
11. Write short notes on:
(a) Man and human geography
(b) Human race
(c) Negroid population group
(d) Religious composition
(e) Buddhist religion
(f) People of Christian religion in India
Ans.
(a) Man and human geography: Human geography is the branch of geography that studies the relationship between humans and their surrounding environment. It focuses on how people adapt to, utilize, and modify the natural environment to meet their needs. It also examines population distribution, settlement patterns, culture, economy, and social activities across different regions of the world.
(b) Human race: According to biologists and anthropologists man seem to have originated in central parts of Africa about 5-6 lakh years ago as a result of the process of evolution. The newly emerged man belonged to a group of species called Homo sapiens. According to anthropologists man seem to have passed through several stages to reach the present level of development. During the later stage, man seem to have migrated to different parts of the world. As a result of the impact and influence of the geographical conditions, further physical differences began to emerge among the people of the world. Nevertheless, people with similar physical features have been placed together to form what is known as human race. The term ‘human race’ refers to a group of people having almost similar physical characteristics which are transferred to the next generation through the process of heredity. On this basis, man has been categorised into three primary human races called Caucasoid, Negroid and Mongoloid races.group: Negroids are mostly found (c) Negroid population gro in Africa, Southern India, Sri Lanka, some parts of south-east Asia and in centelin parts of Oceania. The people belonging to the Negroid racial group have tall stature with dark or dark-brown body skin, curly hair and wide and blunt nose. The sub-races of the Necroid population group are:
(i) Nelotic-Hemitic of eastern Africa.
(ii) Bantu of Central and Southern Africa.
(iii) Bushman and Pigmy of Western Africa.
(iv) Negrito of Southern India and South-east Asia.
(v) Melanesian of South-western Pacific Ocean region.
(vi) Australoid of Oceania.
(d) Religious composition: The set of rules and morals that guide people of different places or groups living on the earth for a proper living is termed as religion. From time immemorial, people all over the world practised some form of religion or other. The four major religions of the world are Christianity, Islam, Hinduism and Buddhism. They constitute about 75% of the world’s population and the rest 25% consists of Sikhs, Jains, Chinese Folk religion, Confucius, Bahai, Judai (Ziu-Himbru), Shinto, Vaishnab, etc. The religious composition of the people of the world is: (according to 2006 estimate)
|
Sl. No. |
Name |
Population size (in crores) |
Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Christianity |
213 |
33.0 |
|
2 |
Islam |
135 |
21.0 |
|
3 |
Hinduism |
90 |
14.0 |
|
4 |
Buddhism |
38 |
6.0 |
|
5 |
Judai religion |
1.6 |
0.2 |
|
6 |
Chinese Folk religion |
39 |
6.1 |
|
7 |
Sikh religion |
2.3 |
0.3 |
|
8 |
Bahai religion |
7 |
0.1 |
|
9 |
Other religions |
124.6 |
19.3 |
(e) Buddhist religion: Buddhism was founded by Gautam Buddha about 2500 years ago in the Bodh Gaya region of Northern India. The two major divisions of Buddhists are Hinayana and Mahayana sects. The main holy book of Buddhism is Tripitaka. According to 2006 estimate, there were about 38 crores Buddhists in the world. They constitute about 6 per cent of the world’s population. Buddhism spread from India to the countries of Bhutan, China, Sri Lanka, South-East Asia, etc.
Distribution :
(i) The Buddhists of Hinayana sect mostly live in Sri Lanka, Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, etc.
(ii) The Buddhists of Mahayana sect are found in countries such as Tibet, Mongolia, Taiwan, Sikiang region of China, Japan, North and South Korea, Bhutan, Vietnam, Malaysia, Brunei, etc.
(f) People of Christian religion in India: According to 2001 census, nearly 2.3 per cent of the population in India are Christians. Christians are mostly found in the states of Nagaland, Mizoram, Meghalaya, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, etc. Christians are of mainly two types, viz. Roman Catholics and Protestants. The Protestants are further divided into several sub-groups each emphasising different aspect of Christianity. All these groups are found in India. They are one of the fastest growing religions in India mostly due to their missionary work throughout the country.
12. Choose the correct answer:
(a) When was human being born on the earth?
(i) 5-6 lakh years ago
(ii) 1-2 lakh years ago
(iii) 50-60 lakh years ago
(iv) 10-12 lakh years ago
Ans. (i) 5-6 lakh years ago
(b) Which is the largest population? religious group in terms of
(i) Islam
(iii) Christian
(ii) Hindu
(iv) Chinese Folk religion
Ans. (iii) Christian
(c) In which continent did man appear/originate first?
(i) Asia
(iii) Europe
(ii) Africa
(iv) Oceania
Ans. (ii) Africa
(d) With which racial did the people of hina belong?
(i) Caucasoid group
(iii) Mongoloid group
(ii) Negroia group
(iv) Australoid group
Ans. (iii) Mongoloid group
Class 9 Geography Chapter 2 – Frequently Asked Questions
Get Free NCERT PDFs
If you want to download free PDFs of any chapter, click the link below and join our WhatsApp group:
Chapter-2
People on the Earth
1. Give a definition of ‘human geography’ and mention its major branches.
Ans. Human geography is defined as the sub-discipline of geography that undertakes the study of the interrelationship between humanity and the natural environment, alongside the analysis of the man-made (cultural) environment, all viewed from a spatial and temporal perspective. This field of study is extensive and encompasses several major and minor branches.
Some of the notable branches of human geography include:
(i) Settlement Geography
(ii) Social Geography
(iii) Economic Geography
(iv) Cultural Geography
(v) Political Geography
(vi) Urban Geography
(vii) Population Geography
(viii) Medical Geography
(ix) Historical Geography
(x) Geography of Regional Development and Planning, and others.
2. Briefly write about the subject matter of human geography.
Ans. Human geography primarily focuses on the systematic analysis of human activities within both the natural and the cultural (man-made) environment, examining the reciprocal impacts each has upon the other. Though vast and human-centric in scope, the core subject matter of human geography can be outlined as follows:
(i) Study of the link between the physical environment and humanity: Human geography investigates the complex relationship between the physical setting and human life. The physical environment significantly shapes human activities, and in turn, people modify and adjust to their environment to sustain their existence.
(ii) Study of the man-made environment and its creation by human beings: This discipline addresses the cultural landscape and the mechanisms by which humans construct this environment. The nature of the man-made environment differs across regions; for example, human settlements are typically dense in plains but notably sparse in hilly areas. A critical study area involves understanding the diverse forms of the cultural environment and the underlying reasons for these variations.
(iii) Study of various human characteristics across different locations: Human geography systematically examines the diversity in human traits across various regions, much like the physical differences observed on the Earth’s surface. Characteristics such as physical structure, religious-linguistic composition, customs, economic activities, and educational attainment vary significantly among the Earth’s population, and these variations form a key focus of the subject.
(iv) Study of ongoing changes and processes: Human geography researches the various dynamic changes and processes that continuously occur in the interaction and relationship between the natural environment and human populations.
3. Write briefly, what you mean by ‘human race’.
Ans. A human race refers to a collection of people who share largely similar physical characteristics and skin colour, and who transmit these shared traits to successive generations through natural reproduction (heredity). Biologists and anthropologists suggest that the human species, known as Homo sapiens, emerged in Central Africa approximately 500,000 to 600,000 years ago via the process of evolution.
However, the influence of diverse climatic and geographical conditions across the globe led to the appearance of people with different physical features from the earliest stages of human existence. Consequently, distinct differences arose in the body structure, skin pigmentation, nose and facial structure, and hair colour among groups settled in different locations. People sharing a common set of physical attributes are grouped together to define a human race. Biologists traditionally classify humankind into three fundamental races: Caucasoid, Negroid, and Mongoloid.
4. Write briefly the bases or criteria of division of human race.
Ans. While the global human population exhibits variations in skin colour and various aspects of physical structure, individuals with comparable physical attributes have been categorized together to form what is known as a human race. The concept of ‘human race’ therefore signifies a group of people possessing nearly identical physical features that are passed down to succeeding generations via heredity.
These groups are primarily distinguished into three broad categories—Caucasoid, Negroid, and Mongoloid—based on the following main criteria:
(i) Skin colour
(ii) Hair colour and texture
(iii) Height
(iv) Structure of the nose (nasal index)
(v) Facial features (e.g., cheekbones, eye folds)
(vi) Structure of the forehead
5. Discuss in brief the origin of human and human race.
Ans. Very little is known about the origin of human beings. According to the theory of evolution proposed by viologists and anthropologists, man seem to have originated from certain type of monkeys like ape, chimpanzee, gorilla, e’s. This supposed to have taken place during the middle of Pleistocene period (about 5-6 lakh years ago) whern the overall natural environment including climate was favourable. This newly emerged animal human species came to be called Homo sapiens. It is also presumed that this process must have taken place in central Africa and later these newly evolved man-like creatures migrated to other parts of the world.Living in different physical environment caused further biological developments in human beings. As a result of the influence of physical environment around them, different physical characteristics began to appear in Homo sapiens settled in different parts of the world. Accordingly, the human beings settled in the hot regions of Africa were identified as Negroid (i.e.dark skin colour), colder regions of earth were named as Caucasoid (i.e. while skin colour) and the colder regions of Central Asia were identified as Mongoloids (i.e. yellow skin colour). Thus, these three groups can be considered as the primary human races of the world. However over the years, a number of sub-races seemed to have emerged from these primary groups. All human beings living today belong to one of these primary groups or from a combination of primary groups or their sub-races.
6. Divide man on the earth based on the physical characteristics like hair, nose, face, height, skin, etc.
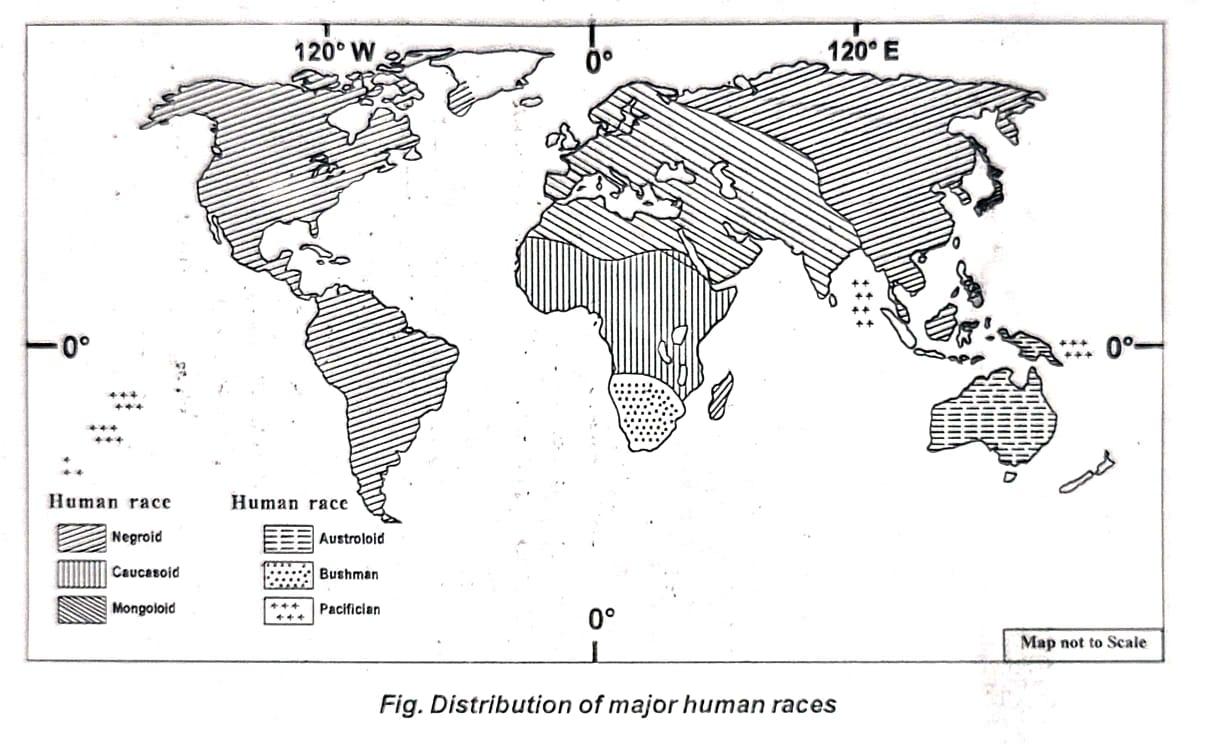
Ans. On the basis of physical features such as hair type, facial shape, nose form, height, and skin colour, human beings on the earth are broadly classified into three major racial groups — the Mongoloid, the Negroid, and the Caucasoid. Each group shows distinct physical traits that developed as an adaptation to different environmental conditions across the world.
7. Mention the characteristics of the three major human races in the world.
Ans. The major human races in the world are:
(i) Caucasoid race
(ii) Negroid race
(iii) Mongoloid raceThe main characteristics of the three major human races are:
|
Sl. No. |
Basics |
Caucasoid race |
Negroid race |
Mongoloid race |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
(i) |
Skin colour |
Pale reddish, white to olive brown. |
Black |
Saffron to yellow brown |
|
(ii) |
Eye colour |
Light blue to dark brown. |
Black to dark brown |
Brown to dark brown |
|
(iii) |
Hair colour |
Light blonde to dark brown. |
Curly |
Black, long and straight |
|
(iv) |
Face |
Narrow to medium. |
Broad to narrow |
Broad and flat |
|
(v) |
Lips |
Thin. |
Thick |
Normal |
|
(vi) |
Nose |
Sharp and narrow. |
Wide and blunt |
Flat or low |
|
(vii) |
Height |
Medium to tall. |
Short to tall |
Relatively small |
|
(viii) |
Head form |
Long to broad and short. |
Elongated |
Generally flattened |
8. Which regions of the world are considered first origin of man? With the help of sketch brir fly write about the spread and distribution of major human races in the world.
Ans. There is no definite evidence to determine the exact time or place where human life first began on Earth. However, according to modern archaeological findings, human beings first appeared in the eastern part of tropical Africa (Old World) nearly one lakh years ago. Around 25,000 to 30,000 years ago, humans began to migrate to various other regions of the world.
Over time, due to continuous migration, geographical influences, and climatic variations, noticeable differences developed in the physical characteristics of human beings. It is believed that the early human form was a blend of the three major races — Caucasoid, Negroid, and Mongoloid. Later, with the process of migration, heredity, and natural selection, distinct racial features began to evolve among populations living in different areas.
It is assumed that the first major migration started from Central Africa, which is regarded as the centre of human origin. From there, human groups gradually moved towards the north and north-eastern regions, possibly using nearby island groups as passageways, since the vast oceans acted as natural barriers.
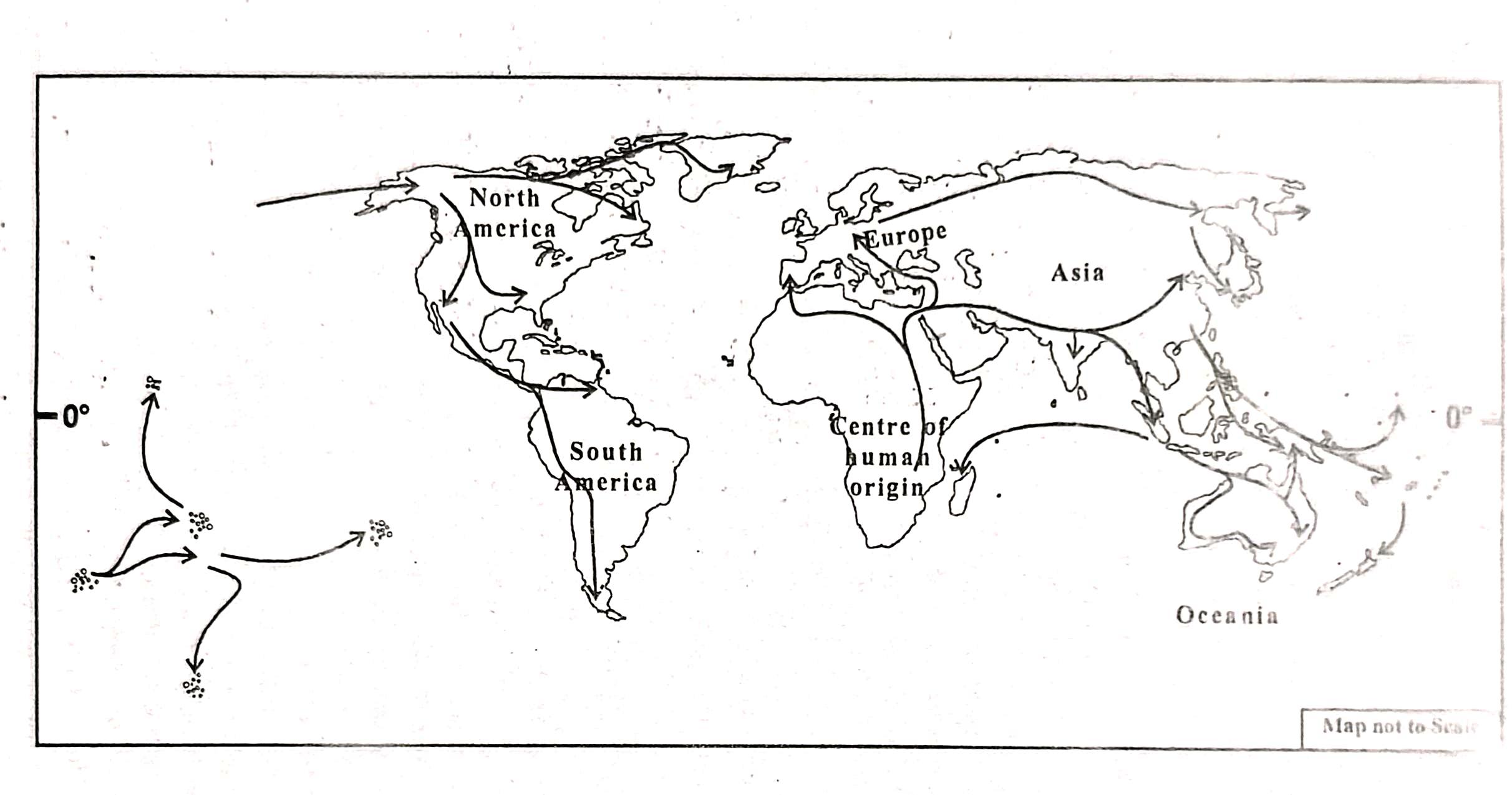
Fig:Human migration and spread
towards east and west. Besides, the snow-covered oceans during the Pleistocene ice-age acted as linkage between the landmasses. This enabled them to cross Bering Strait between Siberia and Alaska. Similarly, the people of Central Asia of Mongoloid racial origin moved towards North, Central and South America. Moreover, people of Caucasoid racial origin migrated from south-west Asia and moved to North and Western Europe and North and East Africa and from Central Africa to South and East Africa and some parts of South Asia.The people residing in India belong to sub-race called Mediterranean class of the Caucasoid racial group who migrated from Southern Europe. The white people living in south Africa, Australia and New Zeeland belong to the Nordic class of the Caucasoid racial group which migrated from Western Europe.Thus, we can say that people living in different parts of the world is a mixed population of different races.
9. What are the major religions? Discuss the salient characteristics and distribution of these religious groups along with their population size.
Ans. The major religions of the world are Christianity, Islam, Hinduism and Buddhism. These four religions constitute about 75% of the world’s population. The population size of these religions as per 2006 estimate is given below:
|
Name |
Population size (in crores |
Percentage |
|---|---|---|
|
1. Christianity 2. Islam 3. Hinduism 4. Buddhism |
213 crores 135 crores 90 crores 38 crores |
33% 21% 14% 6% |
[I] Christianity:
Christianity originated around 2000 years ago under the teachings of Jesus Christ. Although it began in ancient Israel, the religion soon expanded to various parts of the world through active missionary efforts, especially within the Roman Empire. The main characteristics of Christianity include:
(i) Christians believe in one God, making them monotheists.
(ii) It is the largest religion in the world, with nearly 213 crore followers (as per 2006 data).
(iii) Christianity is broadly divided into two main branches—Roman Catholic and Protestant.
(iv) The sacred text of Christianity is the Bible.
[II] Islam:
Islam was established by Prophet Mohammad about 1400 years ago in the desert region of the Middle East. It quickly spread to regions of Africa, South Asia, and South-East Asia. The key features of Islam are:
(i) Followers of Islam, known as Muslims, believe in one God (monotheism).
(ii) The two principal sects of Islam are Shia and Sunni.
(iii) It is the world’s second-largest religion.
(iv) The holy scripture of Islam is the Quran.
[III] Hinduism:
Hinduism is regarded as the oldest religion in the world. It developed after the Aryans settled in the Indo-Gangetic Valley nearly 5000 years ago. The main features of Hinduism are:
(i) The term “Hinduism” is derived from its place of origin—India—situated to the east of the Indus River.
(ii) It originated about 5000 years ago.
(iii) The religion is deeply connected with India’s social and cultural traditions.
(iv) It is followed primarily by the Aryans and Dravidians.
(v) The main sacred texts of Hinduism include the four Vedas, the Ramayana, and the Mahabharata.
[IV] Buddhism:
Buddhism was founded by Lord Gautama Buddha around 2500 years ago in the Bodh Gaya region of northern India. From India, it spread to nearby countries such as Bhutan, China, Sri Lanka, and several parts of South-East Asia. The significant features of Buddhism are:
(i) It has two main branches—Hinayana and Mahayana.
(ii) The principal holy book of Buddhism is the Tripitaka.
10. Write in brief about religious composition and distribution of population in India.
Ans. India is a land of many religions. India has been the birthplace of major religions such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism and Sikhism.
Religious composition: The religious compositions of India are:
|
SI NO. |
Religion |
Percentage |
|---|---|---|
|
(i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) |
Hindus Muslims Christians Sikhs Buddhists |
81.4% 12.4% 2.3% 1.9% 0.8% |
Distribution: The largest religious group in India is the Hindus who live throughout all parts of the country. The chief Islam-dominated state in India is Jammu and Kashmir. People of Islam religion are also found in Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, etc. The Sikhs mostly live in the states of Punjab and Haryana: North-eastern states such as Nagaland, Mizoram and Meghalaya have high concentration of Christians. They are also found in certain pockets in different parts of the country. The Buddhists are mostly found in Sikkim, western part of Arunachal Pradesh, northern part of West Bengal and northern part of Bihar. The Jains mostly live in Rajasthan.
11. Write short notes on:
(a) Man and human geography
(b) Human race
(c) Negroid population group
(d) Religious composition
(e) Buddhist religion
(f) People of Christian religion in India
Ans.
(a) Man and human geography: Human geography is the branch of geography that studies the relationship between humans and their surrounding environment. It focuses on how people adapt to, utilize, and modify the natural environment to meet their needs. It also examines population distribution, settlement patterns, culture, economy, and social activities across different regions of the world.
(b) Human race: According to biologists and anthropologists man seem to have originated in central parts of Africa about 5-6 lakh years ago as a result of the process of evolution. The newly emerged man belonged to a group of species called Homo sapiens. According to anthropologists man seem to have passed through several stages to reach the present level of development. During the later stage, man seem to have migrated to different parts of the world. As a result of the impact and influence of the geographical conditions, further physical differences began to emerge among the people of the world. Nevertheless, people with similar physical features have been placed together to form what is known as human race. The term ‘human race’ refers to a group of people having almost similar physical characteristics which are transferred to the next generation through the process of heredity. On this basis, man has been categorised into three primary human races called Caucasoid, Negroid and Mongoloid races.group: Negroids are mostly found (c) Negroid population gro in Africa, Southern India, Sri Lanka, some parts of south-east Asia and in centelin parts of Oceania. The people belonging to the Negroid racial group have tall stature with dark or dark-brown body skin, curly hair and wide and blunt nose. The sub-races of the Necroid population group are:
(i) Nelotic-Hemitic of eastern Africa.
(ii) Bantu of Central and Southern Africa.
(iii) Bushman and Pigmy of Western Africa.
(iv) Negrito of Southern India and South-east Asia.
(v) Melanesian of South-western Pacific Ocean region.
(vi) Australoid of Oceania.
(d) Religious composition: The set of rules and morals that guide people of different places or groups living on the earth for a proper living is termed as religion. From time immemorial, people all over the world practised some form of religion or other. The four major religions of the world are Christianity, Islam, Hinduism and Buddhism. They constitute about 75% of the world’s population and the rest 25% consists of Sikhs, Jains, Chinese Folk religion, Confucius, Bahai, Judai (Ziu-Himbru), Shinto, Vaishnab, etc. The religious composition of the people of the world is: (according to 2006 estimate)
|
Sl. No. |
Name |
Population size (in crores) |
Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Christianity |
213 |
33.0 |
|
2 |
Islam |
135 |
21.0 |
|
3 |
Hinduism |
90 |
14.0 |
|
4 |
Buddhism |
38 |
6.0 |
|
5 |
Judai religion |
1.6 |
0.2 |
|
6 |
Chinese Folk religion |
39 |
6.1 |
|
7 |
Sikh religion |
2.3 |
0.3 |
|
8 |
Bahai religion |
7 |
0.1 |
|
9 |
Other religions |
124.6 |
19.3 |
(e) Buddhist religion: Buddhism was founded by Gautam Buddha about 2500 years ago in the Bodh Gaya region of Northern India. The two major divisions of Buddhists are Hinayana and Mahayana sects. The main holy book of Buddhism is Tripitaka. According to 2006 estimate, there were about 38 crores Buddhists in the world. They constitute about 6 per cent of the world’s population. Buddhism spread from India to the countries of Bhutan, China, Sri Lanka, South-East Asia, etc.
Distribution :
(i) The Buddhists of Hinayana sect mostly live in Sri Lanka, Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, etc.
(ii) The Buddhists of Mahayana sect are found in countries such as Tibet, Mongolia, Taiwan, Sikiang region of China, Japan, North and South Korea, Bhutan, Vietnam, Malaysia, Brunei, etc.
(f) People of Christian religion in India: According to 2001 census, nearly 2.3 per cent of the population in India are Christians. Christians are mostly found in the states of Nagaland, Mizoram, Meghalaya, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, etc. Christians are of mainly two types, viz. Roman Catholics and Protestants. The Protestants are further divided into several sub-groups each emphasising different aspect of Christianity. All these groups are found in India. They are one of the fastest growing religions in India mostly due to their missionary work throughout the country.
12. Choose the correct answer:
(a) When was human being born on the earth?
(i) 5-6 lakh years ago
(ii) 1-2 lakh years ago
(iii) 50-60 lakh years ago
(iv) 10-12 lakh years ago
Ans. (i) 5-6 lakh years ago
(b) Which is the largest population? religious group in terms of
(i) Islam
(iii) Christian
(ii) Hindu
(iv) Chinese Folk religion
Ans. (iii) Christian
(c) In which continent did man appear/originate first?
(i) Asia
(iii) Europe
(ii) Africa
(iv) Oceania
Ans. (ii) Africa
(d) With which racial did the people of hina belong?
(i) Caucasoid group
(iii) Mongoloid group
(ii) Negroia group
(iv) Australoid group
Ans. (iii) Mongoloid group




