Class 8 Science Chapter 18 – Stars and the Solar System | SCERT Assam (English Medium)
Class 8 Science Chapter 18 – Stars and the Solar System (SCERT Assam – English Medium)
Journey through the cosmos! This chapter covers celestial bodies, constellations visible in Assam, and India’s space achievements like Chandrayaan-3 and Assam’s Zero Orbital Space Mission.
✅ Key Topics:
- Solar system structure (Sun, planets, asteroids)
- Constellations (Orion, Ursa Major, Cassiopeia)
- Moon phases and lunar eclipses
- Artificial satellites and their uses
- ISRO’s role in space exploration
- Light-year concept and star life cycles
🎯 Why Ospin Academy?
- Stargazing tips for Assam’s night sky
- Simplified diagrams of constellations
- Important 5-mark questions on ISRO missions
- YouTube videos on telescope basics
Explore the universe with SCERT-aligned notes and ace your exams!
Class 8 Science (English Medium) PDF Solutions 2025-26 | SCERT Assam
Get the Class 8 Science (English Medium) PDF with detailed solutions, MCQs, and extra practice questions for SCERT Assam 2025-26.
Class 8 Science
Chapter – 18 Ospin Academy
Stars and The Solar System
TEXTBOOK EXERCISES
Choose the correct answer in Questions 1-3.
Q. 1. Which of the following is NOT a member of the solar system?
(a) An asteroid.
(b) A satellite.
(c) A constellation.
(d) A comete.
Ans. (c) A constellation.
Q. 2. Which of the following is NOT a planet of the sun?
(a) Sirius.
(b) Mercury.
(c) Saturn.
(d) Earth.
Ans. (a) Sirius.
Q. 3. Phases of the moon occur because:
(a) we can see only that part of the moon which reflects light towards us.
(b) our distance from the moon keeps changing.
(c) the shadow of the Earth covers only a part of the moon’s surface.
(d) the thickness of the moon’s atmosphere is not constant.
Ans. (c) the shadow of the Earth covers only a part of the moon’s surface.
Q. 4. Fill in the blanks:
(a) The planet which is farthest from the Sun is _________.
Ans. Neptune.
(b) The planet which appears reddish in colour is _________.
Ans. Mars.
(c) A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky is known as a ___________.
Ans. Constellation.
(d) A celestial body that revolves around a planet is known as __________.
Ans. Satellite.
(e) Shooting stars are actually not _________.
Ans. Meteors.
(f) Asteroids are found between the orbits of _________ and _________.
Ans. Mars and Jupiter.
Q. 5. Mark the following statements as true (T) or false (F):
(a) Pole star is a member of the solar system.
Ans. False.
(b) Mercury is the smallest planet of the solar system.
Ans. False.
(c) Uranus is the farthest planet in our solar system.
Ans. False.
(d) INSAT is an artificial satellite.
Ans. True.
(e) There are nine planets in our solar system.
Ans. False.
(f) Constellation Orion can be seen only with the telescope.
Ans. False.
Q. 6. Match items in Column A with one or more items of Column B:
|
Column A |
Column B |
|---|---|
|
(i) Inner planets |
(a) Saturn |
|
(ii) Outer planets |
(b) Pole star |
|
(iii) Constellation |
(c) Great Bear |
|
(iv) Satellite of the Earth |
(d) Moon |
|
(e) Earth |
|
|
(f) Orion |
|
|
(g) Mars |
Ans.
|
Column A |
Column B |
|---|---|
|
(i) Inner planets |
(g) Mars |
|
(e) Earth |
|
|
(ii) Outer planets |
(a) Saturn |
|
(iii) Constellation |
(c) Great Bear |
|
(f) Orion |
|
|
(iv) Satellite of the Earth |
(d) Moon |
Q. 7. In which part of the sky can you find Venus if it is visible as an evening star?
Ans. In western sky.
Q. 8. Name the largest planet of the solar system.
Ans. Jupiter.
Q. 9. What is a constellation? Name any two constellations.
Ans. A group of stars in a recognizable shape is called a constellation. Orion and the Great Bear are constellations.
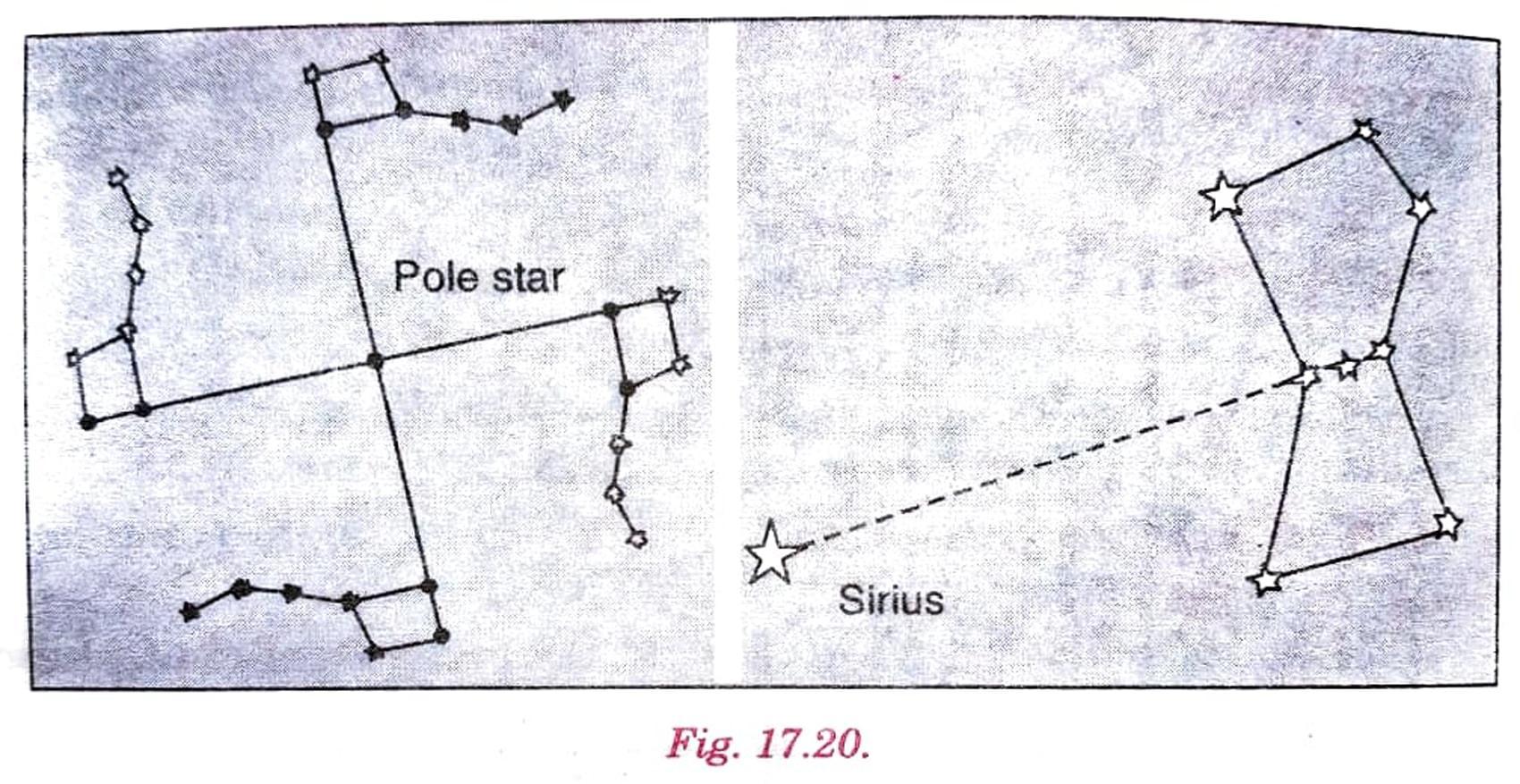
Q. 10. Draw sketches to show the relative positions of prominent stars in:
(i) Ursa Major and
(ii) Orion.
Ans. See Fig. 17.20.
Q. 11. Name two objects other than planets which are members of the solar system.
Ans. Meteors and Asteroids.
Q. 12. Explain how you can locate the Pole Star with the help of Ursa Major.
Ans. Pole star is situated at the end of the- Ursa Major. If a straight line starting from the last two stars is extended towards the north direction, it will lead to the Pole Star.
Q. 13. Do all the stars in the sky move? Explain.
Aus. All the stars in the sky do not move, but they appear to move from east to west. This is actually due to rotation of earth on its axis. Earth moves from west to east. So it appears as the stars are rising from east and as the day dawns they set in the west.
Q. 14. Why is the distance between stars expressed in light years? What do you understand by the statement that a star is eight light years away from the earth?
Ans. Stars are away from the earth millions of kilometres away. It is not convenient to express such a large distance in the units of km. So the distance of stars from the earth is expressed in time taken by light to travel in one year. Eight light years mean time taken by light to travel in eight years.
Q. 15. The radius of Jupiter is 11 time the radius of the earth. Calculate the ratio of the volumes of Jupiter and the earth How many Earths can Jupiter accommodate?
Ans. Let the radius of Earth = R units
Volume of Earth = 4/3 πR³ cubic units
Now, the radius of Jupiter = 11R units.
∴ Volume of Jupiter: 4 3 π(11R)³
= 4/3π(1331R³) cu. units.
Now the ratios of the volume of Jupiter and Earth
= Volume of Jupiter / Volume of the Earth
= 4/3π(1331R³) cu. units / 4/3πR³ cu. units
= 1331/1 = 1331:1
So 1331 Earths can be accommodated in one Jupiter.
Q. 16. Boojha made the solar system (Fig. 17.21). Is the sketch correct? If not, correct it.
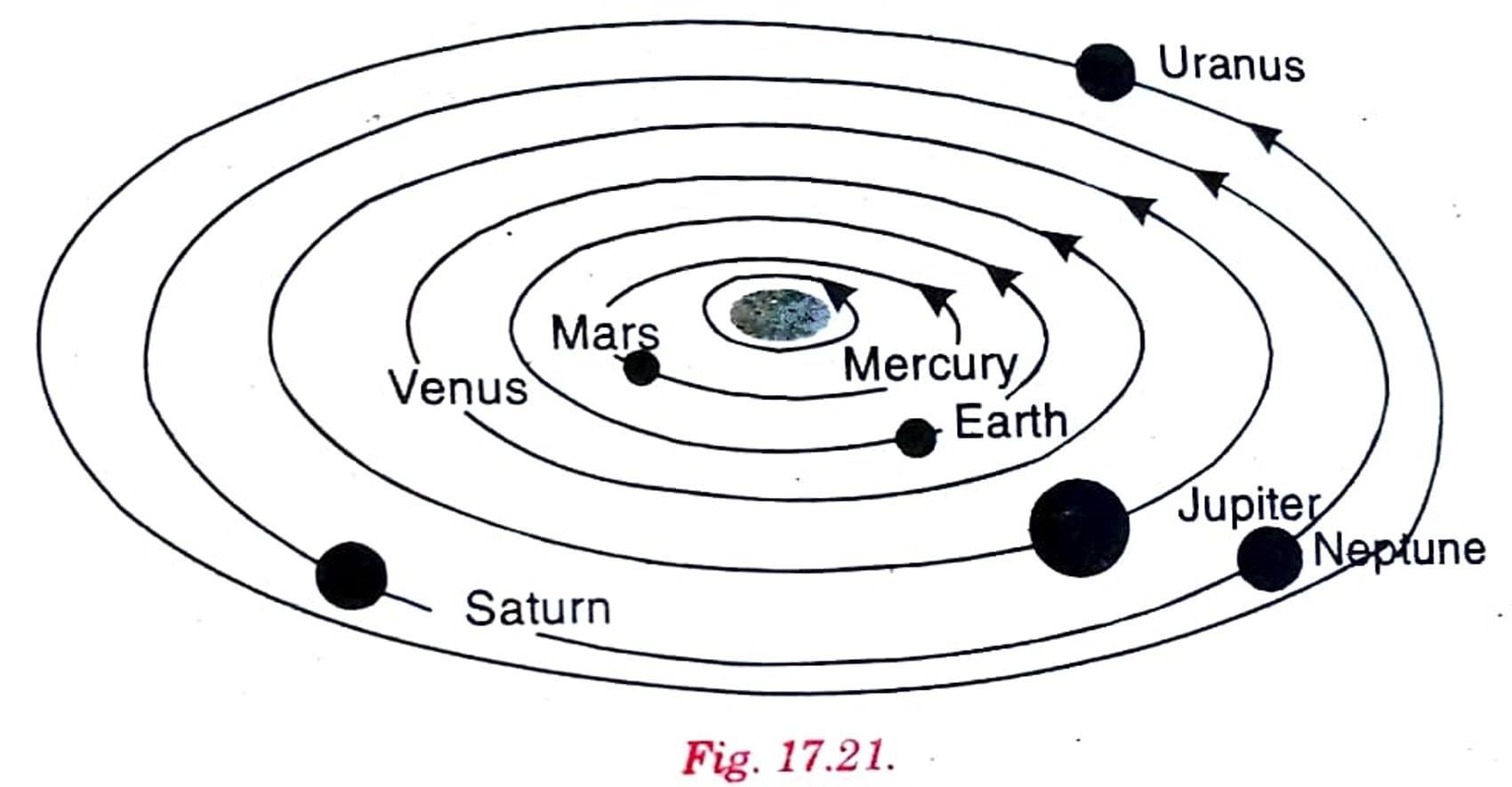
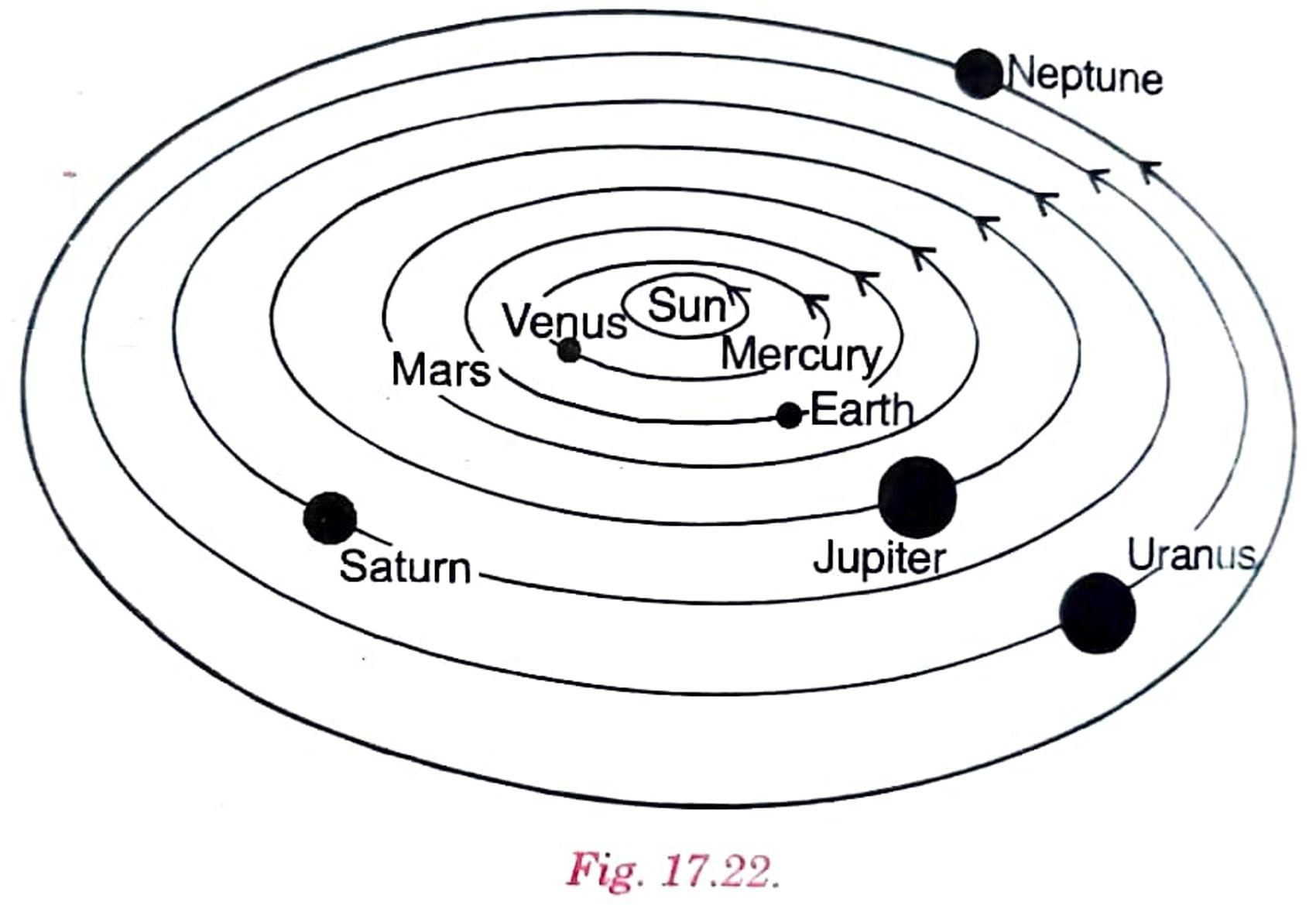
Ans. No, the given sketch is not correct. The following figure is correct.
Class 8 Science Chapter 18 – Stars and Solar System FAQs
Get Free NCERT PDFs
If you want to download free PDFs of any chapter, click the link below and join our WhatsApp group:

